近日在CSDN上看到中軟一道面試題,挺有意思的。
題目:一條小溪上7塊石頭,如圖所示:
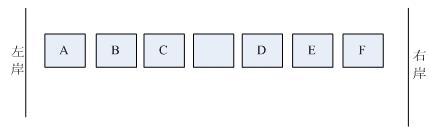
分別有六只青蛙:A,B,C,D,E,F。A,B,C三只蛙想去右岸,它們只會從左向右跳;D,E,F三只蛙想去左岸,它們只會從右向左跳。青蛙每次最多跳到自己前方第2塊石頭上。請問最少要跳幾次所有青蛙上岸。寫出步驟。
這個題是個路徑搜索的問題,在解空間搜索所有的解,并找出最優的解法(即步驟最少的)。
那么怎么算是一個解呢?具體而言就是最后石頭上沒有青蛙了。
我們先給題目建模,7塊石頭,其上可以是沒青蛙,可以有一只往左跳的青蛙,也可以有一只往右跳的青蛙。可以把這7塊石頭看成一個整體,來表示一個狀態。這里我們把這7塊石頭看成一個數組,里面只能有0,1,2三種值,這樣表示,那么初始時為:
1,1,1,0,2,2,2
我們把它再表示成一個數字,來表示狀態值,這個值把這個數組按三進制拼成一個數字,我們用一個輔助函數來做這件事情:
private final int makeS() {
int r=0;
int p=1;
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
{
r+=p*states[i];
p*=3;
}
return r;
}
那么題目現在變成從狀態111022轉換成狀態0000000,所需最少的步驟.
那么狀態是怎樣轉換的呢?
很顯然。,每次青蛙跳都會觸發狀態的轉換,我們在每個狀態時搜索每種可能的轉換,我們記初始狀態為S(S等于三進制111022)記要求解的值為OPT(S),假如可以轉換到t1,t2,...tk.
那么,顯然
OPT(S)=min(1+OPT(t1),1+OPT(t2), .,1+OPT(tk));
.,1+OPT(tk));
另外,由于最終狀態為0,所以OPT(0)=0,就是說已經在最終狀態了,就不需要一步就可以了。
有了上面這個等式,我們可以遞歸求解了,但是如果單純的遞歸,會導致大量的重復計算,所以這里我們用備忘錄的方法,記下已經求解出來的OPT(x),放在一個數組里,由于只有7塊石頭,所以最多我們需要3^7=2187個狀態。我們用一個2187個元素的數組, 其中第i個元素表示OPT(i),初始化每個元素用-1表示還未求解。OPT(0) 可直接初始化為0.
到此我們還有一個問題,怎么能夠在算法結束的時候打印出最優的步驟呢?按照這個步驟,我們可以重建出青蛙是如何在最優的情況下過河的。為此,我們可以再用一個步驟數組,每次在采取最優步驟的時候記錄下來。
整個算法如下:
package test;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
*
* @author Yovn
*
*/
public class FrogJump {
private int steps[];
private int states[];
private static class Step
{
int offset=-1;
int jump;
int jumpTo;
}
private Step jumps[];
private int initS;
public FrogJump()
{
steps=new int[81*27];
states=new int[7];
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)states[i]=1;
for(int i=4;i<7;i++)states[i]=2;
Arrays.fill(steps, -1);
steps[0]=0;
jumps=new Step[81*27];
initS=makeS();
}
public int shortestSteps(int s)
{
if(steps[s]==-1)
{
int minStep=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Step oneStep=new Step();
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
{
if(states[i]==1)
{
if(i>4)
{
states[i]=0;
minStep = recurFind(minStep,oneStep,i,7-i);
states[i]=1;
}
else
{
if(states[i+1]==0)
{
states[i]=0;
states[i+1]=1;
minStep = recurFind(minStep,oneStep,i,1);
states[i]=1;
states[i+1]=0;
}
if(states[i+2]==0)
{
states[i]=0;
states[i+2]=1;
minStep = recurFind(minStep,oneStep,i,2);
states[i]=1;
states[i+2]=0;
}
}
}
else if(states[i]==2)
{
if(i<2)
{
states[i]=0;
minStep = recurFind(minStep,oneStep,i,-1-i);
states[i]=2;
}
else
{
if(states[i-1]==0)
{
states[i]=0;
states[i-1]=2;
minStep = recurFind(minStep,oneStep,i,-1);
states[i]=2;
states[i-1]=0;
}
if(states[i-2]==0)
{
states[i]=0;
states[i-2]=2;
minStep = recurFind(minStep,oneStep,i,-2);
states[i]=2;
states[i-2]=0;
}
}
}
}
steps[s]=minStep;
jumps[s]=oneStep;
}
return steps[s];
}
private final int recurFind(int minStep, Step oneStep, int pos, int jump) {
int toS=makeS();
int r=shortestSteps(toS);
if(r<minStep-1)
{
oneStep.jump=jump;
oneStep.offset=pos;
oneStep.jumpTo=toS;
minStep=r+1;
}
return minStep;
}
public void printPath()
{
int s=initS;
int i=1;
while(s!=0)
{
System.out.println("["+(i++)+"] Frog at #"+jumps[s].offset+" jumps #"+jumps[s].jump);
s=jumps[s].jumpTo;
}
}
private final int makeS() {
int r=0;
int p=1;
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
{
r+=p*states[i];
p*=3;
}
return r;
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
FrogJump fj=new FrogJump();
int steps=fj.shortestSteps(fj.initS);
System.out.println("use "+steps+" steps!");
fj.printPath();
}
}
運行結果:
use 21 steps!
[1] Frog at #2 jumps #1
[2] Frog at #4 jumps #-2
[3] Frog at #5 jumps #-1
[4] Frog at #3 jumps #2
[5] Frog at #1 jumps #2
[6] Frog at #0 jumps #1
[7] Frog at #2 jumps #-2
[8] Frog at #0 jumps #-1
[9] Frog at #4 jumps #-2
[10] Frog at #2 jumps #-2
[11] Frog at #0 jumps #-1
[12] Frog at #5 jumps #2
[13] Frog at #3 jumps #2
[14] Frog at #1 jumps #2
[15] Frog at #5 jumps #2
[16] Frog at #3 jumps #2
[17] Frog at #5 jumps #2
[18] Frog at #6 jumps #-1
[19] Frog at #5 jumps #-2
[20] Frog at #3 jumps #-2
[21] Frog at #1 jumps #-2





 .
.
