一、概述
SpringMVC在2.5版本后新增了注解功能,2.5版本以前的基本通過繼承Controller體系來開發業務控制器,2.5版本后Controller體系中BaseCommandController及其子類AbstractCommandController、AbstractFormController、AbstractWizardFormController、
相比傳統的繼承Controller體系中某些類的方式,SpringMVC的注解具有以下優點:
1、Controller不再需要繼承某個特定類,只是簡單的POJO。
2、請求映射的配置非常方便靈活。
3、參數綁定機制非常方便豐富。
4、可以根據不同的http方法或者參數,細粒度處理不同的http請求
首先需要在應用的dispatcher-servlet.xml 啟動注解機制
注:雖然我們的Controller不需要再繼承任何類,但出于規范,我們仍然命名為***Controller.java,并統一放在com.demo.web.controller包中。
SimpleFormController、CancellableFormController等都已經被標示為@Deprecated,建議不再使用。
相比傳統的繼承Controller體系中某些類的方式,SpringMVC的注解具有以下優點:
1、Controller不再需要繼承某個特定類,只是簡單的POJO。
2、請求映射的配置非常方便靈活。
3、參數綁定機制非常方便豐富。
4、可以根據不同的http方法或者參數,細粒度處理不同的http請求
二、示例
下面通過對SpringMVC注解的詳細介紹來看一下上述優點。首先需要在應用的dispatcher-servlet.xml 啟動注解機制
<context:annotation-config />
<!-- 設置注解驅動 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!-- 設置掃描的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.demo.web.controller" />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping" />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter" />
<!-- 設置注解驅動 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!-- 設置掃描的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.demo.web.controller" />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping" />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter" />
注:雖然我們的Controller不需要再繼承任何類,但出于規范,我們仍然命名為***Controller.java,并統一放在com.demo.web.controller包中。
1、@Controller注解
簡單示例
package com.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
String index() {
return "index";
}
}
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
String index() {
return "index";
}
}
在一個POJO上面使用 @Controller 就可以標注該POJO是一個Controller,就這么簡單。 @Controller注解定義在org.springframework.steretype包中。
使用方式: @Controller 或者 @Controller("indexController)。 org.springframework.steretype包中還包含 @Componenet @Service @Respository
三個注解。@Component是通用標注,@Controller標注web控制器,@Service標注Servicec層的服務,@Respository標注DAO層的數據訪問。
public @ResponseBody boolean inactive(@RequestParam("accountId") Long accountId,
@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent,
@CookieValue("loginId") String loginId) {
return accountService.inactiveAccount(accountId);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "list/{pageNo}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String list(@PathVariable int pageNo) {
return "/account/list";
}
3.2 @RequestHeader 綁定httpRequest頭部信息,@RequestHeader("User-Agent") 完整形式為 @RequestHeader(value="User-Agebt",required=true, defaultValue=null)
3.3 @CookieValue 綁定一個Cookie值,@CookieValue("loginId") 完整形式為 @CookieValue(value="loginId",required=true,defaultValue=null)
3.4 @RequestBody 將httpRequest的body綁定到方法參數上
3.5 @ModelAttribute 有兩種使用方式: 1)在方法級別,指定方法的返回值綁定到model中; 2)方法參數級別,指定model中的值綁定到方法的入參上 示例如下:
例如訪問: http://localhost:8080/accounts/info.htm
返回數據如下:
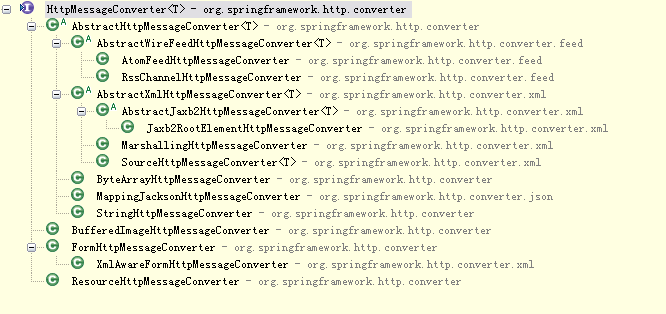
@Request 和 @ReponseBody 使用了HttpMessageConverter機制。下面是HttpMessageConverter的繼承體系。
常用的有如下幾個:
入參可以包含ModelMap或者Model,其實這兩者是一個東西,作用一樣。也可以采用index3式的傳統寫法,返回一個ModelAndView對象。
1、BindingResult參數必須跟在一個JavaBean參數后面
2、錯誤會被自動的綁定到model中,便于渲染模板時使用
3、不支持@RequestBody等類型的參數形式
使用方式: @Controller 或者 @Controller("indexController)。 org.springframework.steretype包中還包含 @Componenet @Service @Respository
三個注解。@Component是通用標注,@Controller標注web控制器,@Service標注Servicec層的服務,@Respository標注DAO層的數據訪問。
2、使用@RequestMapping注解處理請求映射
SpringMVC中注解基本都包含在 org.springframework.web.bind.annotation 包中。先看一下@RequestMapping 注解的源碼。
@Target( { ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
/**
* 指定映射的URL.可以在類層次和方法層次使用。方式如下:
* @RequestMapping("/add_")或 @RequestMapping(value = "/add")
* 支持Ant風格的URL映射,如 @RequestMapping("/myPath/*.htm")
* 在類層次指定了映射后,可以在方法層次再指定相對路徑
*/
String[] value() default {};
/**
* 指定HttpRequest的方法, 如:GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE, TRACE.
* 使用舉例: @RequestMapping(value = "/add_activity", method = RequestMethod.GET)
*/
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
/**
* 指定HttpRequest中包含的參數,使用方式如下:
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something",params="myParam") 請求包含myParam參數
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something",params="myParam=myValue")請求包含myParam參數,并且該參數值為myValue
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something",params="!myParam") 請求不包含myParam參數
*/
String[] params() default {};
/**
* 指定HttpRequest中包含的頭部信息,使用方式如下:
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers="content-type")請求包含該頭部
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers="content-type=text/*")請求包含特定值的頭部
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers="!content-type")請求不包含該頭部
*/
String[] headers() default {};
}
注:如果在類層次指定了映射,則方法層次上都將繼承類層次的映射@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
/**
* 指定映射的URL.可以在類層次和方法層次使用。方式如下:
* @RequestMapping("/add_")或 @RequestMapping(value = "/add")
* 支持Ant風格的URL映射,如 @RequestMapping("/myPath/*.htm")
* 在類層次指定了映射后,可以在方法層次再指定相對路徑
*/
String[] value() default {};
/**
* 指定HttpRequest的方法, 如:GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE, TRACE.
* 使用舉例: @RequestMapping(value = "/add_activity", method = RequestMethod.GET)
*/
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
/**
* 指定HttpRequest中包含的參數,使用方式如下:
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something",params="myParam") 請求包含myParam參數
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something",params="myParam=myValue")請求包含myParam參數,并且該參數值為myValue
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something",params="!myParam") 請求不包含myParam參數
*/
String[] params() default {};
/**
* 指定HttpRequest中包含的頭部信息,使用方式如下:
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers="content-type")請求包含該頭部
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers="content-type=text/*")請求包含特定值的頭部
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers="!content-type")請求不包含該頭部
*/
String[] headers() default {};
}
3、獲取HttpRequest中得參數
@RequestMapping("active")
public @ResponseBody boolean active(Long accountId) {
return accountService.activeAccount(accountId);
}
@RequestMapping("inactive")public @ResponseBody boolean active(Long accountId) {
return accountService.activeAccount(accountId);
}
@RequestMapping("active")
public @ResponseBody boolean active(Account account) {
return accountService.activeAccount(accountId);
}
public @ResponseBody boolean active(Account account) {
return accountService.activeAccount(accountId);
}
public @ResponseBody boolean inactive(@RequestParam("accountId") Long accountId,
@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent,
@CookieValue("loginId") String loginId) {
return accountService.inactiveAccount(accountId);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "list/{pageNo}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String list(@PathVariable int pageNo) {
return "/account/list";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "add", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String add(@RequestBody String body) {
return "/account/add";
}
public String add(@RequestBody String body) {
return "/account/add";
}
active方法的入參 accountId,如果請求中有名為 accountId的參數,則會進行默認綁定,不僅基本類型,javabean的屬性也可以默認進行綁定;
如果需要明確綁定,使用@RequestParam。 一般建議進行明確指定。
3.1 @RequestParam 綁定httpRequest中參數,@RequestParam("accountId") 完整形式為 @RequestParam(value="accountId",required=true,defaultValue=null)如果需要明確綁定,使用@RequestParam。 一般建議進行明確指定。
3.2 @RequestHeader 綁定httpRequest頭部信息,@RequestHeader("User-Agent") 完整形式為 @RequestHeader(value="User-Agebt",required=true, defaultValue=null)
3.3 @CookieValue 綁定一個Cookie值,@CookieValue("loginId") 完整形式為 @CookieValue(value="loginId",required=true,defaultValue=null)
3.4 @RequestBody 將httpRequest的body綁定到方法參數上
3.5 @ModelAttribute 有兩種使用方式: 1)在方法級別,指定方法的返回值綁定到model中; 2)方法參數級別,指定model中的值綁定到方法的入參上 示例如下:
@ModelAttribute("countryList")
public List<String> getCountries() {
return new ArrayList<String>();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "search", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String searchAccount(@ModelAttribute("accountId") Long accountId) {
return "/search";
}
public List<String> getCountries() {
return new ArrayList<String>();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "search", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String searchAccount(@ModelAttribute("accountId") Long accountId) {
return "/search";
}
4、使用@ResponseBody 生成response
適用于webservice的數據交換,或ajax異步請求,text、json或者xml格式的數據交換。
例如訪問: http://localhost:8080/accounts/info.htm
@RequestMapping(value = "info")
public @ResponseBody Account getAccount() {
Account a = new Account();
a.setId(123L);
a.setName("zhangsan");
return a;
}
public @ResponseBody Account getAccount() {
Account a = new Account();
a.setId(123L);
a.setName("zhangsan");
return a;
}
返回數據如下:
{"name":"zhangsan","id":123}
從上面例子可以看出,使用@ResponseBody后,返回的javabean默認被序列化成json格式的數據并被寫入到response body中。@Request 和 @ReponseBody 使用了HttpMessageConverter機制。下面是HttpMessageConverter的繼承體系。

常用的有如下幾個:
StringHttpMessageConverter ---字符串
MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter ----json
ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter ----字節數組
MarshallingHttpMessageConverter -----xml
5、使用模板技術生成response
適用于一般頁面請求。可以使用velocity freemarker等模板技術,在dispatcher-servlet.xml中需要設置viewResolver。
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(ModelMap modelMap) {
modelMap.put("name", "liucs");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name","liucs");
return "index";
}
如上面代碼index1和index2所示,不使用@ResponseBody注解。 返回一個String類型,這個String是viewname, 如果是重定向,return "redirect:/index.htm".public String index(ModelMap modelMap) {
modelMap.put("name", "liucs");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name","liucs");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/index")
public ModelAndView index3() throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("index");
mav.addObject("name", "liucs");
return mav;
}
public ModelAndView index3() throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("index");
mav.addObject("name", "liucs");
return mav;
}
入參可以包含ModelMap或者Model,其實這兩者是一個東西,作用一樣。也可以采用index3式的傳統寫法,返回一個ModelAndView對象。
6、數據驗證
@InitBinder標注
@InitBinder
public void myInitBinder(WebDataBinder binder){
binder.setDisallowedFields(new String[]{"id"});
}
通過在方法中聲明一個BindingResult參數來啟動綁定和驗證public void myInitBinder(WebDataBinder binder){
binder.setDisallowedFields(new String[]{"id"});
}
@RequestMapping("update")
public void update(@ModelAttribute("account") Account account,BindingResult bindResult) {
if(bindResult.hasErrors()){
//……
}
}
需要注意以下限制:public void update(@ModelAttribute("account") Account account,BindingResult bindResult) {
if(bindResult.hasErrors()){
//……
}
}
1、BindingResult參數必須跟在一個JavaBean參數后面
2、錯誤會被自動的綁定到model中,便于渲染模板時使用
3、不支持@RequestBody等類型的參數形式


