I/O View ByteBuffer - Primitive Types
The ByteBuffer is produced by "wrapping" an eight-byte array, which is then displayed via view buffers of all the different primitive types. You can see in the following diagram the way the data appears differently when read from the different types of buffers:
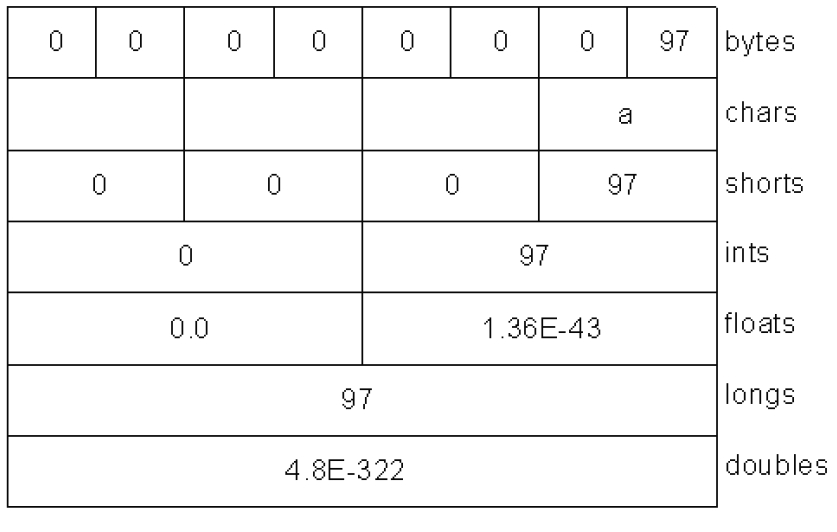
A ByteBuffer stores data in bug endian form, and data sent over a network always uses big endian order.
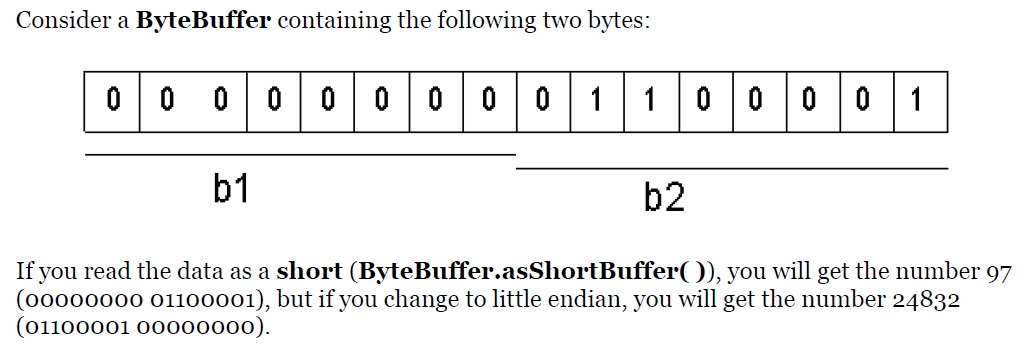
You can change the endian-ness of ByteBuffer using order() with an argument of ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN or ByteBOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN.
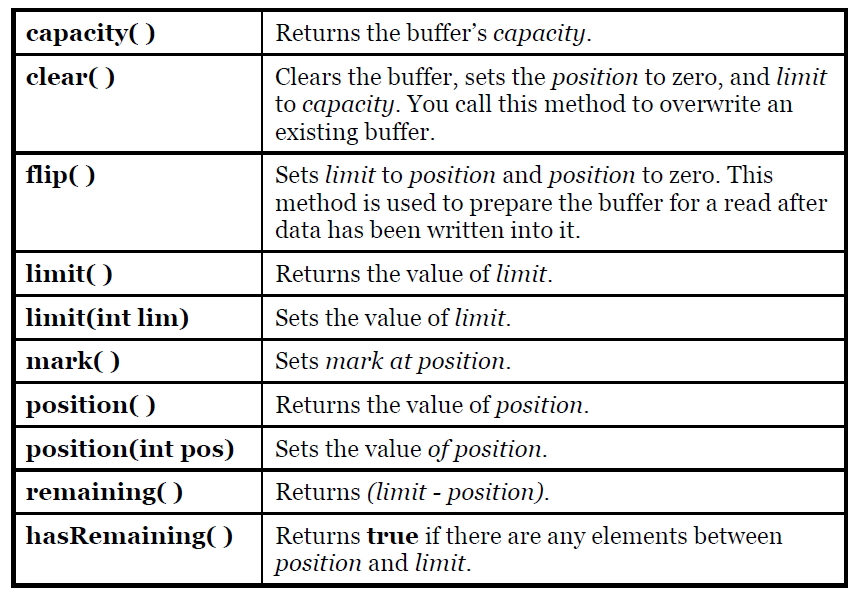
If you want to write a byte array to a file, then you wrap the byte array using the ByteBuffer.wrap() method, open a channel on the FileOutputStream using the getChannel() method, and then write data into FileChannel from this ByteBuffer.


package think.in.java.io;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.DoubleBuffer;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
import java.nio.IntBuffer;
import java.nio.LongBuffer;
import java.nio.ShortBuffer;
public class ViewBuffers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//-------------ByteBuffer-----------
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,'a'});
bb.rewind();
System.out.println("-----Byte Buffer-----");
while(bb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(bb.position() + " -> " + bb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------CharBuffer-----------
CharBuffer cb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asCharBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Char Buffer-----");
while(cb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(cb.position() + " -> " + cb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------FloatBuffer-----------
FloatBuffer fb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asFloatBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Float Buffer-----");
while(fb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(fb.position() + " -> " + fb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------IntBuffer-----------
IntBuffer ib = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asIntBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Int Buffer-----");
while(ib.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(ib.position() + " -> " + ib.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------LongBuffer-----------
LongBuffer lb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asLongBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Long Buffer-----");
while(lb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(lb.position() + " -> " + lb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------ShortBuffer-----------
ShortBuffer sb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asShortBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Short Buffer-----");
while(sb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(sb.position() + " -> " + sb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------DoubleBuffer-----------
DoubleBuffer db = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asDoubleBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Double Buffer-----");
while(db.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(db.position() + " -> " + db.get() + ", ");
}
}
}
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.DoubleBuffer;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
import java.nio.IntBuffer;
import java.nio.LongBuffer;
import java.nio.ShortBuffer;
public class ViewBuffers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//-------------ByteBuffer-----------
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,'a'});
bb.rewind();
System.out.println("-----Byte Buffer-----");
while(bb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(bb.position() + " -> " + bb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------CharBuffer-----------
CharBuffer cb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asCharBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Char Buffer-----");
while(cb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(cb.position() + " -> " + cb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------FloatBuffer-----------
FloatBuffer fb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asFloatBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Float Buffer-----");
while(fb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(fb.position() + " -> " + fb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------IntBuffer-----------
IntBuffer ib = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asIntBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Int Buffer-----");
while(ib.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(ib.position() + " -> " + ib.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------LongBuffer-----------
LongBuffer lb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asLongBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Long Buffer-----");
while(lb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(lb.position() + " -> " + lb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------ShortBuffer-----------
ShortBuffer sb = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asShortBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Short Buffer-----");
while(sb.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(sb.position() + " -> " + sb.get() + ", ");
}
//-------------DoubleBuffer-----------
DoubleBuffer db = ((ByteBuffer)bb.rewind()).asDoubleBuffer();
System.out.println("-----Double Buffer-----");
while(db.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(db.position() + " -> " + db.get() + ", ");
}
}
}
// Output:
-----Byte Buffer-----
0 -> 0,
1 -> 0,
2 -> 0,
3 -> 0,
4 -> 0,
5 -> 0,
6 -> 0,
7 -> 97,
-----Char Buffer-----
0 -> ,
1 -> ,
2 -> ,
3 -> a,
-----Float Buffer-----
0 -> 0.0,
1 -> 1.36E-43,
-----Int Buffer-----
0 -> 0,
1 -> 97,
-----Long Buffer-----
0 -> 97,
-----Short Buffer-----
0 -> 0,
1 -> 0,
2 -> 0,
3 -> 97,
-----Double Buffer-----
0 -> 4.8E-322,
-----Byte Buffer-----
0 -> 0,
1 -> 0,
2 -> 0,
3 -> 0,
4 -> 0,
5 -> 0,
6 -> 0,
7 -> 97,
-----Char Buffer-----
0 -> ,
1 -> ,
2 -> ,
3 -> a,
-----Float Buffer-----
0 -> 0.0,
1 -> 1.36E-43,
-----Int Buffer-----
0 -> 0,
1 -> 97,
-----Long Buffer-----
0 -> 97,
-----Short Buffer-----
0 -> 0,
1 -> 0,
2 -> 0,
3 -> 97,
-----Double Buffer-----
0 -> 4.8E-322,
A ByteBuffer stores data in bug endian form, and data sent over a network always uses big endian order.
You can change the endian-ness of ByteBuffer using order() with an argument of ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN or ByteBOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN.

If you want to write a byte array to a file, then you wrap the byte array using the ByteBuffer.wrap() method, open a channel on the FileOutputStream using the getChannel() method, and then write data into FileChannel from this ByteBuffer.

posted on 2012-11-07 10:46 鹽城小土包 閱讀(201) 評(píng)論(0) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類(lèi): J2EE


