1. SIPp概述
1.1 介紹
SIPp是一個(gè)測(cè)試SIP協(xié)議性能的工具軟件。這是一個(gè)GPL的開(kāi)放源碼軟件。
它包含了一些基本的SipStone用戶代理工作流程(UAC和UAS),并可使用INVITE和B YE建立和釋放多個(gè)呼叫。它也可以讀XML的場(chǎng)景文件,即描述任何性能測(cè)試的配置文件。它能動(dòng)態(tài)顯示測(cè)試運(yùn)行的統(tǒng)計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)(呼叫速率、信號(hào)來(lái)回的延遲,以及 消息統(tǒng)計(jì))。周期性地把CSV統(tǒng)計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)儲(chǔ),在多個(gè)套接字上的TCP和UDP,利用重新傳輸管理的多路復(fù)用。在場(chǎng)景定義文件中可以使用正規(guī)表達(dá)式,動(dòng)態(tài)調(diào) 整呼叫速率。
SIPp可以用來(lái)測(cè)試許多真實(shí)的SIP設(shè)備,如SIP代理,B2BUAs,SIP媒體服務(wù)器,SIP/x網(wǎng)關(guān),SIP PBX,等等,它也可以模仿上千個(gè)SIP代理呼叫你的SIP系統(tǒng)。
關(guān)于SIPp從google上搜索到很多,可是關(guān)于SIPp的中文說(shuō)明資料較少,或者很多都是不齊全的安裝使用說(shuō)明。
SIPp的網(wǎng)址:http://sipp.sourceforge.net/
1.2 用途
SIPp一般來(lái)進(jìn)行AS的壓力測(cè)試,圖示如下:
UAC(發(fā)起端,主叫)--------------------AS---------------------UAS(接收端,被叫)
其中UAC和UAS都有SIPp來(lái)?yè)?dān)任。因此可以由它來(lái)控制每秒有多少個(gè)caps,也可由它來(lái)控制一個(gè)呼叫持續(xù)多長(zhǎng)時(shí)間等。
2. 安裝
2.1 Windows版安裝
很簡(jiǎn)單,省略。
3. SIPp的使用
3.1 運(yùn)行SIPp
選擇“程序”->”Sipp_3.1”->“Start sipp”,運(yùn)行界面如下所示:
在命令行運(yùn)行:sipp,出現(xiàn)幫助信息,如下所示:
 the scenarios.
the scenarios.

 First line of this file say whether the data is to be
First line of this file say whether the data is to be

 read in sequence (SEQUENTIAL), random (RANDOM), or user
read in sequence (SEQUENTIAL), random (RANDOM), or user

 (USER) order.
(USER) order.

 Each line corresponds to one call and has one or more
Each line corresponds to one call and has one or more

 ';' delimited data fields. Those fields can be referred
';' delimited data fields. Those fields can be referred

 as [field0], [field1],
as [field0], [field1],  in the xml scenario file.
in the xml scenario file.

 Several CSV files can be used simultaneously (syntax:
Several CSV files can be used simultaneously (syntax:

 -inf f1.csv -inf f2.csv
-inf f1.csv -inf f2.csv  )
)

 -infindex : file field
-infindex : file field

 Create an index of file using field. For example -inf
Create an index of file using field. For example -inf

 users.csv -infindex users.csv 0 creates an index on the
users.csv -infindex users.csv 0 creates an index on the

 first key.
first key.

 -ip_field : Set which field from the injection file contains the IP
-ip_field : Set which field from the injection file contains the IP

 address from which the client will send its messages.
address from which the client will send its messages.

 If this option is omitted and the '-t ui' option is
If this option is omitted and the '-t ui' option is

 present, then field 0 is assumed.
present, then field 0 is assumed.

 Use this option together with '-t ui'
Use this option together with '-t ui'

 -l : Set the maximum number of simultaneous calls. Once this
-l : Set the maximum number of simultaneous calls. Once this

 limit is reached, traffic is decreased until the number
limit is reached, traffic is decreased until the number

 of open calls goes down. Default:
of open calls goes down. Default:

 (3 * call_duration (s) * rate).
(3 * call_duration (s) * rate).

 -lost : Set the number of packets to lose by default (scenario
-lost : Set the number of packets to lose by default (scenario

 specifications override this value).
specifications override this value).

 -m : Stop the test and exit when 'calls' calls are processed
-m : Stop the test and exit when 'calls' calls are processed

 -mi : Set the local media IP address (default: local primary
-mi : Set the local media IP address (default: local primary

 host IP address)
host IP address)

 -master : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the master number
-master : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the master number

 -max_recv_loops : Set the maximum number of messages received read per
-max_recv_loops : Set the maximum number of messages received read per

 cycle. Increase this value for high traffic level. The
cycle. Increase this value for high traffic level. The

 default value is 1000.
default value is 1000.

 -max_sched_loops : Set the maximum number of calsl run per event loop.
-max_sched_loops : Set the maximum number of calsl run per event loop.

 Increase this value for high traffic level. The default
Increase this value for high traffic level. The default

 value is 1000.
value is 1000.

 -max_reconnect : Set the the maximum number of reconnection.
-max_reconnect : Set the the maximum number of reconnection.



 -max_retrans : Maximum number of UDP retransmissions before call ends on
-max_retrans : Maximum number of UDP retransmissions before call ends on

 timeout. Default is 5 for INVITE transactions and 7 for
timeout. Default is 5 for INVITE transactions and 7 for

 others.
others.

 -max_invite_retrans: Maximum number of UDP retransmissions for invite
-max_invite_retrans: Maximum number of UDP retransmissions for invite

 transactions before call ends on timeout.
transactions before call ends on timeout.

 -max_non_invite_retrans: Maximum number of UDP retransmissions for non-invite
-max_non_invite_retrans: Maximum number of UDP retransmissions for non-invite

 transactions before call ends on timeout.
transactions before call ends on timeout.

 -max_log_size : What is the limit for error and message log file sizes.
-max_log_size : What is the limit for error and message log file sizes.



 -max_socket : Set the max number of sockets to open simultaneously.
-max_socket : Set the max number of sockets to open simultaneously.

 This option is significant if you use one socket per
This option is significant if you use one socket per

 call. Once this limit is reached, traffic is distributed
call. Once this limit is reached, traffic is distributed

 over the sockets already opened. Default value is 50000
over the sockets already opened. Default value is 50000

 -mb : Set the RTP echo buffer size (default: 2048).
-mb : Set the RTP echo buffer size (default: 2048).

 -mp : Set the local RTP echo port number. Default is 6000.
-mp : Set the local RTP echo port number. Default is 6000.

 -nd : No Default. Disable all default behavior of SIPp which
-nd : No Default. Disable all default behavior of SIPp which

 are the following:
are the following:

 - On UDP retransmission timeout, abort the call by
- On UDP retransmission timeout, abort the call by

 sending a BYE or a CANCEL
sending a BYE or a CANCEL

 - On receive timeout with no ontimeout attribute, abort
- On receive timeout with no ontimeout attribute, abort

 the call by sending a BYE or a CANCEL
the call by sending a BYE or a CANCEL

 - On unexpected BYE send a 200 OK and close the call
- On unexpected BYE send a 200 OK and close the call

 - On unexpected CANCEL send a 200 OK and close the call
- On unexpected CANCEL send a 200 OK and close the call

 - On unexpected PING send a 200 OK and continue the call
- On unexpected PING send a 200 OK and continue the call

 - On any other unexpected message, abort the call by
- On any other unexpected message, abort the call by

 sending a BYE or a CANCEL
sending a BYE or a CANCEL

 -nr : Disable retransmission in UDP mode.
-nr : Disable retransmission in UDP mode.

 -nostdin : Disable stdin.
-nostdin : Disable stdin.

 -p : Set the local port number. Default is a random free port
-p : Set the local port number. Default is a random free port

 chosen by the system.
chosen by the system.

 -pause_msg_ign : Ignore the messages received during a pause defined in
-pause_msg_ign : Ignore the messages received during a pause defined in

 the scenario
the scenario

 -periodic_rtd : Reset response time partition counters each logging
-periodic_rtd : Reset response time partition counters each logging

 interval.
interval.

 -r : Set the call rate (in calls per seconds). This value can
-r : Set the call rate (in calls per seconds). This value can

 bechanged during test by pressing '+','_','*' or '/'.
bechanged during test by pressing '+','_','*' or '/'.

 Default is 10.
Default is 10.

 pressing '+' key to increase call rate by 1 *
pressing '+' key to increase call rate by 1 *

 rate_scale,
rate_scale,

 pressing '-' key to decrease call rate by 1 *
pressing '-' key to decrease call rate by 1 *

 rate_scale,
rate_scale,

 pressing '*' key to increase call rate by 10 *
pressing '*' key to increase call rate by 10 *

 rate_scale,
rate_scale,

 pressing '/' key to decrease call rate by 10 *
pressing '/' key to decrease call rate by 10 *

 rate_scale.
rate_scale.

 If the -rp option is used, the call rate is calculated
If the -rp option is used, the call rate is calculated

 with the period in ms given by the user.
with the period in ms given by the user.

 -rp : Specify the rate period for the call rate. Default is 1
-rp : Specify the rate period for the call rate. Default is 1

 second and default unit is milliseconds. This allows
second and default unit is milliseconds. This allows

 you to have n calls every m milliseconds (by using -r n
you to have n calls every m milliseconds (by using -r n

 -rp m).
-rp m).

 Example: -r 7 -rp 2000 ==> 7 calls every 2 seconds.
Example: -r 7 -rp 2000 ==> 7 calls every 2 seconds.

 -r 10 -rp 5s => 10 calls every 5 seconds.
-r 10 -rp 5s => 10 calls every 5 seconds.



 -rate_scale : Control the units for the '+', '-', '*', and '/' keys.
-rate_scale : Control the units for the '+', '-', '*', and '/' keys.



 -rate_increase : Specify the rate increase every -fd units (default is
-rate_increase : Specify the rate increase every -fd units (default is

 seconds). This allows you to increase the load for each
seconds). This allows you to increase the load for each

 independent logging period.
independent logging period.

 Example: -rate_increase 10 -fd 10s
Example: -rate_increase 10 -fd 10s

 ==> increase calls by 10 every 10 seconds.
==> increase calls by 10 every 10 seconds.

 -rate_max : If -rate_increase is set, then quit after the rate
-rate_max : If -rate_increase is set, then quit after the rate

 reaches this value.
reaches this value.

 Example: -rate_increase 10 -rate_max 100
Example: -rate_increase 10 -rate_max 100

 ==> increase calls by 10 until 100 cps is hit.
==> increase calls by 10 until 100 cps is hit.

 -no_rate_quit : If -rate_increase is set, do not quit after the rate
-no_rate_quit : If -rate_increase is set, do not quit after the rate

 reaches -rate_max.
reaches -rate_max.

 -recv_timeout : Global receive timeout. Default unit is milliseconds. If
-recv_timeout : Global receive timeout. Default unit is milliseconds. If

 the expected message is not received, the call times out
the expected message is not received, the call times out

 and is aborted.
and is aborted.

 -send_timeout : Global send timeout. Default unit is milliseconds. If a
-send_timeout : Global send timeout. Default unit is milliseconds. If a

 message is not sent (due to congestion), the call times
message is not sent (due to congestion), the call times

 out and is aborted.
out and is aborted.

 -reconnect_close : Should calls be closed on reconnect?
-reconnect_close : Should calls be closed on reconnect?

 -reconnect_sleep : How long (in milliseconds) to sleep between the close and
-reconnect_sleep : How long (in milliseconds) to sleep between the close and

 reconnect?
reconnect?

 -ringbuffer_files: How many error/message files should be kept after
-ringbuffer_files: How many error/message files should be kept after

 rotation?
rotation?

 -ringbuffer_size : How large should error/message files be before they get
-ringbuffer_size : How large should error/message files be before they get

 rotated?
rotated?

 -rsa : Set the remote sending address to host:port for sending
-rsa : Set the remote sending address to host:port for sending

 the messages.
the messages.

 -rtp_echo : Enable RTP echo. RTP/UDP packets received on port defined
-rtp_echo : Enable RTP echo. RTP/UDP packets received on port defined

 by -mp are echoed to their sender.
by -mp are echoed to their sender.

 RTP/UDP packets coming on this port + 2 are also echoed
RTP/UDP packets coming on this port + 2 are also echoed

 to their sender (used for sound and video echo).
to their sender (used for sound and video echo).

 -rtt_freq : freq is mandatory. Dump response times every freq calls
-rtt_freq : freq is mandatory. Dump response times every freq calls

 in the log file defined by -trace_rtt. Default value is
in the log file defined by -trace_rtt. Default value is

 200.
200.

 -s : Set the username part of the resquest URI. Default is
-s : Set the username part of the resquest URI. Default is

 'service'.
'service'.

 -sd : Dumps a default scenario (embeded in the sipp executable)
-sd : Dumps a default scenario (embeded in the sipp executable)

 -sf : Loads an alternate xml scenario file. To learn more
-sf : Loads an alternate xml scenario file. To learn more

 about XML scenario syntax, use the -sd option to dump
about XML scenario syntax, use the -sd option to dump

 embedded scenarios. They contain all the necessary help.
embedded scenarios. They contain all the necessary help.

 -oocsf : Load out-of-call scenario.
-oocsf : Load out-of-call scenario.



 -oocsn : Load out-of-call scenario.
-oocsn : Load out-of-call scenario.

 -skip_rlimit : Do not perform rlimit tuning of file descriptor limits.
-skip_rlimit : Do not perform rlimit tuning of file descriptor limits.

 Default: false.
Default: false.

 -slave : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the slave number
-slave : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the slave number

 -slave_cfg : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the file where the master
-slave_cfg : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the file where the master

 and slave addresses are stored
and slave addresses are stored

 -sn : Use a default scenario (embedded in the sipp executable).
-sn : Use a default scenario (embedded in the sipp executable).

 If this option is omitted, the Standard SipStone UAC
If this option is omitted, the Standard SipStone UAC

 scenario is loaded.
scenario is loaded.

 Available values in this version:
Available values in this version:

 - 'uac' : Standard SipStone UAC (default).
- 'uac' : Standard SipStone UAC (default).

 - 'uas' : Simple UAS responder.
- 'uas' : Simple UAS responder.

 - 'regexp' : Standard SipStone UAC - with regexp and
- 'regexp' : Standard SipStone UAC - with regexp and

 variables.
variables.

 - 'branchc' : Branching and conditional branching in
- 'branchc' : Branching and conditional branching in

 scenarios - client.
scenarios - client.

 - 'branchs' : Branching and conditional branching in
- 'branchs' : Branching and conditional branching in

 scenarios - server.
scenarios - server.

 Default 3pcc scenarios (see -3pcc option):
Default 3pcc scenarios (see -3pcc option):



 - '3pcc-C-A' : Controller A side (must be started after
- '3pcc-C-A' : Controller A side (must be started after

 all other 3pcc scenarios)
all other 3pcc scenarios)

 - '3pcc-C-B' : Controller B side.
- '3pcc-C-B' : Controller B side.

 - '3pcc-A' : A side.
- '3pcc-A' : A side.

 - '3pcc-B' : B side.
- '3pcc-B' : B side.

 -stat_delimiter : Set the delimiter for the statistics file
-stat_delimiter : Set the delimiter for the statistics file

 -stf : Set the file name to use to dump statistics
-stf : Set the file name to use to dump statistics

 -t : Set the transport mode:
-t : Set the transport mode:

 - u1: UDP with one socket (default),
- u1: UDP with one socket (default),

 - un: UDP with one socket per call,
- un: UDP with one socket per call,

 - ui: UDP with one socket per IP address The IP
- ui: UDP with one socket per IP address The IP

 addresses must be defined in the injection file.
addresses must be defined in the injection file.

 - t1: TCP with one socket,
- t1: TCP with one socket,

 - tn: TCP with one socket per call,
- tn: TCP with one socket per call,

 - l1: TLS with one socket,
- l1: TLS with one socket,

 - ln: TLS with one socket per call,
- ln: TLS with one socket per call,

 - c1: u1 + compression (only if compression plugin
- c1: u1 + compression (only if compression plugin

 loaded),
loaded),

 - cn: un + compression (only if compression plugin
- cn: un + compression (only if compression plugin

 loaded). This plugin is not provided with sipp.
loaded). This plugin is not provided with sipp.

3.2 使用SIPp進(jìn)行壓力測(cè)試
3.2.1啟動(dòng)服務(wù)端
首先查知本機(jī)的IP,例如筆者本機(jī)的IP為192.168.2.45。在SIPp的運(yùn)行窗口運(yùn)行:
 sipp -sn uas -i 192.168.2.45 -p 5060
sipp -sn uas -i 192.168.2.45 -p 5060 出現(xiàn)的命令窗口的內(nèi)容類似如下:

3.2.2啟動(dòng)和運(yùn)行客戶端
再開(kāi)啟一個(gè)SIPp界面。
啟動(dòng)客戶端使用:sipp -sn uac….,使用如下:
 sipp -sn uac -m 1 -i 192.168.2.45 -p 6060 -s 01012345678 192.168.2.154
sipp -sn uac -m 1 -i 192.168.2.45 -p 6060 -s 01012345678 192.168.2.154 啟動(dòng)后命令窗口如下所示:
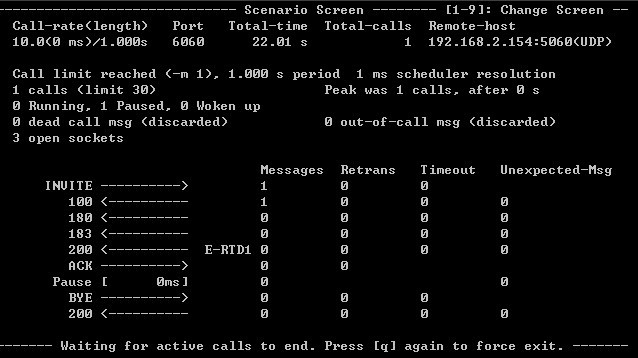
其中:
-m:該參數(shù)表示每秒的caps數(shù),若沒(méi)寫該參數(shù),默認(rèn)為每秒10個(gè)caps;
-i:這個(gè)用于指定本機(jī)的ip,若本機(jī)只有一個(gè)ip,可以不指定,若有多個(gè)IP,需要指定該參數(shù);
-p:指定本機(jī)的端口,可以不指定;
-s:該參數(shù)用于指定要呼叫的電話號(hào)碼;
192.168.1.154為AS的IP地址,沒(méi)有指定端口時(shí),默認(rèn)指向的端口為5060。
注意:因?yàn)?/span>UAC和UAS都在筆者機(jī)器,IP為:192.168.2.45,因此AS端還需要對(duì)應(yīng)配置,將落地等的IP地址等都指向該IP。對(duì)于我們的環(huán)境來(lái)說(shuō),需要配置SCF的config.as.ACD文件,修改成:
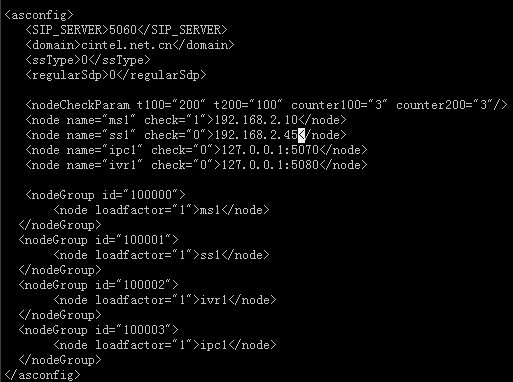
筆者修改了ss1的IP為:192.168.2.45.
在使用uac前,可使用SIP軟終端來(lái)測(cè)試下是不是呼叫后落地是不是落在本機(jī)。
3.2.3查看運(yùn)行結(jié)果
在運(yùn)行:
 sipp -sn uac -i 192.168.2.45 -p 6060 -s 01012345678 192.168.2.154
sipp -sn uac -i 192.168.2.45 -p 6060 -s 01012345678 192.168.2.154 后(該句為10caps),可查看UAS和UAC的界面,服務(wù)端的界面類似如下所示:
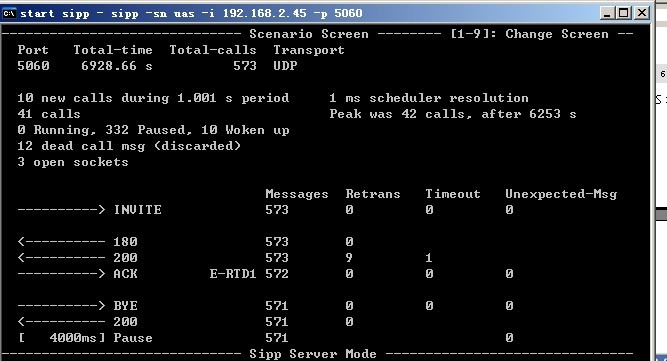
UAC端的界面類似如下所示:

因?yàn)楣P者的AS沒(méi)有發(fā)183的流程,所以它的次數(shù)是為0的,后續(xù)章節(jié)還會(huì)說(shuō)到如果不是SIPp的參考流程時(shí)該怎么做。
3.2.4查看AS所在的Linux機(jī)器的性能情況
1)inmon
公司的SCF提供inmon來(lái)查看自動(dòng)機(jī)掛接等的情況,如下所示:
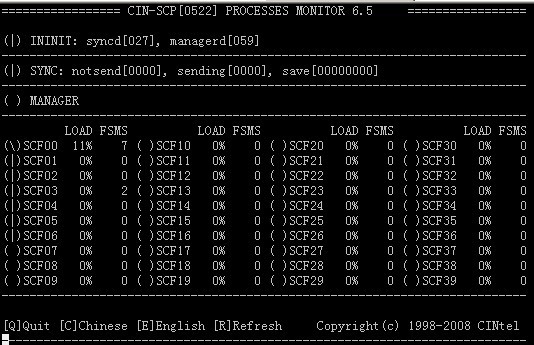
其中FSMS表示當(dāng)前掛著的自動(dòng)機(jī)數(shù),是需要關(guān)注的項(xiàng)。
2)vmstat
vmstat 命令報(bào)告關(guān)于內(nèi)核線程、虛擬內(nèi)存、磁盤、陷阱和 CPU 活動(dòng)的統(tǒng)計(jì)信息。由 vmstat 命令生成的報(bào)告可以用于平衡系統(tǒng)負(fù)載活動(dòng)。系統(tǒng)范圍內(nèi)的這些統(tǒng)計(jì)信息(所有的處理器中)都計(jì)算出以百分比表示的平均值,或者計(jì)算其總和。
例如筆者使用:
vmstat 3
表示每隔3s顯示內(nèi)核線程、虛擬內(nèi)存、磁盤、陷阱和 CPU 活動(dòng)的統(tǒng)計(jì)信息。界面如下所示:
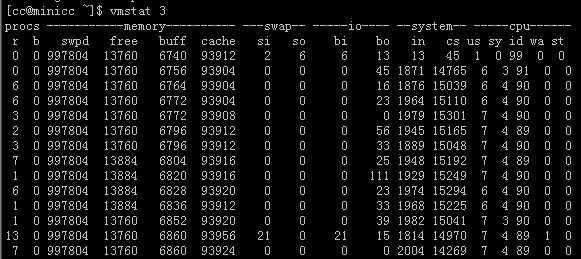
重點(diǎn)要關(guān)注的項(xiàng)是io和cpu等信息。
3)top
top命令提供了實(shí)時(shí)的對(duì)系統(tǒng)處理器的狀態(tài)監(jiān)視。它將顯示系統(tǒng)中CPU最“敏感”的任務(wù)列表。
運(yùn)行top命令后,AS所在Linux機(jī)器的顯示效果如下:
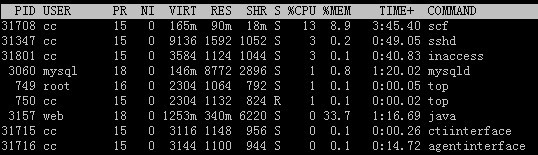
因?yàn)閼?yīng)用主要為cc和mysql,所以要重點(diǎn)關(guān)注這兩者是否穩(wěn)定。
主要關(guān)注的項(xiàng)是VIRT和RES,如果這兩者一直增加,那很可能程序或其它地方存在內(nèi)存泄露。
3.2.5其它
在UAC端運(yùn)行的過(guò)程中:
1) 按“+”鍵表示在當(dāng)前caps的基礎(chǔ)中加1;
2) 按“-”鍵表示在當(dāng)前caps的基礎(chǔ)中減1;
3) 按“*”鍵表示在當(dāng)前caps的基礎(chǔ)中+運(yùn)行起點(diǎn)的caps,例如10caps,按“*”后,變成20,再按“*”變成30.
posted on 2009-09-11 13:45
阿蜜果 閱讀(15279)
評(píng)論(7) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類:
協(xié)議