groovy開發入門
自己軟件開發經驗不是很好,還須向大家學習!希望大家支持下我!有不足之處請大家批評指正。Groovy就是java世界的動態語言
一:快速開始(gettingStart)
安裝JDK環境
Groovy需要JDK1.4以上版本的支持。因此在安裝groovy時首先要安裝JDK。
JDK安裝步驟:
• 下載自己喜歡的JDK版本。(下載網址:http://java.sun.com)
• 下載Groovy:
Groovy的 下載首頁截圖

點擊Download
進入下載頁面
Groovy最新版本:Groovy 1.6-RC-2

我下載的是:Download Windows-Installer: Binary Release 安裝版本
運行安裝者
設置JAVA_HOME 環境變量. 在Windows平臺里,步驟如下:
(1)打開系統"控制面板"
單擊"高級"選項卡
單擊"環境變量" 按鈕
添加一個名稱為"JAVA_HOME" 的新的系統環境變量,并且將你的Java的安裝目錄作為它的值 (例如,我的是C:"Program Files"Java"jdk1.6.0(版本號))
你也可以添加 %JAVA_HOME%"bin到你的系統的PATH變量中
(2)右擊我的電腦屬性

點擊高級選項

點擊環境變量
點擊新建選項:
具體設置

Path:

我用的Jdk版本是Jdk1.6
• 運行安裝文件。(更改安裝路徑到:C:"Program Files"Java"jdk1.6.0(版本號))
• 設置JAVA_HOME環境變量(如我的
• 在系統path中增加:%JAVA_HOME%"bin
注:對于1.1-rc-1以上版本需要JDK1.5版或更高的版本。
點擊自己下載的Groovy windows安裝版本
安裝可以是默認的安裝全點擊下一步(next):
安裝就完成啦
(Note: as an alternative to setting a system environment variable, you can create yourself a '.bat' or '.cmd' file which sets
the variable. You then need to run that batch file in any console window in which you wish to run Java and double clicking on
.bat' or '.cmd' files containing Java invocation instructions won't work. If you are unsure about what this means, follow
the earlier instructions.)
Note: JDK 1.5 is required for version 1.1-rc-1. In earlier versions of JDK (notably 1.4.2) the compiller throws an exception:
*nested exception is org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.InvokerInvocationException: java.lang.NoSuchMethodError:
java.lang.String.replace(Ljava/lang/CharSequence;Ljava/lang/CharSequence;)Ljava/lang/String;
The method "replace" was introduced in JDK 1.5 and is not supportedin earlier versions. This is also a reason why GRails
framework doesn't run on JRE 1.4
(1)如果你是安裝版本Groovy環境變量不需要我們設置,在安裝的時候就自動設置好啦。
(2)如果不是,請自己嘗試Groovy設置如下:
設置你的Groovy環境變量
從下載頁面下載Groovy安裝器或者二進制包,并且跟著介紹進行安裝即可。(當前有一個問題,就是在windows下,你的安裝路徑不能含有空格
,即,要將其缺省的安裝路徑"c:"Program Files"Groovy" 改成象"c:"Groovy"這樣的路徑)
或者這樣
從站點上得到Groovy發行版的copy,并且copy它到你硬盤上的某個地方。
解壓縮這個groovy包到你硬盤的某個空間,如我的在 C:"dev"groovy-1.0-jsr-06
設置GROOVY_HOME環境變量. 在Windows下,作如下步驟:
添中新的系統環境變量GROOVY_HOME 并且將值設為你的groovy安裝的路徑( 我的是 C:"dev"groovy-1.0-jsr-06)
打開命令行窗口,并且鍵入"set" 然后打回車,查看你的環境變量設置是否已經正確。
可選的,你也可以添加 %GROOVY_HOME%"bin 到你的PATH環境變量中
通過雙擊試著運行groovyConsole.bat。如果它不能工作,打開一人命令行窗口,將目錄改變到bin目錄,并且運行它看他返回什么錯誤信息。
二:運行groovy
Groovy安裝:目錄
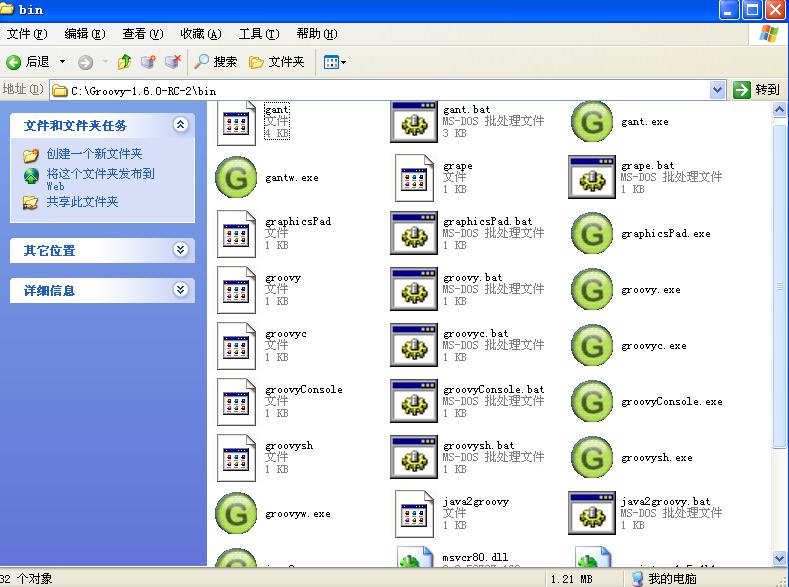
我們需要點擊groovyConsole.bat文件:
文件詳細內容如下:
|
@if "%DEBUG%" == "" @echo off @rem @rem $Revision: 2770 $ $Date: 2005-08-29 12:49:42 +0200 (Mo, 29. Aug 2005) $ @rem @rem Set local scope for the variables with windows NT shell if "%OS%"=="Windows_NT" setlocal :begin @rem Determine what directory it is in. set DIRNAME=%~dp0 if "%DIRNAME%" == "" set DIRNAME=." "%DIRNAME%"startGroovy.bat" "%DIRNAME%" groovy.ui.Console %* @rem End local scope for the variables with windows NT shell if "%OS%"=="Windows_NT" endlocal |
安裝完整無誤的話 運行groovyConsole.bat就會啟動groovyConsole.exe,出來一個編輯框。

上面的是文本輸入框:根據groovy的語法輸入要顯示的內容:
下面的是內容輸出框:顯示上面的內容:
開始運行groovy:


Hello, World
在 groovyConsole運行窗口的頂部,鍵入println "Hello, World!"
并且鍵入 <CTRL-R>.
注意,在控制臺窗口中(即 groovyConsole窗口前面的黑色的那個),文體得到打印并且 groovyConsole的下部顯示 :
groovy> println "Hello, World!"
null
以"groovy>"開頭的行正是控制臺處理的文本. "null" 是表達式的值. 因為表達式沒有任何值可以打印 ,所以groovyConsole打印為"null"
接下來,再試一些實際的值,用下面的字符串來替換控制臺里的文本:
123+45*67
或者你喜歡的任何表達式然后按<CTRL-R> (I'm going to stop telling you to hit <CTRL-R>, I think you get the idea). 現在, groovyConsole下面打印的值有更多的含義.
Variables
You can assign values to variables for later use. Try the following:x = 1
println x
x = new java.util.Date()
println x
x = -3.1499392
println x
x = false
println x
x = "Hi"
println x
Lists and Maps
The Groovy language has built-in support for two important data types, lists and maps (Lists can be operated as arrays in Java language). Lists are used to store ordered collections of data. For example an integer list of your favorite integers might look like this:myList = [1776, -1, 33, 99, 0, 928734928763]
You can access a given item in the list with square bracket notation (indexes start at 0):
println myList[0]
Should result in this output:
1776
You can get the length of the list with the "size" method:
println myList.size()
Should print out:
6
But generally you shouldn't need the length, because unlike Java, the preferred method to loop over all the elements in an list is to use the "each" method, which is described below in the "Code as Data" section.
Another native data structure is called a map. A map is used to store "associative arrays" or "dictionaries". That is unordered collections of heterogeneous, named data. For example, let's say we wanted to store names with IQ scores we might have:
scores = [ "Brett":100, "Pete":"Did not finish", "Andrew":86.87934 ]
Note that each of the values stored in the map is of a different type. Brett's is an integer, Pete's is a string, and Andrew's is a floating point number. We can access the values in a map in two main ways:
println scores["Pete"]
println scores.Pete
Should produce the output:
Did not finish
Did not finish
To add data to a map, the syntax is similar to adding values to an list. For example, if Pete re-took the IQ test and got a 3, we might:
scores["Pete"] = 3
Then later when we get the value back out, it will be 3.
println scores["Pete"]
should print out 3.
Also as an aside, you can create an empty map or an empty list with the following:
emptyMap = [:]
emptyList = []
To make sure the lists are empty, you can run the following lines:
println emptyMap.size()
println emptyList.size()
Should print a size of 0 for the List and the Map.
條件表達式
One of the most important features of any programming language is the ability to execute different code under different conditions. The simplest way to do this is to use the '''if''' construct. For example:amPM = Calendar.getInstance().get(Calendar.AM_PM)
if (amPM == Calendar.AM)
{
println("Good morning")
} else {
println("Good evening")
}
Don't worry too much about the first line, it's just some code to determine whether it is currently before noon or after. The rest of the code executes as follows: first it evaluates the expression in the parentheses, then depending on whether the result is '''true''' or '''false''' it executes the first or the second code block. See the section below on boolean expressions.
Note that the "else" block is not required, but the "then" block is:
amPM = Calendar.getInstance().get(Calendar.AM_PM)
if (amPM == Calendar.AM)
{
println("Have another cup of coffee.")
}
Boolean表達式
There is a special data type in most programming languages that is used to represent truth values, '''true''' and '''false'''. The simplest boolean expression are simply those words. Boolean values can be stored in variables, just like any other data type:myBooleanVariable = true
A more complex boolean expression uses one of the boolean operators:
==
!=
>
>=
<
<=
Most of those are probably pretty intuitive. The equality operator is '''==''' to distinguish from the assignment operator '''='''. The opposite of equality is the '''!=''' operator, that is "not equal"
So some examples:
titanicBoxOffice = 1234600000
titanicDirector = "James Cameron"
trueLiesBoxOffice = 219000000
trueLiesDirector = "James Cameron"
returnOfTheKingBoxOffice = 752200000
returnOfTheKingDirector = "Peter Jackson"
theTwoTowersBoxOffice = 581200000
theTwoTowersDirector = "PeterJackson"
titanicBoxOffice > returnOfTheKingBoxOffice // evaluates to true
titanicBoxOffice >= returnOfTheKingBoxOffice // evaluates to true
titanicBoxOffice >= titanicBoxOffice // evaulates to true
titanicBoxOffice > titanicBoxOffice // evaulates to false
titanicBoxOffice + trueLiesBoxOffice < returnOfTheKingBoxOffice + theTwoTowersBoxOffice // evaluates to false
titanicDirector > returnOfTheKingDirector // evaluates to false, because "J" is before "P"
titanicDirector < returnOfTheKingDirector // evaluates to true
titanicDirector >= "James Cameron" // evaluates to true
titanicDirector == "James Cameron" // evaluates to true
Boolean expressions are especially useful when used in conjunction with the '''if''' construct. For example:
if (titanicBoxOffice + trueLiesBoxOffice > returnOfTheKingBoxOffice + theTwoTowersBoxOffice)
{
println(titanicDirector + " is a better director than " + returnOfTheKingDirector)
}
An especially useful test is to test whether a variable or expression is null (has no value). For example let's say we want to see whether a given key is in a map:
suvMap = ["Acura MDX":""$36,700", "Ford Explorer":""$26,845"]
if (suvMap["Hummer H3"] != null)
{
println("A Hummer H3 will set you back "+suvMap["Hummer H3"]);
}
Generally null is used to indicate the lack of a value in some location.
Debugging and Troubleshooting Tips
Print out the class of a variable that you're interested in with myVar.getClass(). Then look up the documentation for that class.
If you're having trouble with a complex expression, pare it down to a simpler expression and evaluate that. Then build up to your more complex expression.
Try restarting the groovyConsole (this will clear out all the variables so you can start over.
Look for the topic you're interested in in the Groovy User Guide
If you are a Java developer
you might want to check on the Differences from Java
also there afew a few Things to remember
Labels parameters
posted on 2009-02-08 12:20 mike zeseler 閱讀(3017) 評論(5) 編輯 收藏


