深入理解動態(tài)規(guī)劃的一系列問題(3)
繼續(xù)上一篇的探討,對于有向無環(huán)圖我們可以通過動態(tài)規(guī)劃解決,那么對于有向有環(huán)圖呢?這里列出一個例子解決 有向有環(huán)圖的動態(tài)規(guī)劃解。
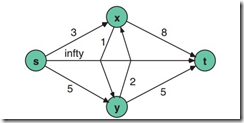
如前所述,在解決圖路徑的動態(tài)規(guī)劃問題時,我們遞歸或者迭代求解,列出DPFE方程。這里仍舊拿上一個例子來說,為了把無環(huán)變?yōu)橛协h(huán),加一條邊(y,x)=2,并且假設(shè)圖是沒有自循環(huán)節(jié)點(diǎn)的,也就是節(jié)點(diǎn)不能到達(dá)自己。這樣問題就變?yōu)橐粋€經(jīng)典的Shortest Path in Cyclic Graph(SPC)——我們討論的第三個動態(tài)規(guī)劃問題,圖形如下:
如果依舊像之前一樣列方程,會發(fā)現(xiàn),f(x)=min{b(x,y)+f(y), b(x,t)+f(t)},f(y)=min{b(y,x)+f(x),b(y,t)+f(t)},這里兩個方程f(x)和f(y)互相依賴,無法直接求解。為此,要引入一種叫做“松弛”(relaxation)的技術(shù),當(dāng)我們想求一個數(shù)列x*=min{a1,a2,…,aN}的最小值時,可以把它等價為x*=min{min{…min{a1,a2},a3},…},aN}。我們把一個全局問題降級成了處理一系列兩個元素的比較問題引入了一系列xi變量,令x1=a1,那么x2=min{x1,a2},x3=min{x2,a3},……依次得到遞歸解xi=min{x(i-1),ai},其中i>0,且初始條件x1=a1,不過一般為了一致性,我們多定義一個x0=∞,這樣x1=min{x0,a1}。那么松弛帶來的第一個表示方法就是對于常規(guī)問題S={x1,x2,…,xm},Sx’代表在選擇了x后的下一個狀態(tài),成本函數(shù)還是C(x|S),表示f(S)=min{min{…min{C(x1|S)+f(Sx1’),C(x2|S)+f(Sx2’)},…},C(xm|S)+f(Sxm’)},使用這種表示方法解決問題,需要先把S的元素排序,f(Sxi’)需要先被預(yù)先計算出來。換種思路用stage decision階段決策來看松弛,那么結(jié)果就是f(k,S)=min x{C(x|k,s)+f(k-1,Sx’)},對于每個S都要計算一個序列f(0,S),f(1,S)…來逼近f(S),這個序列的最小值就是問題的解即f(S)=min{f(k,S)}。可以看出f(k,S)并不單調(diào),所以還需要全局再求一次最值,所以松弛會再定義一個F(k,S),使得F(k,S)=min{F(k-1,S), min{C(x|k,S)+F(k-1,Sx’)}},這樣一來,函數(shù)變?yōu)閱握{(diào),且在f(S)收斂。
回到SPC問題,因?yàn)槠胀ǚ匠坛霈F(xiàn)了互相依賴,因此利用松弛技術(shù),我們把依賴化解掉,利用第一種漸進(jìn)逼近法,我們先定義f(s)=f(x)=f(y)=∞,f(t)=0,這時第一輪迭代,f(s)=min{3+∞,5+∞,∞+0}=∞,f(x)=min{1+∞, 8+0}=8,f(y)=min{2+∞,5+0}=5,f(t)=0,這樣,就把本來互相依賴的f(x)和f(y)化解了死鎖,讓他們有了初始值,接下來繼續(xù)迭代,f(s)=min{3+8, 5+5, ∞+0}=10,f(x)=min{1+5,8+0}=6,f(y)=min{2+8,5+0}=5,f(t)=0,最后迭代f(s)=min{3+6,5+5,∞+0}=9,得到最終解。
利用第二種階段決策方法,有f(k,p)=min q{b(p,q)+f(k-1,q)},f(k,p)表示從p到終點(diǎn)的最短路徑長度,路徑有k段。基礎(chǔ)條件是f(0,t)=0,f(0,p)=∞當(dāng)p≠t,f(k,t)=∞當(dāng)k>0,于是第一輪迭代,f(1,s)=min{3+f(0,x),5+f(0,y),∞+f(0,t)}=∞,f(1,x)=min{1+f(0,y),8+f(0,t)}=8,f(1,y)=min{2+f(0,x),5+f(0,t)}=5,f(1,t)=∞;第二輪迭代,f(2,s)=min{3+f(1,x),5+f(1,y),∞+f(1,t)}=10,f(2,x)=min{1+f(1,y),8+f(1,t)}=6,f(2,y)=min{2+f(1,x),5+f(1,t)}=10,f(2,t)=∞;最后迭代,f(3,s)=min{3+f(2,x),5+f(2,y),∞+f(2,t)}=9,f(3,x)=min{1+f(2,y),8+f(2,t)}=11,f(3,y)=min{2+f(2,x),5+f(2,t)}=8,f(3,t)=∞;最后計算f(s)=min{f(0,s),f(1,s),f(2,s),f(3,s)}=min{∞,∞,10,9}=9,f(x)=min{∞,8,6,11}=6,f(y)=min{∞,5,10,8}=5,f(t)=min{0,∞,∞,∞}=0。
階段決策需要再求一次最值,且迭代求出了所有解,這并不優(yōu)雅,使用第三種方法——真正的松弛技術(shù):定義F(k,p)是從p到t的最短路徑長度,由k或更少段路徑組成。那么目標(biāo)可以等價于F(N-1,s),基本條件是F(0,t)=0,F(xiàn)(0,p)=∞當(dāng)p≠t,F(xiàn)(k,t)=∞當(dāng)k>0,DPFE為F(k,p)=min q{b(p,q)+F(k-1,q)},松弛后的形式為F(k,p)=min{min{…min{b(p,q1)+F(k-1,q1),b(p,q2)+F(k-1,q2)},…},b(p,qm)+F(k-1,qm)}。這種松弛技術(shù)也是Bellman-Ford算法的基礎(chǔ),Bellman-Ford算法可以求出從單一節(jié)點(diǎn)到所有其他節(jié)點(diǎn)的最短路,思路就是不斷松弛,計算從起點(diǎn)開始到其他節(jié)點(diǎn)的最短路徑。同時還有Floyd-Warshall算法,依據(jù)松弛技術(shù),求得圖模型里的所有節(jié)點(diǎn)對的最短路徑,時間復(fù)雜度O(n3),空間復(fù)雜度O(n2)。這兩種算法可以參看《算法導(dǎo)論》或者wikipedia,這里不再詳述。
source code:DPFE
1: /*
2: * Copyright (C) 2013 changedi
3: *
4: * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
5: * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
6: * You may obtain a copy of the License at
7: *
8: * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
9: *
10: * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
11: * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
12: * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
13: * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
14: * limitations under the License.
15: */
16: package com.jybat.dp;
17: 18: import java.util.HashSet;
19: import java.util.Set;
20: 21: public class ShortestPathCyclic {
22: 23: private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
24: 25: private static Set<Integer> path = new HashSet<Integer>();
26: // nodes (s,x,y,t) = {0,1,2,3}, so (s,x) = 3 means d[0][1] = 3
27: private static int[][] distance = {
28: { INF, 5, 3, INF }, 29: { INF, INF, 2, 5 }, 30: { INF, 1, INF, 8 }, 31: { INF, INF, INF, INF } 32: }; 33: 34: private static Set<Integer> possibleNextNodes(int node) {
35: Set<Integer> result = new HashSet<Integer>();
36: for (int i = 0; i < distance[node].length; i++) {
37: if (distance[node][i] != INF) {
38: result.add(new Integer(i));
39: } 40: }41: return result;
42: } 43: 44: public static double f(int currentNode, Set<Integer> nodesVisited){
45: if(currentNode==3) return 0.0;
46: else{
47: Set<Integer> possibleSuccessors = possibleNextNodes(currentNode); 48: possibleSuccessors.removeAll(nodesVisited);49: double min = Double.MAX_VALUE;
50: for(Integer a : possibleSuccessors){
51: Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
52: set.addAll(nodesVisited); 53: set.add(a);54: double dis = distance[currentNode][a]+f(a,set);
55: if(dis<min) {
56: min = dis; 57: } 58: }59: return min;
60: } 61: } 62: 63: /**
64: * @param args
65: */
66: public static void main(String[] args) {
67: path.add(0);68: double shortest = f(0,path);
69: System.out.println(shortest); 70: } 71: 72: }source code:松弛法
1: /*
2: * Copyright (C) 2013 changedi
3: *
4: * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
5: * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
6: * You may obtain a copy of the License at
7: *
8: * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
9: *
10: * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
11: * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
12: * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
13: * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
14: * limitations under the License.
15: */
16: package com.jybat.dp;
17: 18: import java.util.HashSet;
19: import java.util.Set;
20: 21: public class ShortestPathCyclic2 {
22: 23: private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
24: 25: // nodes (s,x,y,t) = {0,1,2,3}, so (s,x) = 3 means d[0][1] = 3
26: private static int[][] distance = {
27: { INF, 5, 3, INF }, 28: { INF, INF, 2, 5 }, 29: { INF, 1, INF, 8 }, 30: { INF, INF, INF, INF } 31: }; 32: 33: private static Set<Integer> possibleNextNodes(int node) {
34: Set<Integer> result = new HashSet<Integer>();
35: for (int i = 0; i < distance[node].length; i++) {
36: if (distance[node][i] != INF) {
37: result.add(new Integer(i));
38: } 39: }40: return result;
41: } 42: 43: public static double f(int currentNode, int noOfEdgesToTarget){
44: if(currentNode==3)
45: return 0.0;
46: else if(noOfEdgesToTarget==0&¤tNode!=3)
47: return INF;
48: else{
49: Set<Integer> possibleSuccessors = possibleNextNodes(currentNode);50: double min = Double.MAX_VALUE;
51: for(Integer d : possibleSuccessors){
52: double dis = distance[currentNode][d]+f(d,noOfEdgesToTarget-1);
53: if(dis<min) {
54: min = dis; 55: } 56: }57: return min;
58: } 59: } 60: 61: /**
62: * @param args
63: */
64: public static void main(String[] args) {
65: double shortest = f(0,3);
66: System.out.println(shortest); 67: } 68: 69: }posted on 2014-03-24 09:44 changedi 閱讀(1960) 評論(1) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類: 算法