1、示例翻譯:
<inbound>
<stdio:inbound-endpoint system="IN" transformer-refs="StdinToNameString"/>
</inbound>
<component class="org.mule.example.hello.Greeter"/>
<outbound>
<filtering-router>
<vm:outbound-endpoint path="chitchatter"/>
<payload-type-filter expectedType="org.mule.example.hello.NameString"/>
</filtering-router>
</outbound>
</service>
class="org.mule.example.hello.StdinToNameString"/>
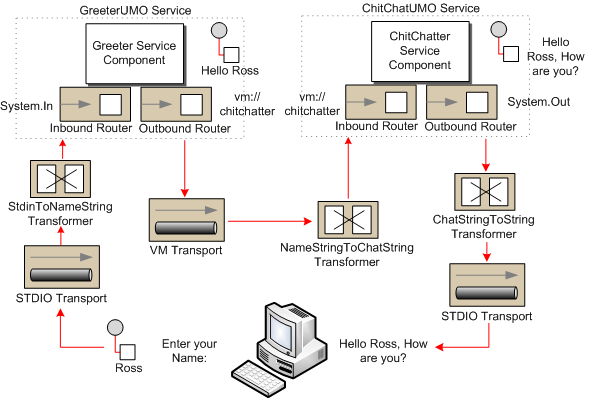
注意: Mule是依靠反射獲知Greeter內部各個方法需要的傳參類型,然后再根據目前消息格式調用正確的消息處理方法。Greeter處理完消息后、mule把消息分發到了端點:vm://chitchatter:名為chitchatter的in-memory queue內存隊列。ChitChatUMO服務組件正在監聽這個隊列(也就是說chitchatter隊列是 GreeterUMO的輸出、ChitChatUMO的輸入,這樣來使得兩個服務組件先后處理一條消息)
<inbound>
<vm:inbound-endpoint path="chitchatter" transformer-refs="NameStringToChatString"/>
</inbound>
<component class="org.mule.example.hello.ChitChatter"/>
<outbound>
<pass-through-router>
<stdio:outbound-endpoint system="OUT" transformer-refs="ChatStringToString" />
</pass-through-router>
</outbound>
</service>
ChitChatUMO服務組件又配置了兩個轉換器:NameStringToChatString、ChatStringToString。ChitChatter組件類的輸入參數為 ChatString 類型,所以NameStringToChatString轉換器將消息格式從NameString轉為 ChatString、然后再調用 ChitChatter組件(流程:GreeterUMO -> vm://chitchatter -> NameStringToChatString -> ChitChatter -> ChatStringToString -> System.out)
注意Java bean是不含有任何路由邏輯的, Mule配置文件將它們組織到一起,任何已有的pojo、web services都可以照此辦理并在它們之間傳輸消息。
二、Stock Quote (演示了如何調用ASPX web service、使用XSLT轉換、反序列化StockQuote Java bean以及使用REST和SOAP調用服務。例子需要訪問互聯網上的公共.NET服務、主要是咱也不知道人家都有哪些股票代碼有數據。源碼就不看了)
1、示例翻譯:通過System.in接收股票代碼、調用StockQuote服務、通過XSLT轉換器將返回結果轉換格式、通過XmlToObject轉換器再將結果轉換為StockQuote類型、隨后將股票報價打印到System.out
(例子用到了類似spring的屬性占位符特性來從配置文件取得一些信息、配置多個轉換器并“串聯”起來、其中還用到xslt轉換器)
<service name="HTTPPostSample">
<inbound>
<vm:inbound-endpoint path="stockquote"
responseTransformer-refs="ToString XmlDecoder Xslt XmlToObject"/>
</inbound>
<http:rest-service-component
serviceUrl="http://www.webservicex.net/stockquote.asmx/GetQuote"
httpMethod="POST">
<http:payloadParameterName value="symbol"/>
</http:rest-service-component>
</service>
</model>
配置當中還用到所謂的REST service component , 它使用了REST服務包裝器代理了一個REST服務、這樣使得該service服務看上去似乎是本地的component組件一般(和CXF的web服務包裝器差不多),REST服務包裝器有一些配置屬性:serviceUrl就是 訪問REST服務的url、payloadParameterName是傳參名 ,本例中只有一個參數"symbol"——股票代碼、httpMethod是方法名 ——GET或POST。
我隨便傳了個代碼過去返回了無數據的xml:
<StockQuotes><Stock><Symbol>002339</Symbol><Last>0.00</Last><Date>N/A</Date><Time>N/A</Time><Change>N/A</Change><Open>N/A</Open><High>N/A</High><Low>N/A</Low><Volume>N/A</Volume><MktCap>N/A</MktCap><PreviousClose>N/A</PreviousClose><PercentageChange>N/A</PercentageChange><AnnRange>N/A - N/A</AnnRange><Earns>N/A</Earns><P-E>N/A</P-E><Name>002339</Name></Stock></StockQuotes>
</string>
Web Service版和REST版原理類似,只是服務配置是不同的。Web Service版顯式配置了outbound pass-through路由,它將輸入從一個endpoint直接傳輸到outbound Axis endpoint,不作任何改變或處理。另外outbound endpoint向Stock Quote service股票報價服務請求時是帶參數的。
<service name="serviceProxy">
<inbound>
<vm:inbound-endpoint path="stockquote"
responseTransformer-refs="ToString XmlDecoder Xslt XmlToObject"/>
</inbound>
<outbound>
<pass-through-router>
<axis:outbound-endpoint address="http://www.webservicex.net/stockquote.asmx?method=GetQuote"
responseTransformer-refs="XmlDecoder Xslt XmlToObject"
soapAction="[methodNamespace][method]">
<axis:soap-method method="qname{GetQuote:http://www.webserviceX.NET/}">
<axis:soap-parameter parameter="symbol" type="string" mode="IN"/>
<axis:soap-parameter parameter="GetQuoteResult" type="string" mode="OUT"/>
</axis:soap-method>
</axis:outbound-endpoint>
</pass-through-router>
</outbound>
</service>
</model>
三、Error Handler (演示了如何使用Spring beans作為service component以及向多個出站endpoint發布消息,使用了文件監控inbound+郵件outbound)
示例包含兩個services: ExceptionManager 異常管理器 和 BusinessErrorManager業務錯誤管理器。
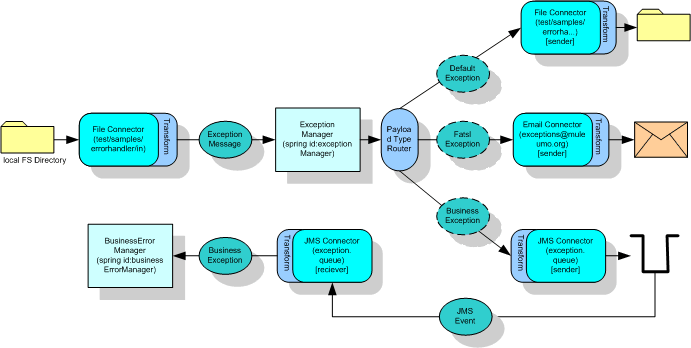
BusinessErrorManager是個簡單的service,它通過JMS接收業務異常消息并將消息記錄到控制臺,以此模仿真實的異常處理應用。
ExceptionManager接收異常消息并根據異常消息的類型進行某些處理動作。例如如果收到致命異常則會向系統管理員發送郵件;收到標準系統異常則寫入本地文件log,例子演示的不是異常處理、演示的是:
- 所有的service components都是以spring bean的形式在一個mule配置文件當中配置的。
- error manager擁有多個outbound endpoints出站端點,例子演示了消息如何發布到不同端點。
- 消息是Java對象形式,并且需要在XML形式之間互相轉換。例子演示了鏈接多個轉換器。
<spring:bean id="errorManager" class="org.mule.example.errorhandler.ErrorManager">
<spring:property name="handlers">
<spring:list>
<spring:ref local="fatalHandler"/>
<spring:ref local="defaultHandler"/>
<spring:ref local="businessHandler"/>
</spring:list>
</spring:property>
</spring:bean>
<model name="errorhandler-test">
<service name="Error Manager">
<inbound>
<inbound-endpoint address="file://./test-data/in"
transformer-refs="XMLToExceptionBean ExceptionBeanToErrorMessage">
<file:filename-wildcard-filter pattern="*.xml"/>
</inbound-endpoint>
</inbound>
<pooled-component>
<prototype-object class="org.mule.example.errorhandler.ErrorManager">
<properties>
<spring:entry key="handlers">
<spring:list>
<spring:ref local="fatalHandler"/>
<spring:ref local="defaultHandler"/>
<spring:ref local="businessHandler"/>
</spring:list>
</spring:entry>
</properties>
</prototype-object>
</pooled-component>
<outbound>
<filtering-router>
<file:outbound-endpoint path="test-data/exceptions"
outputPattern="Exception-[UUID].xml"
transformer-refs="ErrorMessageToExceptionBean ExceptionBeanToXML"/>
<!-- Check ErrorMessage.getThrowable() exception type -->
<expression-filter evaluator="groovy" expression="payload.throwable instanceof org.mule.api.DefaultMuleException"/>
</filtering-router>
<filtering-router>
<smtp:outbound-endpoint user="${smtp.username}" password="${smtp.password}"
host="${smtp.host}" port="${smtp.port}"
to="${email.toAddress}" from="${email.fromAddress}"
subject="${email.subject}"
transformer-refs="ErrorMessageToExceptionBean ExceptionBeanToXML StringToEmailMessage"/>
<!-- Check ErrorMessage.getThrowable() exception type -->
<expression-filter evaluator="groovy" expression="payload.throwable instanceof org.mule.api.lifecycle.FatalException"/>
</filtering-router>
<filtering-router>
<outbound-endpoint address="jms://exception.queue"
transformer-refs="ErrorMessageToExceptionBean ExceptionBeanToXML ObjectToJMSMessage"/>
<!-- Check ErrorMessage.getThrowable() exception type -->
<expression-filter evaluator="groovy" expression="payload.throwable instanceof org.mule.example.errorhandler.exceptions.BusinessException"/>
</filtering-router>
<custom-catch-all-strategy class="org.mule.routing.LoggingCatchAllStrategy"/>
</outbound>
</service>
四、Loan Broker (基于Enterprise Integration Patterns book 一 EIP書中的例子 ,mule不鳥JBI和SCA,唯遵SEDA和EIP,有個性)
Loan Broker貸款中介(也叫loan agent service)是mule的主要演示例子,顧名思義,就是客戶向銀行申請貸款的故事。先看一下背景知識:
以往的貸款請求流程如下圖
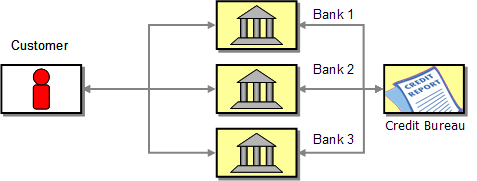
1) 客戶customer 向不同的銀行bank 發起請求搜尋最優利率。
2) 每家銀行都要向客戶詢問社保號碼ss、貸款數量以及期限。
3) 每家銀行都要對該客戶做信用背景調查:通常是咨詢征信所credit bureau (通過征信中介credit agency ),最后銀行才能根據這些信息發放貸款。
4) 客戶接收到所有銀行的反饋以后,從中選擇一家最好的,比如說利率最低
加貸款中介以后,這個處理流程可以更加自動化、允許客戶在線獲取更多銀行的實時反饋,耗時要比一家一家詢問少得多:
1) 接收到客戶請求以后,loan broker貸款中介從征信所獲取該客戶的信用信息。
2) 替該客戶向貸方服務lender service 列出的所有銀行發出貸款請求(例子中這個服務啥也沒做只是個意思)
3) 將反饋的貸款額度信息打包發送回用戶供選擇(例子中就是選擇返回利率最低的那家銀行)
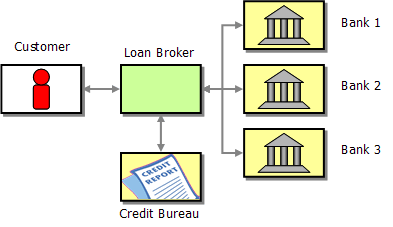
1、貸款中介服務http/rest(接收客戶的http貸款請求,包含社保號、貸款額、期限并負責相應放貸信息)。
2、征信所服務EJB(由貸款中介公司管理的EJB外部服務,做信用檢查的,暴露一個名為creditAgency的EJB的getCreaditProfile方法)
3、征信所網關(例子中的網關做的事情都是:在JMS消息總線和 外部應用或服務/征信所服務應用 之間整理請求)
4、貸方服務VM(根據客戶的資信評分等信息選擇請貸的銀行,本地pojo組件,決定請求哪幾家銀行)
5、貸方網關(在消息總線到貸方服務應用之間整理請求)
6、銀行網關(向多家銀行分發貸款請求)
7、還有幾家銀行bank(soap協議的消息服務、為了簡化、所有銀行暴露同樣的ws接口。當然你也可以配置不同接口的多家銀行)。
例子涉及異步的請求/響應處理模型;對JMS、http/rest、vm、soap、EJB各種協議的調用;把bank暴露為ws。總線中的消息用LoanQuoteRequest 代表,本例中這是個javaBean格式,但是實際中往往是個xml格式(用了ESB,我發現對消息這個東東來說格式是五花八門的:javabean pojo、xml、http參數、stdio、soap甚至json...)
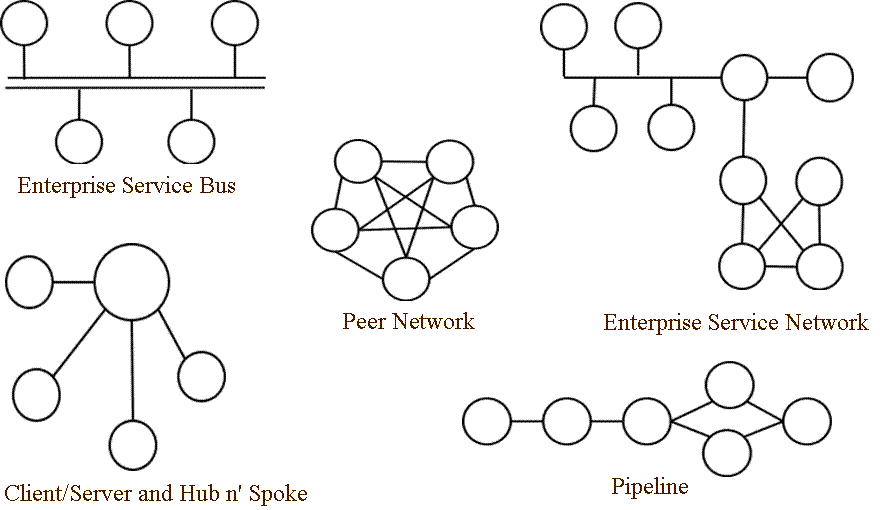
loan broker的示例包含ESB和ESN兩種布局的版本,含義參見Mule Topologies的5種拓撲布局:
ESB、ESN企業服務網、對等網(這不又成了點對點了么,不推薦)、C/S以hub為中心的輻射方式(可能性能有問題,不推薦)、管道方式(服務編排?)
1、示例翻譯:
Loan Broker ESB基于當前的Loan Broker示例 但是實現了一個完整的ESB架構,該例子演示了如何使用HTTP/REST、 Web Services、EJB、JMS,他是根據典型ESB實現來配置的。
Loan Broker ESB使用了JMS消息總線以提供在不同組件和應用間的公共消息通道:
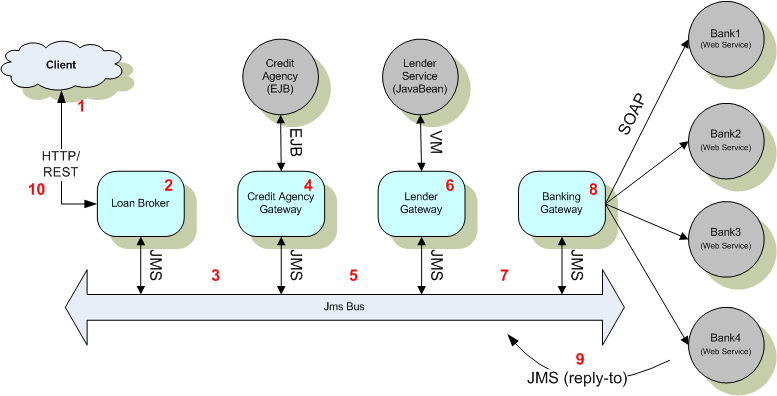
組件:
1、Loan Broker Service貸款中介服務 :接收貸款請求(信息包括SS社保號碼、貸款額度、期限)并負責收集放貸反饋向客戶反饋。
2、Credit Agency Service征信所服務 :外部服務提供者、它對客戶的授信進行檢驗以確保合理的放貸額度。
3、Credit Agency Gateway征信所網關 :在消息總線和征信所應用之間整理請求。
4、Lender Service貸方服務 :基于客戶的資信評分,放貸額度和期限,由貸方服務選擇請求貸款的銀行。
5、Lender Gateway貸方網關 :從消息總線到貸方應用之間整理請求。
6、Banking Gateway銀行網關 :基于貸方列表、向一家或多家銀行分發貸款請求。
總體流程:
- 客戶應用向LoanBroker 貸款中介服務 發出 CustomerQuoteRequest消息 。
- LoanBroker 貸款中介服務 創建一個 LoanQuoteRequest 消息,這是總線通用消息格式。
- Mule通過JMS向Credit Agency Gateway 征信所網關 發送該消息。
- 網關整理請求、調用CreditAgency EJB組件,RelectionMessageBuilder自動將CreditProfile附加到LoanQuoteRequest 消息上 。
- Mule通過JMS向Lender Gateway貸方網關 發送該消息.
- 貸方網關 使用VM傳輸調用貸方服務 .
- Mule通過JMS向Banking Gateway銀行網關 發送該消息.
- Banking Gateway銀行網關 通過Axis實現的SOAP調用銀行服務.
- 每家銀行都把自己的貸款報價附加到請求中并通過應答地址ReplyTo 發回LoanBroker 貸款中介服務 。應答地址是由Banking Gateway銀行網關 提供的.
-
LoanBroker 貸款中介服務 的ResponseRouter響應路由接收對應答地址 的響應,它選擇最低利率并返回客戶。
本例中,消息總線上的通用消息格式是java bean格式。一般情況下如JMS規范要求總線內的通用消息是xml格式,但是mule允許你使用任何數據格式,兩種格式各有優缺,xml的文本消息允許你方便的直接實施xslt轉換器之類,bean方式在component中更便于編碼處理,兩種方式也都方便用路由器去根據消息內容做路由判斷。我們先來定義這個消息bean:LoanQuoteRequest(org.mule.example.loanbroker.messages.LoanBrokerQuoteRequest):
{
/**
* Serial version
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 46866005259682607L;
/** The customer request
* The request contains Customer info and loan amount and duration */
private CustomerQuoteRequest customerRequest;
/** credit profile for the customer */
private CreditProfile creditProfile;
/** A list of lenders for this request */
private Bank[] lenders;
/** A loan quote from a bank */
private LoanQuote loanQuote;
//get/set方法


}
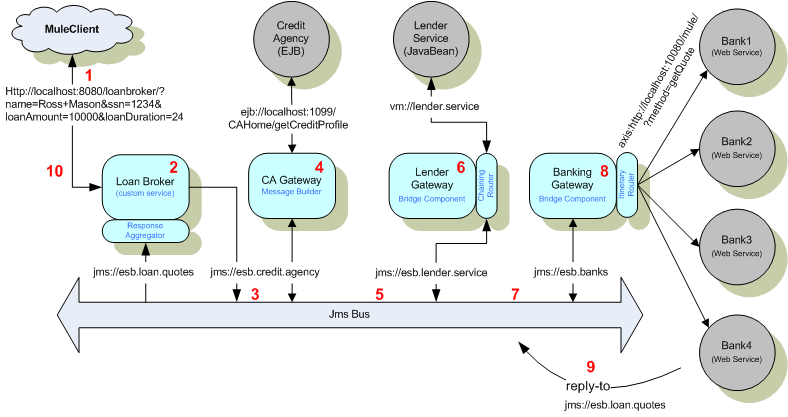
客戶的初始請求觸發整個事件處理流,客戶使用瀏覽器以htt協議請求mule rest服務,這個服務當然得向外暴露,暴露的方式就是配置貸款中介端點 (CustomerRequestsREST)
這句話的配置含義:
1、內嵌Jetty servlet引擎
2、mule啟動jetty在8888端口上監聽rest請求
3、把rest servlet綁定到/loanbroker上下文
來自客戶的初始rest請求格式為:
貸款中介端點 以http參數形式接收下來,需要轉換為CustomerQuoteRequest對象,所以增加了一個自定義轉換器:
這個轉換器要用在貸款中介端點 上,在貸款中介服務的入站inbound配置上、入站端點endpoint引用了貸款中介端點(CustomerRequestsREST)、同時也引用了這個轉換器。也就是說從貸款中介端點 上接收的rest請求都直接用這個轉換器予以轉換:
<description>
The LoanBroker service is our 'entry' service that accepts requests from the outside world
</description>
<inbound>
<inbound-endpoint ref="CustomerRequestsREST" transformer-refs="RestRequestToCustomerRequest" />


@import url(http://www.aygfsteel.com/CuteSoft_Client/CuteEditor/Load.ashx?type=style&file=SyntaxHighlighter.css);@import url(/css/cuteeditor.css);


