如何測試Nginx的高性能
簡介
Nginx ("engine x") 是一個高性能的HTTP和反向代理服務器,也是一個IMAP/POP3/SMTP代理服務器;
作為一款輕量級的Web服務器,具有占有內存少,并發能力強等優勢,是高連接并發場景下Apache的不錯的替代品;
本篇主要介紹Nginx作為Web服務器時,相對于Apache的性能優勢;
下一篇將會介紹Nginx作為方向代理服務器的實現;
重要特點
非阻塞:數據復制時,磁盤I/O的第一階段是非阻塞的;
事件驅動:通信機制采用epoll模型,支持更大的并發連接;
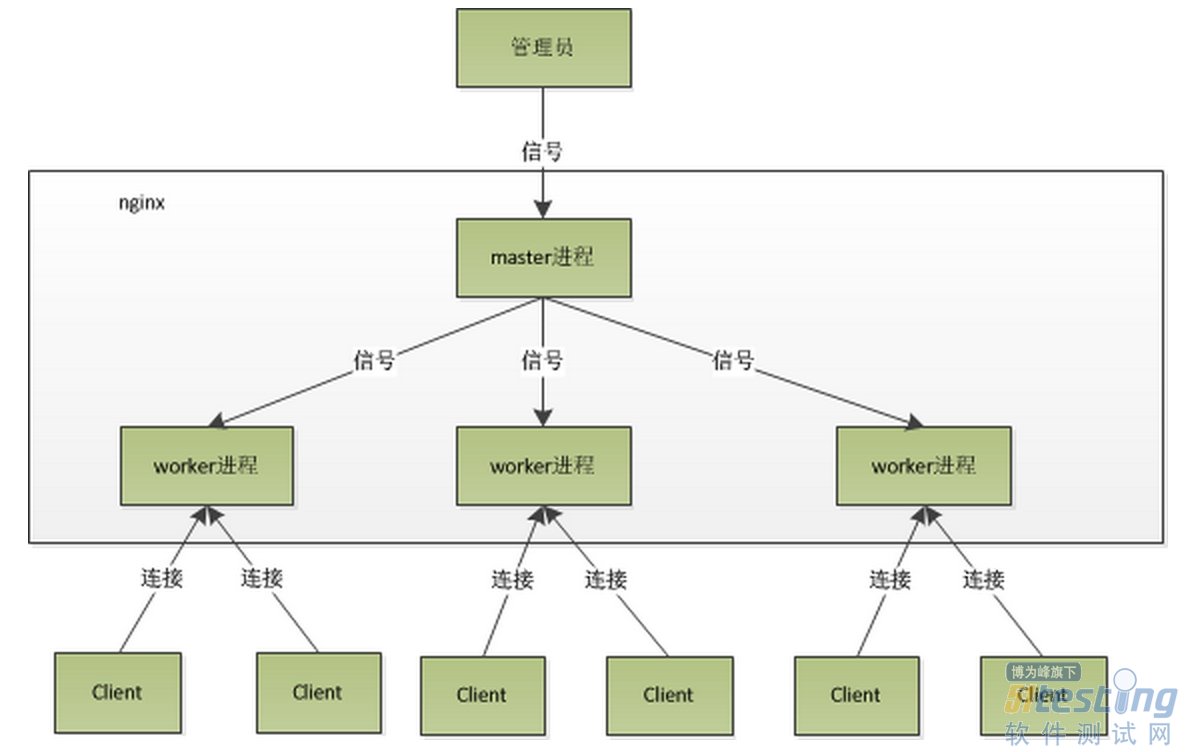
master/worker結構:一個master進程,生成一個或多個worker進程;
基礎架構
Nginx如何實現高并發:
I/O模型采用異步非阻塞的事件驅動機制,由進程循環處理多個準備好的事件,如epoll機制;
Nginx與Apache對高并發處理上的區別:
對于Apache,每個請求都會獨占一個工作線程,當并發量增大時,也會產生大量的工作線程,導致內存占用急劇上升,同時線程的上下文切換也會導致CPU開銷增大,導致在高并發場景下性能下降嚴重;
對于Nginx,一個worker進程只有一個主線程,通過事件驅動機制,實現循環處理多個準備好的事件,從而實現輕量級和高并發;
部署配置
安裝
yum -y groupinstall “Development tools” yum -y groupinstall “Server Platform Development” yum install gcc openssl-devel pcre-devel zlib-devel groupadd -r nginx useradd -r -g nginx -s /sbin/nologin -M nginx tar xf nginx-1.4.7.tar.gz cd nginx-1.4.7 mkdir -pv /var/tmp/nginx ./configure \ --prefix=/usr \ --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx \ --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \ --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \ --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \ --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid \ --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \ --user=nginx \ --group=nginx \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_flv_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ \ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ \ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ \ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi \ --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi \ --with-pcre make && make install |
配置:
vi /etc/init.d/nginx # 配置服務腳本 #!/bin/sh # # nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon # # chkconfig: - 85 15 # description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse \ # proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server # processname: nginx # config: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx # pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid # Source function library. . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions # Source networking configuration. . /etc/sysconfig/network # Check that networking is up. [ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0 nginx="/usr/sbin/nginx" prog=$(basename $nginx) NGINX_CONF_FILE="/etc/nginx/nginx.conf" [ -f /etc/sysconfig/nginx ] && . /etc/sysconfig/nginx lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx make_dirs() { # make required directories user=`nginx -V 2>&1 | grep "configure arguments:" | sed 's/[^*]*--user=\([^ ]*\).*/\1/g' -` options=`$nginx -V 2>&1 | grep 'configure arguments:'` for opt in $options; do if [ `echo $opt | grep '.*-temp-path'` ]; then value=`echo $opt | cut -d "=" -f 2` if [ ! -d "$value" ]; then # echo "creating" $value mkdir -p $value && chown -R $user $value fi fi done } start() { [ -x $nginx ] || exit 5 [ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6 make_dirs echo -n $"Starting $prog: " daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE retval=$? echo [ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile return $retval } stop() { echo -n $"Stopping $prog: " killproc $prog -QUIT retval=$? echo [ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile return $retval } restart() { configtest || return $? stop sleep 1 start } reload() { configtest || return $? echo -n $"Reloading $prog: " killproc $nginx -HUP RETVAL=$? echo } force_reload() { restart } configtest() { $nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE } rh_status() { status $prog } rh_status_q() { rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1 } case "$1" in start) rh_status_q && exit 0 $1 ;; stop) rh_status_q || exit 0 $1 ;; restart|configtest) $1 ;; reload) rh_status_q || exit 7 $1 ;; force-reload) force_reload ;; status) rh_status ;; condrestart|try-restart) rh_status_q || exit 0 ;; *) echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}" exit 2 esac chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx # 復***務腳本執行權限 vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # 編輯主配置文件 worker_processes 2; error_log /var/log/nginx/nginx.error.log; pid /var/run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server { listen 80; server_name xxrenzhe.lnmmp.com; access_log /var/log/nginx/nginx.access.log main; location / { root /www/lnmmp.com; index index.php index.html index.htm; } error_page 404 /404.html; error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root /www/lnmmp.com; } location ~ \.php$ { root /www/lnmmp.com; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } } } vi /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params # 編輯fastcgi參數文件 fastcgi_param GATEWAY_INTERFACE CGI/1.1; fastcgi_param SERVER_SOFTWARE nginx; fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string; fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method; fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type; fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri; fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_URI $document_uri; fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root; fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol; fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr; fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port; fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr; fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port; fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name; |
啟動服務:
service nginx configtest # 服務啟動前先驗證配置文件是否正確
service nginx start
ps -ef |grep nginx # 檢查nginx進程,尤其是worker進程是否與worker_processes值一致
ss -antupl |grep 80 # 檢查服務端口是否啟動
性能測試
測試說明
每次測試都進行3次,最后數據取平均值;
對比測試中的Apache采用event的MPM機制,最大化提高Apache的并發性能;
每次測試后,都需重新啟動服務(httpd或nginx),以防止多次測試數據不準;
測試工具:webbench
優點:比ab能更好的模擬并發請求,最大支持模擬30000并發連接;
測試方法
# 安裝wenbench wget http://blog.s135.com/soft/linux/webbench/webbench-1.5.tar.gz tar xf webbench-1.5.tar.gz cd webbench-1.5 make && make install # 測試 webbench -c 100 -t 30 http://172.16.25.112/nginx.html # 測試靜態文件訪問 webbench -c 20 -t 30 http://172.16.25.112/test_mem.php # 測試動態文件訪問 |
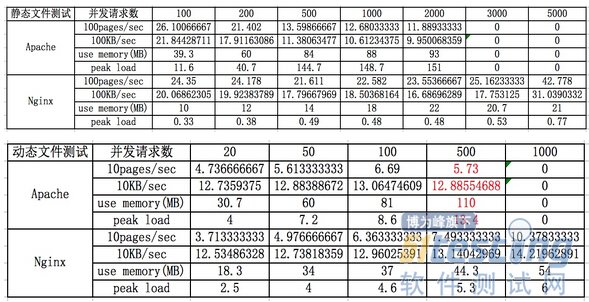
測試數據
分析趨勢圖
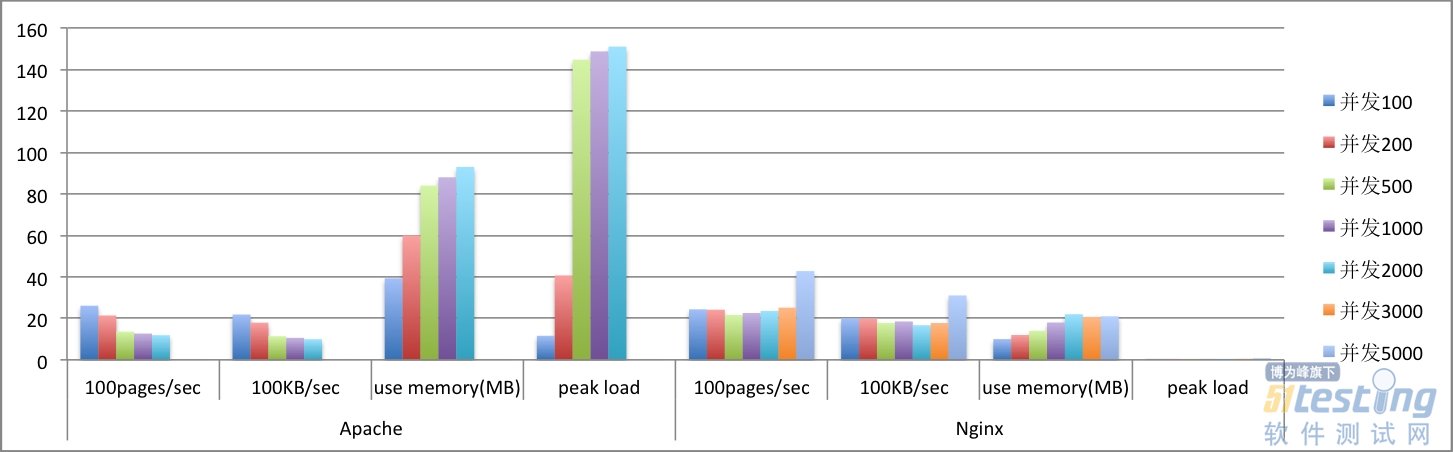
靜態文件訪問趨勢圖
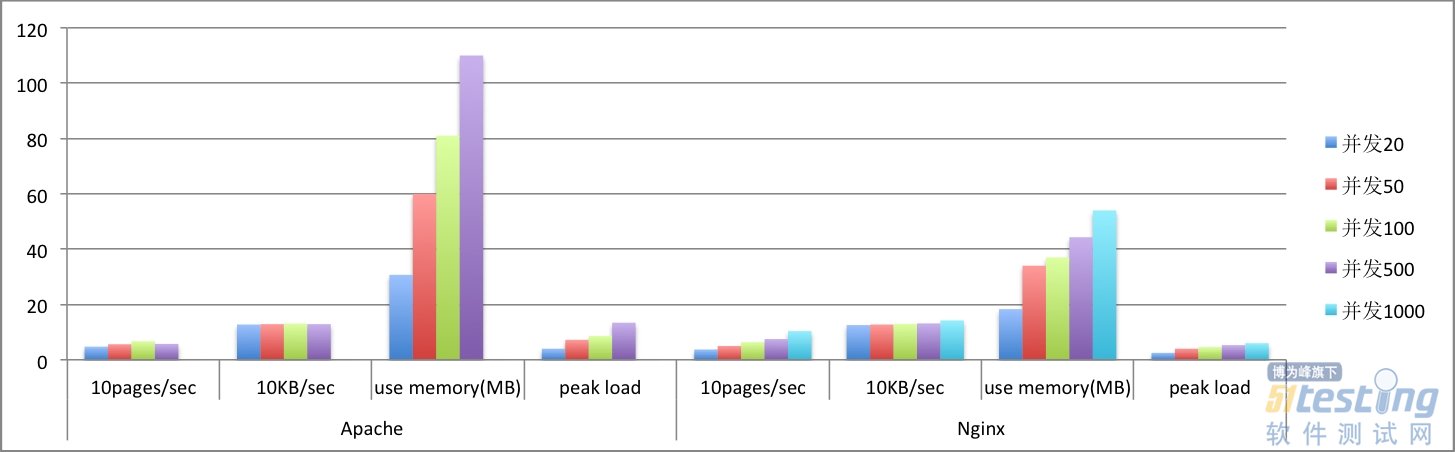
動態文件訪問趨勢圖
總結
綜合上面測試得出的趨勢圖可以看出:
靜態文件測試時,低并發(200以下)情況下,Nginx和Apach的處理能力相當(2000pages/sec左右),當并發數超過200后,則 Apache的處理能力開始下降,而Nginx保持穩定;同時隨著并發量的增大,Apache令人詬病的內存占用和負載開始急劇上升,與此同 時,Nginx在內存占用和負載方面的略微提升則可以忽略不計了;
動態文件測試時,低并發 (100以下)情況下,Nginx和Apache的處理能力相當(650pages/sec左右),但Nginx的內存占用和負載峰值只有Apache的 50%左右;在高并發情況下(100以上),Apach的動態處理能力開始下滑,當并發達到500時,開始出現失敗的請求,說明此時已達到的Apache 的處理上限了,而反觀Nginx,雖然處理動態請求會消耗更多的內存,但其處理能力隨著并發量的上升而上升,即使并發1000動態請求,也未達到其處理能 力上限;
故不管是在靜態文件請求還是動態文件請求方面,Nginx的性能都是強勢優于Apache的;雖然可以通過系統調優的方式提高Apache的處理性能,但和Nginx相比,還是不足以打動技術狂熱份子的吧,哈哈!
posted on 2014-05-23 10:04 順其自然EVO 閱讀(2382) 評論(0) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類: 測試學習專欄