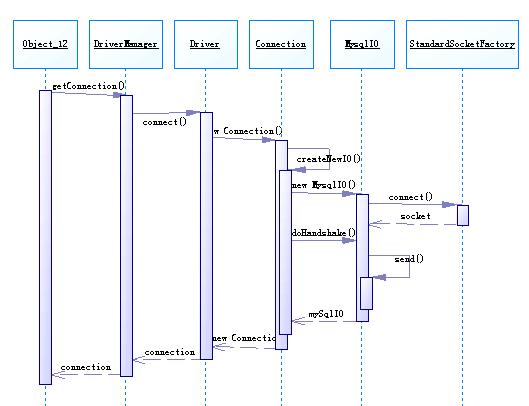
從時序圖中可以看到,createNewIO()就是新建了一個com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlIO,利用 com.mysql.jdbc.StandardSocketFactory來創建一個socket。然后就由這個mySqlIO來與MySql服務器進行握手(doHandshake()),這個doHandshake主要用來初始化與Mysql server的連接,負責登陸服務器和處理連接錯誤。在其中會分析所連接的mysql server的版本,根據不同的版本以及是否使用SSL加密數據都有不同的處理方式,并把要傳輸給數據庫server的數據都放在一個叫做packet的 buffer中,調用send()方法往outputStream中寫入要發送的數據。
useServerPreparedStmts置為true的話,mysql驅動可以通過PreparedStatement的子類ServerPreparedStatement來實現真正的PreparedStatement的功能
第一位表示數據包的開始位置,就是數據存放的起始位置,一般都設置為0,就是從第一個位置開始。第二和第三個字節標識了這個數據包的大小,注意的是,這個大小是出去標識的4個字節的大小,對于非最后一個數據包來說,這個大小都是一樣的,就是splitSize,也就是maxThreeBytes,它的值是 255 * 255 * 255。
最后一個字節中存放的就是數據包的編號了,從0開始遞增。
在標識位設置完畢之后,就可以把255 * 255 * 255大小的數據從我們準備好的待發送數據包中copy出來了,注意,前4位已經是標識位了,所以應該從第五個位置開始copy數據
# packetToSend = compressPacket(headerPacket, HEADER_LENGTH,
# splitSize, HEADER_LENGTH);
LoadBalancingConnectionProxy
package java.lang.reflect 。 proxy .
http://developer.51cto.com/art/200907/137823.htm
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/connector-j-reference-implementation-notes.html
PreparedStatements are implemented by the driver, as MySQL
does not have a prepared statement feature. Because of this,
the driver does not implement
getParameterMetaData() or
getMetaData() as it would require the
driver to have a complete SQL parser in the client.
Starting with version 3.1.0 MySQL Connector/J, server-side
prepared statements and binary-encoded result sets are used
when the server supports them.
但這是不是說PreparedStatement沒用呢?不是的,PreparedStatement有其他的好處:
1.代碼的可讀性和可維護性
2.最重要的一點是極大地提高了安全性,可以防止SQL注入
然后我又看了一些網上其他人的經驗,基本和我的判斷一致,有兩點要特別提請大家注意:
1.并不是說PreparedStatement在所有的DB上都不會提高效率,PreparedStatement需要服務器端的支持,比如在
Oracle上就會有顯著效果。上面說的測試都是在MySQL上測試的,我找到了一個MySQL架構師的帖子,比較明確地說明了MySQL不支持
PreparedStatement。
2.即便PreparedStatement不能提高性能,在少數使用時甚至會降低效率,但仍然應該使用PreparedStatement!因為其他好
處實在是太大了!當然,當SQL查詢比較復雜時,可能PreparedStatement好處會更大,只是我沒有測試,不敢肯定。
3.既然PreparedStatement不能提高效率,那PreparedStatement Pool也就沒有必要了。但可以看到每次新建Connection的開銷實在很大,因此Connection Pool絕對必要。



