JUnit源碼分析 (三)——Template Method模式
Posted on 2007-04-06 09:54 dennis 閱讀(2667) 評論(0) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類: 模式與架構 、源碼解讀 在JUnit執行測試時,我們經常需要初始化一些環境供測試代碼使用,比如數據庫連接、mock對象等等,這些初始化代碼應當在每一個測試之前執行并在測試方法運行后清理。在JUnit里面就是相應的setUp和tearDown方法。如果沒有這兩個方法,那么我們要在每個測試方法的代碼內寫上一大堆重復的初始化和清理代碼,這是多么愚蠢的做法。那么JUnit是怎么讓setUp和tearDown在測試執行前后被調用的呢?
如果你查看下TestCase方法,你會發現TestCase和TestSuite的run()方法都是將執行測試的任務委托給了TestResult,由TestResult去執行測試代碼并收集測試過程中的信息(這里用到了Collecting Parameter模式)。
我們直接找到TestResult,看看它的run方法:
這里實例化了一個內部類,內部類實現了Protectable接口的 protect()方法,并執行傳入的TestCase的runBare()方法,顯然,真正的測試代碼在TestCase的runBare()方法中,讓我們來看下:
Template Method模式
類行為模式的一種
1.意圖:定義一個操作中的算法的骨架,而將一些延遲步驟到子類中。Template Method使得子類可以不改變一個算法的結構即可重定義該算法的某些步驟。
2.適用場景:
1)一次性實現算法的不變部分(基本骨架),將可變的行為留給子類來完成
2)子類中的公共部分(比如JUnit中的初始化和清理)被抽取到一個公共父類中以避免代碼重復。
3)控制了子類的擴展,這里其實也有類似回調函數的性質,具體步驟先在骨架中注冊,在具體執行時被回調。
3.UML圖和結構
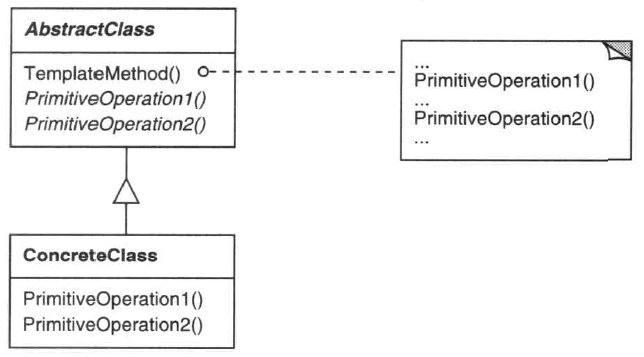
抽象父類定義了算法的基本骨架(模板方法),而不同的子類實現具體的算法步驟,客戶端由此可以與算法的更改隔離。
4.效果:
1)模板方法是代碼復用的基本技術,在類庫中經常使用,可以減少大量的代碼重復
2)通過隔離算法的不變和可變部分,增加了系統的靈活性,擴展算法的某些步驟將變的很容易。
了解了Template Method模式之后,讓我們回到JUnit的源碼,看看runTest()方法,這里主要應用的是java的反射技術,對于學習反射技術的有參考價值:
如果你查看下TestCase方法,你會發現TestCase和TestSuite的run()方法都是將執行測試的任務委托給了TestResult,由TestResult去執行測試代碼并收集測試過程中的信息(這里用到了Collecting Parameter模式)。
public TestResult run() {
TestResult result= createResult();
run(result);
return result;
}
/**
* Runs the test case and collects the results in TestResult.
* This is the template method that defines the control flow
* for running a test case.
*/
public void run(TestResult result) {
result.run(this);
}
TestResult result= createResult();
run(result);
return result;
}
/**
* Runs the test case and collects the results in TestResult.
* This is the template method that defines the control flow
* for running a test case.
*/
public void run(TestResult result) {
result.run(this);
}
我們直接找到TestResult,看看它的run方法:
/**
* Runs a TestCase.
*/
protected void run(final TestCase test) {
startTest(test);
Protectable p = new Protectable() {
public void protect() throws Throwable {
test.runBare();
}
};
runProtected(test, p);
endTest(test);
}
* Runs a TestCase.
*/
protected void run(final TestCase test) {
startTest(test);
Protectable p = new Protectable() {
public void protect() throws Throwable {
test.runBare();
}
};
runProtected(test, p);
endTest(test);
}
這里實例化了一個內部類,內部類實現了Protectable接口的 protect()方法,并執行傳入的TestCase的runBare()方法,顯然,真正的測試代碼在TestCase的runBare()方法中,讓我們來看下:
//將被子類實現
protected void setUp() throws Throwable {
}
//同上,將被具體的TestCase實現
protected void tearDown() throws Throwable {
}
/**
* 模板方法
* Runs the bare test sequence.
* @exception Throwable if any exception is thrown
*/
public void runBare() throws Throwable {
setUp();
try {
runTest();
}
finally {
tearDown();
}
}
真相水落石出,對于每一個測試方法,都遵循這樣的模板:setUp->執行測試 runTest()->tearDown。這正是模板方式模式的一個應用例子。什么是template method模式呢?protected void setUp() throws Throwable {
}
//同上,將被具體的TestCase實現
protected void tearDown() throws Throwable {
}
/**
* 模板方法
* Runs the bare test sequence.
* @exception Throwable if any exception is thrown
*/
public void runBare() throws Throwable {
setUp();
try {
runTest();
}
finally {
tearDown();
}
}
Template Method模式
類行為模式的一種
1.意圖:定義一個操作中的算法的骨架,而將一些延遲步驟到子類中。Template Method使得子類可以不改變一個算法的結構即可重定義該算法的某些步驟。
2.適用場景:
1)一次性實現算法的不變部分(基本骨架),將可變的行為留給子類來完成
2)子類中的公共部分(比如JUnit中的初始化和清理)被抽取到一個公共父類中以避免代碼重復。
3)控制了子類的擴展,這里其實也有類似回調函數的性質,具體步驟先在骨架中注冊,在具體執行時被回調。
3.UML圖和結構

抽象父類定義了算法的基本骨架(模板方法),而不同的子類實現具體的算法步驟,客戶端由此可以與算法的更改隔離。
4.效果:
1)模板方法是代碼復用的基本技術,在類庫中經常使用,可以減少大量的代碼重復
2)通過隔離算法的不變和可變部分,增加了系統的靈活性,擴展算法的某些步驟將變的很容易。
了解了Template Method模式之后,讓我們回到JUnit的源碼,看看runTest()方法,這里主要應用的是java的反射技術,對于學習反射技術的有參考價值:
protected void runTest() throws Throwable {
Method runMethod= null;
try {
runMethod= getClass().getDeclaredMethod(fName, new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
fail("Method \""+fName+"\" not found");
}
if (runMethod != null && !Modifier.isPublic(runMethod.getModifiers())) {
fail("Method \""+fName+"\" should be public");
}
try {
runMethod.invoke(this, new Class[0]);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.fillInStackTrace();
throw e.getTargetException();
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.fillInStackTrace();
throw e;
}
}
Method runMethod= null;
try {
runMethod= getClass().getDeclaredMethod(fName, new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
fail("Method \""+fName+"\" not found");
}
if (runMethod != null && !Modifier.isPublic(runMethod.getModifiers())) {
fail("Method \""+fName+"\" should be public");
}
try {
runMethod.invoke(this, new Class[0]);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.fillInStackTrace();
throw e.getTargetException();
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.fillInStackTrace();
throw e;
}
}



