Activiti in Action(實戰Activiti)-第一章 BPMN 2.0: what’s in it for developers?(6)
Posted on 2011-01-03 17:59 網路冷眼@BlogJava 閱讀(3450) 評論(1) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類: Java 、Java EE 、BPM1.4.2 Detailed process modeling (詳細的流程建模)
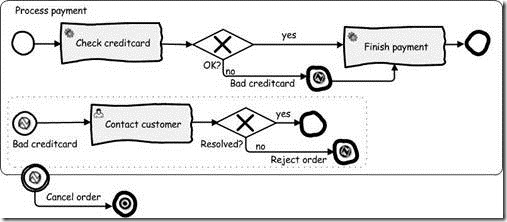
Although a book ordering process may seem simple at first hand, when looking at it in more detail a lot of process logic is needed. In this section we’ll focus on detailing the process payment task by adding validation and error handling logic. This also means we’ll need BPMN 2.0 constructs that are part of the descriptive or level 2 palette. In figure 1.8 the subprocess process payment is shown, which is a more detailed model of the process payment task of figure 1.7.
盡管訂書流程也許直接看起來很簡單,但是當深入觀察時,發現需要添加更多的流程邏輯。本節通過增加驗證和錯誤處理邏輯,我們將關注詳細的支付任務流程。這也意味著我們將需要描述性部分或者水平2調色板的BPMN 2.0構件。在圖1.8顯示了支付流程的子流程。它是圖1.7中描述的支付流程的詳細模型。
Figure 1.8 The extracted process payment subprocess from the book order process model. The subprocess shows the use of error end and start events and the use of terminate end event.
圖 1.8 從訂書流程模型摘取的支付子流程。子流程顯示了錯誤和開始事件的使用和終止結束事件的使用。
As you can see we use a number of additional BPMN 2.0 constructs in the process model of figure 1.8. So let’s first look at these extra element definitions in table 1.2.
正如你所見,我們使用了圖1.8流程模型的額外的BPMN 2.0構件。所以讓我們來看看表1.2中那些另外的元素定義。
Table 1.2 Overview of the additional BPMN 2.0 constructs used in figure 1.8.
表1.2 圖1.8中使用的額外的BPMN 2.0構件的描述
In figure 1.8 we made the tasks more specific by adding a type identifier. For example the check credit card task is modeled as a service task, because the validity of the credit card can be checked by invoking a web service. We also added a user task to indicate that the task has to be performed by a human. The contact customer activity is a user task, because an employee of the book store has to get in contact with the customer to solve the bad credit card problem.
在圖 1.8中,通過增加類型標識符,我們讓任務更加特殊。例如,將信用卡檢查任務建模為服務任務。因為信用卡的有效性檢查可以通過調用Web Service來執行。我們也增加一個用戶任務指示它必須由人來執行。聯系客戶活動是一個用戶任務,因為書店員工不得不聯系客戶來解決信用卡問題。
In the process payment subprocess shown in figure 1.8, we see a couple of other new BPMN 2.0 constructs. First note that a subprocess always starts with a start event. First the credit card information is validated by invoking an automated task. Then we check the outcome of this credit card validation with an exclusive gateway. In case the credit card validation was successful the payment is finished and the subprocess is ended.
在圖1.8所示的支付流程中,我們看見一對其它的新的BPMN 2.0構件。首先注意子流程總是從開始事件開始。通過調用自動任務,首先驗證信用卡信息,然后采用排他網關檢查信用卡驗證的結果。一旦信用卡驗證成功,支付完成,那么子流程結束。
When the credit card validation didn’t succeed an error end event throws an exception. This exception is caught within the subprocess by the error start event handling the bad credit card exception. In this case the customer is contacted personally by an employee of the book store to see if the credit card information was not received in a good manner or that the customer can pay in another way. If the payment can be settled with the customer a normal end event in the exception handler is reached and the subprocess is completed by executing the finish payment service task.
當信用卡驗證不成功,一個錯誤結束事件拋出一個異常。通過錯誤開始事件處理失敗的信用卡異常,在子流程捕獲異常。在這種情況下,書店的員工查看是否收到信用卡信息,或者客戶以其它方式支付。如果是由客戶來處理,將到達一個異常處理的正常結束事件。通過執行完成的支付服務任務,完成子流程。

![clip_image002[11] clip_image002[11]](http://www.aygfsteel.com/images/blogjava_net/lewhwa/Windows-Live-Writer/1b01dade415f_F7C8/clip_image002%5B11%5D_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image002[9] clip_image002[9]](http://www.aygfsteel.com/images/blogjava_net/lewhwa/Windows-Live-Writer/1b01dade415f_F7C8/clip_image002%5B9%5D_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image002[7] clip_image002[7]](http://www.aygfsteel.com/images/blogjava_net/lewhwa/Windows-Live-Writer/1b01dade415f_F7C8/clip_image002%5B7%5D_thumb.jpg)






