流式IO
流(Stream)是字節(jié)的源或目的。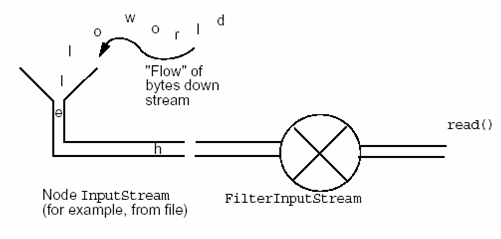
兩種基本的流是:輸入流(Input Stream)和輸出流(Output Stream)。可從中讀出一系列字節(jié)的對(duì)象稱(chēng)為輸入流。而能向其中寫(xiě)入一系列字節(jié)的對(duì)象稱(chēng)為輸出流。
流的分類(lèi)
節(jié)點(diǎn)流:從特定的地方讀寫(xiě)的流類(lèi),例如:磁盤(pán)或一塊內(nèi)存區(qū)域。
過(guò)濾流:使用節(jié)點(diǎn)流作為輸入或輸出。過(guò)濾流是使用一個(gè)已經(jīng)存在的輸入流或輸出流連接創(chuàng)建的。
InputStream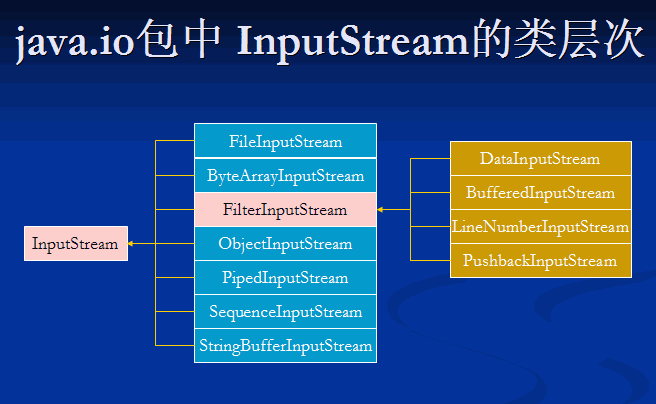
三個(gè)基本的讀方法
abstract int read() :讀取一個(gè)字節(jié)數(shù)據(jù),并返回讀到的數(shù)據(jù),如果返回-1,表示讀到了輸入流的末尾。
int read(byte[] b) :將數(shù)據(jù)讀入一個(gè)字節(jié)數(shù)組,同時(shí)返回實(shí)際讀取的字節(jié)數(shù)。如果返回-1,表示讀到了輸入流的末尾。
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) :將數(shù)據(jù)讀入一個(gè)字節(jié)數(shù)組,同時(shí)返回實(shí)際讀取的字節(jié)數(shù)。如果返回-1,表示讀到了輸入流的末尾。off指定在數(shù)組b中存放數(shù)據(jù)的起始偏移位置;len指定讀取的最大字節(jié)數(shù)。
其它方法
long skip(long n) :在輸入流中跳過(guò)n個(gè)字節(jié),并返回實(shí)際跳過(guò)的字節(jié)數(shù)。
int available() :返回在不發(fā)生阻塞的情況下,可讀取的字節(jié)數(shù)。
void close() :關(guān)閉輸入流,釋放和這個(gè)流相關(guān)的系統(tǒng)資源。
void mark(int readlimit) :在輸入流的當(dāng)前位置放置一個(gè)標(biāo)記,如果讀取的字節(jié)數(shù)多于readlimit設(shè)置的值,則流忽略這個(gè)標(biāo)記。
void reset() :返回到上一個(gè)標(biāo)記。
boolean markSupported() :測(cè)試當(dāng)前流是否支持mark和reset方法。如果支持,返回true,否則返回false。
java.io包中 InputStream的類(lèi)層次
OutputStream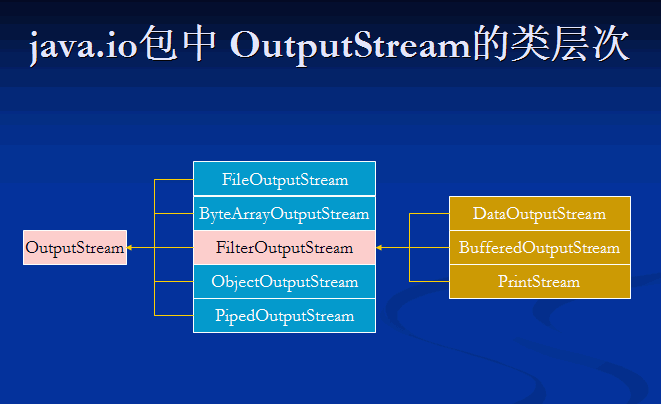
三個(gè)基本的寫(xiě)方法
abstract void write(int b) :往輸出流中寫(xiě)入一個(gè)字節(jié)。
void write(byte[] b) :往輸出流中寫(xiě)入數(shù)組b中的所有字節(jié)。
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) :往輸出流中寫(xiě)入數(shù)組b中從偏移量off開(kāi)始的len個(gè)字節(jié)的數(shù)據(jù)。
其它方法
void flush() :刷新輸出流,強(qiáng)制緩沖區(qū)中的輸出字節(jié)被寫(xiě)出。
void close() :關(guān)閉輸出流,釋放和這個(gè)流相關(guān)的系統(tǒng)資源。
java.io包中 OutputStream的類(lèi)層次
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo1:在控制臺(tái)讀取鍵盤(pán)輸入,然后顯示。Ctrl+C結(jié)束運(yùn)行
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6
 int data;
int data;7

8

 while ((data = System.in.read()) != - 1 )
while ((data = System.in.read()) != - 1 )  {
{9
 System.out.write(data);
System.out.write(data);10
 }
} 11

12
 }
} 13

14
 }
} 15

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
基本的流類(lèi)
1、FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
節(jié)點(diǎn)流,用于從文件中讀取或往文件中寫(xiě)入字節(jié)流。如果在構(gòu)造FileOutputStream時(shí),文件已經(jīng)存在,則覆蓋這個(gè)文件。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo2:將字符串寫(xiě)入特定文件,注意write方法只接收字符數(shù)組。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );7

8

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 9
 * 注意:FileOutputStream的write方法接收字符數(shù)組,不能接收String字符串,
* 注意:FileOutputStream的write方法接收字符數(shù)組,不能接收String字符串,10
 * 所以要用String的getBytes方法生成一個(gè)字符數(shù)組
* 所以要用String的getBytes方法生成一個(gè)字符數(shù)組11
 */
*/ 12
 fos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());
fos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes()); 13
 fos.close();
fos.close();14

15
 }
} 16

17
 }
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
String的構(gòu)造方法的API:
------------
Java API:
------------
String
public String(byte[] bytes,
int offset,
int length)
構(gòu)造一個(gè)新的 String,方法是使用指定的字符集解碼字節(jié)的指定子數(shù)組。新的 String 的長(zhǎng)度是一個(gè)字符集函數(shù),因此不能等于該子數(shù)組的長(zhǎng)度。
當(dāng)給定字節(jié)在給定字符集中無(wú)效的情況下,該構(gòu)造方法無(wú)指定的行為。當(dāng)需要進(jìn)一步控制解碼過(guò)程時(shí),應(yīng)使用 CharsetDecoder 類(lèi)。
參數(shù):
bytes - 要解碼為字符的字節(jié)
offset - 要解碼的首字節(jié)的索引
length - 要解碼的字節(jié)數(shù)
拋出:
IndexOutOfBoundsException - 如果 offset 和 length 參數(shù)索引字符超出 bytes 數(shù)組的范圍
從以下版本開(kāi)始:
JDK1.1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo3:將字符串寫(xiě)入特定文件,注意write方法只接收字符數(shù)組。
然后通過(guò)文件輸出流讀取數(shù)據(jù),注意使用String特定的構(gòu)造方法。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );7

8

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 9
 * 注意:FileOutputStream的write方法接收字符數(shù)組,不能接收String字符串,
* 注意:FileOutputStream的write方法接收字符數(shù)組,不能接收String字符串,10
 * 所以要用String的getBytes方法生成一個(gè)字符數(shù)組
* 所以要用String的getBytes方法生成一個(gè)字符數(shù)組11
 */
*/ 12
 fos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());
fos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes()); 13
 fos.close();
fos.close();14

15
 // 使用String的這個(gè)構(gòu)造方法:
// 使用String的這個(gè)構(gòu)造方法:16
 // String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
// String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) 17

18
 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream( " 1.txt " );19
 byte [] buf = new byte [ 100 ];
byte [] buf = new byte [ 100 ];20
 int len = fis.read(buf);
int len = fis.read(buf);21

22
 // 使用String的這個(gè)構(gòu)造方法:
// 使用String的這個(gè)構(gòu)造方法:23
 // String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
// String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) 24
 System.out.println( new String(buf, 0 , len));
System.out.println( new String(buf, 0 , len));25
 fis.close(); // 使用完后記得關(guān)閉文件流
fis.close(); // 使用完后記得關(guān)閉文件流 26

27
 }
} 28

29
 }
} 30

31

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:http://www.cnblogs.com
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2、BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
過(guò)濾流,需要使用已經(jīng)存在的節(jié)點(diǎn)流來(lái)構(gòu)造,提供帶緩沖的讀寫(xiě),提高了讀寫(xiě)的效率。
------------
Java API:
------------
構(gòu)造方法摘要
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的緩沖輸出流,以將數(shù)據(jù)寫(xiě)入指定的基礎(chǔ)輸出流。
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size)
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的緩沖輸出流,以將具有指定緩沖區(qū)大小的數(shù)據(jù)寫(xiě)入指定的基礎(chǔ)輸出流。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BufferedOutputStream
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的緩沖輸出流,以將數(shù)據(jù)寫(xiě)入指定的基礎(chǔ)輸出流。
參數(shù):
out - 基礎(chǔ)輸出流。
BufferedOutputStream
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out,
int size)
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的緩沖輸出流,以將具有指定緩沖區(qū)大小的數(shù)據(jù)寫(xiě)入指定的基礎(chǔ)輸出流。
參數(shù):
out - 基礎(chǔ)輸出流。
size - 緩沖區(qū)的大小。
拋出:
IllegalArgumentException - 如果 size <= 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo4:通過(guò)一個(gè)OutputStream對(duì)象來(lái)構(gòu)造一個(gè)BufferedOutputStream對(duì)象。
而FileOutputStream類(lèi)是OutputStream類(lèi)的子類(lèi),所以可以用它來(lái)構(gòu)造。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6

7
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );8
 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);9
 bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());
bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());10
 }
} 11

12
 }
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:1.txt文件為空。原因:緩沖區(qū)沒(méi)有寫(xiě)滿(mǎn),程序沒(méi)有向文件寫(xiě)數(shù)據(jù)。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
解決方法1:使用flush()方法:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo4:使用flush()方法,可以使程序立即向文件寫(xiě)數(shù)據(jù)。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6

7
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );8
 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);9
 bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());
bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());10

11
 bos.flush();
bos.flush();12
 }
} 13

14
 }
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:數(shù)據(jù)被寫(xiě)入相應(yīng)的文件。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
解決方法2:使用close()方法:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo5:使用close()方法,同樣可以使程序立即向文件寫(xiě)數(shù)據(jù)。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6

7
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );8
 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);9
 bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());
bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());10

11
 bos.close();
bos.close();12
 }
} 13

14
 }
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:數(shù)據(jù)被寫(xiě)入相應(yīng)的文件。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
flush()和close()的區(qū)別:
還要使用流對(duì)象,還需要寫(xiě)數(shù)據(jù),使用flush(),否則使用close()。
另外,使用close()將關(guān)閉自己的流對(duì)象,同時(shí)會(huì)關(guān)閉與之相關(guān)的流對(duì)象,如FileOutputStream流。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo6:使用BufferedInputStream流,從文件中讀取數(shù)據(jù)。
同樣要用InputStream流對(duì)象或者其子類(lèi)的對(duì)象來(lái)構(gòu)造。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6

7
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " 1.txt " );8
 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);9
 bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());
bos.write( " http://www.cnblogs.com " .getBytes());10

11
 bos.close();
bos.close();12

13
 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream( " 1.txt " );
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream( " 1.txt " );14
 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);15
 byte [] buf = new byte [ 100 ];
byte [] buf = new byte [ 100 ];16
 int len = bis.read(buf);
int len = bis.read(buf);17

18
 // 使用String的這個(gè)構(gòu)造方法:
// 使用String的這個(gè)構(gòu)造方法:19
 // String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)
// String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) 20
 System.out.println( new String(buf, 0 , len));
System.out.println( new String(buf, 0 , len));21
 bis.close();
bis.close();22
 }
} 23

24
 }
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:輸出http://www.cnblogs.com
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3、DataInputStream和DataOutputStream
過(guò)濾流,需要使用已經(jīng)存在的節(jié)點(diǎn)流來(lái)構(gòu)造,提供了讀寫(xiě)Java中的基本數(shù)據(jù)類(lèi)型的功能。
------------
Java API:
------------
java.io
類(lèi) DataOutputStream
java.lang.Object
java.io.OutputStream
java.io.FilterOutputStream
java.io.DataOutputStream
所有已實(shí)現(xiàn)的接口:
Closeable, DataOutput, Flushable
public class DataOutputStream
extends FilterOutputStream
implements DataOutput
數(shù)據(jù)輸出流允許應(yīng)用程序以適當(dāng)方式將基本 Java 數(shù)據(jù)類(lèi)型寫(xiě)入輸出流中。然后,應(yīng)用程序可以使用數(shù)據(jù)輸入流將數(shù)據(jù)讀入。
從以下版本開(kāi)始:
JDK1.0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
構(gòu)造方法摘要
DataOutputStream(OutputStream out)
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的數(shù)據(jù)輸出流,將數(shù)據(jù)寫(xiě)入指定基礎(chǔ)輸出流。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DataOutputStream
public DataOutputStream(OutputStream out)
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的數(shù)據(jù)輸出流,將數(shù)據(jù)寫(xiě)入指定基礎(chǔ)輸出流。計(jì)數(shù)器 written 被設(shè)置為零。
參數(shù):
out - 基礎(chǔ)輸出流,將被保存供以后使用。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo7:使用DataOutputStream流,將基本數(shù)據(jù)類(lèi)型以二進(jìn)制形式寫(xiě)入文件中。
同樣要用InputStream流對(duì)象或者其子類(lèi)的對(duì)象來(lái)構(gòu)造,
這里使用BufferedOutputStream對(duì)象來(lái)構(gòu)造。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6

7
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " dos.txt " ); // 獲得寫(xiě)入文件功能
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " dos.txt " ); // 獲得寫(xiě)入文件功能 8
 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); // 獲得緩沖功能
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); // 獲得緩沖功能 9
 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos); // 獲得寫(xiě)入基本類(lèi)型功能
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos); // 獲得寫(xiě)入基本類(lèi)型功能 10

11

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 12
 * 定義8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象
* 定義8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象13
 */
*/ 14
 byte b = 3 ;
byte b = 3 ;15
 short s = 4 ;
short s = 4 ;16
 int i = 78 ;
int i = 78 ;17
 long l = 100000 ;
long l = 100000 ; 18
 char ch = ' a ' ;
char ch = ' a ' ;19
 boolean bl = false ;
boolean bl = false ;20
 float f = 4.5f ;
float f = 4.5f ;21
 double d = 4.0001 ;
double d = 4.0001 ;22

23

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 24
 * 將8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象寫(xiě)入文件中
* 將8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象寫(xiě)入文件中25
 */
*/ 26
 dos.writeByte(b);
dos.writeByte(b);27
 dos.writeShort(s);
dos.writeShort(s);28
 dos.writeInt(i);
dos.writeInt(i);29
 dos.writeLong(l);
dos.writeLong(l);30
 dos.writeChar(ch);
dos.writeChar(ch);31
 dos.writeBoolean(bl);
dos.writeBoolean(bl);32
 dos.writeFloat(f);
dos.writeFloat(f);33
 dos.writeDouble(d);
dos.writeDouble(d);34
 dos.close();
dos.close();35
 }
} 36

37
 }
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:8種基本類(lèi)型的數(shù)據(jù)以二進(jìn)制形式寫(xiě)入指定的文件中。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo8:從指定的文件中讀取8種基本類(lèi)型的數(shù)據(jù)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class StreamDemo
public class StreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception  {
{6

7
 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " dos.txt " ); // 獲得寫(xiě)入文件功能
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream( " dos.txt " ); // 獲得寫(xiě)入文件功能 8
 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); // 獲得緩沖功能
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); // 獲得緩沖功能 9
 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos); // 獲得寫(xiě)入基本類(lèi)型功能
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos); // 獲得寫(xiě)入基本類(lèi)型功能 10

11

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 12
 * 定義8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象
* 定義8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象13
 */
*/ 14
 byte b = 3 ;
byte b = 3 ;15
 short s = 4 ;
short s = 4 ;16
 int i = 78 ;
int i = 78 ;17
 long l = 100000 ;
long l = 100000 ; 18
 char ch = ' a ' ;
char ch = ' a ' ;19
 boolean bl = false ;
boolean bl = false ;20
 float f = 4.5f ;
float f = 4.5f ;21
 double d = 4.0001 ;
double d = 4.0001 ;22

23

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 24
 * 將8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象寫(xiě)入文件中
* 將8種基本類(lèi)型的對(duì)象寫(xiě)入文件中25
 */
*/ 26
 dos.writeByte(b);
dos.writeByte(b);27
 dos.writeShort(s);
dos.writeShort(s);28
 dos.writeInt(i);
dos.writeInt(i);29
 dos.writeLong(l);
dos.writeLong(l);30
 dos.writeChar(ch);
dos.writeChar(ch);31
 dos.writeBoolean(bl);
dos.writeBoolean(bl);32
 dos.writeFloat(f);
dos.writeFloat(f);33
 dos.writeDouble(d);
dos.writeDouble(d);34
 dos.close();
dos.close();35

36
 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream( " dos.txt " );
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream( " dos.txt " );37
 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);38
 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis);39
 System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readByte());40
 System.out.println(dis.readShort());
System.out.println(dis.readShort());41
 System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());42
 System.out.println(dis.readLong());
System.out.println(dis.readLong());43
 System.out.println(dis.readChar());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());44
 System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());45
 System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());46
 System.out.println(dis.readDouble());
System.out.println(dis.readDouble());47
 dis.close();
dis.close();48
 }
} 49

50
 }
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:數(shù)據(jù)正常輸出:
3
4
78
100000
a
false
4.5
4.0001
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4、PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream
管道流,用于線程間的通信。一個(gè)線程的PipedInputStream對(duì)象從另一個(gè)線程的PipedOutputStream對(duì)象讀取輸入。要使管道流有用,必須同時(shí)構(gòu)造管道輸入流和管道輸出流。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------
Java API:
------------
java.io
類(lèi) PipedInputStream
java.lang.Object
java.io.InputStream
java.io.PipedInputStream
所有已實(shí)現(xiàn)的接口:
Closeable
public class PipedInputStream
extends InputStream
傳送輸入流應(yīng)該連接到傳送輸出流;傳送輸入流會(huì)提供要寫(xiě)入傳送輸出流的所有數(shù)據(jù)字節(jié)。通常,數(shù)據(jù)由某個(gè)線程從 PipedInputStream 對(duì)象讀取,并由其他線程將其寫(xiě)入到相應(yīng)的 PipedOutputStream。不建議對(duì)這兩個(gè)對(duì)象嘗試使用單個(gè)線程,因?yàn)檫@樣可能會(huì)死鎖該線程。傳送輸入流包含一個(gè)緩沖區(qū),可在緩沖區(qū)限定的范圍內(nèi)將讀操作和寫(xiě)操作分離開(kāi)。
從以下版本開(kāi)始:
JDK1.0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------
Java API:
------------
java.io
類(lèi) PipedOutputStream
java.lang.Object
java.io.OutputStream
java.io.PipedOutputStream
所有已實(shí)現(xiàn)的接口:
Closeable, Flushable
public class PipedOutputStream
extends OutputStream
傳送輸出流可以連接到傳送輸入流,以創(chuàng)建通信管道。傳送輸出流是管道的發(fā)送端。通常,數(shù)據(jù)由某個(gè)線程寫(xiě)入 PipedOutputStream 對(duì)象,并由其他線程從連接的 PipedInputStream 讀取。不建議對(duì)這兩個(gè)對(duì)象嘗試使用單個(gè)線程,因?yàn)檫@樣可能會(huì)死鎖該線程。
從以下版本開(kāi)始:
JDK1.0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------
Java API:
------------
connect
public void connect(PipedInputStream snk)
throws IOException
將此傳送輸出流連接到接收者。如果此對(duì)象已經(jīng)連接到其他某個(gè)傳送輸入流,則拋出 IOException。
如果 snk 為未連接的傳送輸入流,而 src 為未連接的傳送輸出流,則可以通過(guò)以下任一調(diào)用使其連接:
src.connect(snk)
或:
snk.connect(src)
這兩個(gè)調(diào)用的效果相同。
參數(shù):
snk - 要連接的傳送輸入流。
拋出:
IOException - 如果發(fā)生 I/O 錯(cuò)誤。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demo9:利用管道輸入流和輸出流進(jìn)行通訊。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 import java.io. * ;
import java.io. * ;2

3

 public class PipedStreamDemo
public class PipedStreamDemo  {
{4

5

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{6
 PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream();
PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream();7
 PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream();
PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream();8

9

 try
try  {
{10
 pos.connect(pis);
pos.connect(pis); 11
 // pis.connect(pos); 二選一即可
// pis.connect(pos); 二選一即可 12

13
 new Producer(pos).start();
new Producer(pos).start();14
 new Consumer(pis).start();
new Consumer(pis).start();15

 } catch (IOException e)
} catch (IOException e)  {
{16
 // TODO 自動(dòng)生成 catch 塊
// TODO 自動(dòng)生成 catch 塊 17
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();18
 }
} 19
 }
} 20

21
 }
} 22

23

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 24
 * 生產(chǎn)者線程
* 生產(chǎn)者線程25
 */
*/ 26

 class Producer extends Thread
class Producer extends Thread  {
{27

28
 private PipedOutputStream pos;
private PipedOutputStream pos;29

30

 public Producer(PipedOutputStream pos)
public Producer(PipedOutputStream pos)  {
{31
 this .pos = pos;
this .pos = pos;32
 }
} 33

34

 public void run()
public void run()  {
{35

 try
try  {
{36
 pos.write( " Hello, welcome you! " .getBytes());
pos.write( " Hello, welcome you! " .getBytes());37
 pos.close();
pos.close();38

 } catch (Exception e)
} catch (Exception e)  {
{39
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();40
 }
} 41
 }
} 42

43
 }
} 44

45

 /**/ /*
/**/ /* 46
 * 消費(fèi)者線程
* 消費(fèi)者線程47
 */
*/ 48

 class Consumer extends Thread
class Consumer extends Thread  {
{49

50
 private PipedInputStream pis;
private PipedInputStream pis;51

52

 public Consumer(PipedInputStream pis)
public Consumer(PipedInputStream pis)  {
{53
 this .pis = pis;
this .pis = pis;54
 }
} 55

56

 public void run()
public void run()  {
{57

 try
try  {
{58
 byte [] buf = new byte [ 100 ];
byte [] buf = new byte [ 100 ];59
 int len = pis.read(buf);
int len = pis.read(buf);60
 System.out.println( new String(buf, 0 , len));
System.out.println( new String(buf, 0 , len));61
 pis.close(); // 關(guān)閉輸入流
pis.close(); // 關(guān)閉輸入流 62

 } catch (Exception e)
} catch (Exception e)  {
{63
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();64
 }
} 65
 }
} 66

67
 }
} 68

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:輸出Hello, welcome you!
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------



