|
The Goal
Keep walking…… |
- Model-based adapters
與SWT widgets一起工作的JFace類(lèi)可稱為model-based adapters [或helper classes].這些adapter可以分為4類(lèi):
1.Viewers
將GUI組件中的信息與外觀分離 [與SWT不同]
2.Actions and contributions
簡(jiǎn)化了事件的處理,將用戶命令的反應(yīng)與引發(fā)反應(yīng)的事件分離
3.Image and font registries
注冊(cè)機(jī)制,資源可以被按需分配和釋放
4.Dialogs and wizards
信息框、錯(cuò)誤框、進(jìn)度框與向?qū)Э虻?/font>
- SET/JFace應(yīng)用程序的三段式結(jié)構(gòu)
package com.swtjface.Ch2;
import org.eclipse.jface.window.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
public class HelloSWT_JFace extends ApplicationWindow {
public HelloSWT_JFace() {
super(null); //1.Window allocation
}
protected Control createContents(Composite parent) {
Text helloText = new Text(parent, SWT.CENTER);
helloText.setText("Hello SWT and JFace!");
parent.pack();
return parent; //2.Window presentation
/*處理窗口的設(shè)計(jì),由于ApplicationWindow的可視部分不能被直接access,此方法連同一個(gè)Composite來(lái)控制GUI的顯示,此container對(duì)象[Composite]是所有被加入應(yīng)用程序的GUI組件的父件*/
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloSWT_JFace awin = new HelloSWT_JFace();
awin.setBlockOnOpen(true);
awin.open();
Display.getCurrent().dispose();? //3.Window operation
/*負(fù)責(zé)GUI的實(shí)際運(yùn)作。在分派好ApplicationWindow的資源之后,main方法使窗口顯示,當(dāng)setBlockOnOpen()方法以一個(gè)true參數(shù)被調(diào)用的時(shí)候,窗口關(guān)閉。然后ApplicationWindow的open()方法被調(diào)用,根據(jù)createContent()方法所返回的Composite來(lái)顯示窗口。然后程序通過(guò)dispose()方法釋放GUI的Display實(shí)例.因?yàn)榇顺绦蛑械乃衱idget都是display的child,所以一旦釋放Display,所有的widget都被釋放*/
}
}
- SWT與SWT/JFace的區(qū)別
SWT將GUI的外觀和操作都放在它的Shell類(lèi)里,而SWT/JFace卻將兩者分離開(kāi)來(lái)了,其中外觀由createContents()方法內(nèi)的Compsite來(lái)控制,而操作部分大體上是通過(guò)ApplicationWindow類(lèi)的實(shí)例來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
- ApplicationWindow
SWT/JFace同樣需要一個(gè)單獨(dú)的Display實(shí)例,但是只要ApplicationWindow通過(guò)一個(gè)null參數(shù)來(lái)構(gòu)建,那么就會(huì)創(chuàng)建它自己的Shell。參閱下圖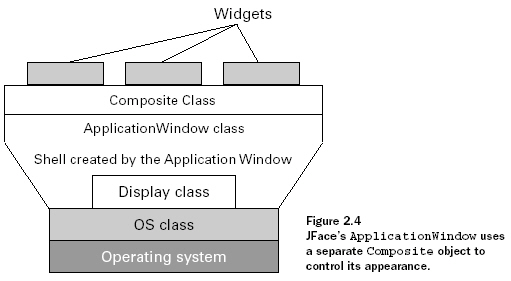
ApplicationWindow在Shell的基礎(chǔ)上提供了更多的途徑來(lái)設(shè)計(jì)窗口,其相關(guān)方法如下:
addMenuBar()
Configures the window with a top-level menu
addToolBar()
Adds a toolbar beneath the main menu
addStatusLine()
Creates a status area at the bottom of the window
setStatus(String)
Displays a message in the status area
getSeparator()
Returns the line separating the menu from the window
setDefaultImage(Image)
Displays an image when the application has no shell
setExceptionHandler(IExceptionHandler)
Configures the application to handle exceptions according to the specified interface
-
SWT應(yīng)用程序的三段式結(jié)構(gòu):
package com.swtjface.Ch2;
import org.eclipse.swt.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
public class HelloSWT {
public static void main (String [] args) {
Display display = new Display();
Shell shell = new Shell(display); //1.Allocation and initialization。
/*生成一個(gè)Display和Shell類(lèi)的實(shí)例,GUI獲取底層平臺(tái)的資源并開(kāi)辟了一個(gè)主窗口。*/Text helloText = new Text(shell, SWT.CENTER);
helloText.setText("Hello SWT!");
helloText.pack();//2.Adding widgets to the shell
/* 在 Shell 上加入一個(gè)文本小部件。The code in this section also sets the parameters for these widgets, containers, and events to make sure they look and act as required.其中pack()方法是tell the Shell and Text components to use only as much space as they need.*/
shell.pack();shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()){
if (!display.readAndDispatch()) display.sleep();
}
display.dispose(); //3.GUI operation
/*一旦Shell的open()方法被調(diào)用,應(yīng)用程序的主窗口和其子部件都會(huì)被呈現(xiàn)。只要Shell保持在打開(kāi)狀態(tài),Display實(shí)例就會(huì)通過(guò)它的readAndDispatch()方法來(lái)追蹤在操作系統(tǒng)事件隊(duì)列中的相關(guān)用戶事件。當(dāng)窗口關(guān)閉時(shí),與Display對(duì)象(包括Shell以及其子部件等)相聯(lián)系的資源就全部釋放*/
}
}
- Display 類(lèi)
Display 類(lèi)并不是可見(jiàn)的,但它負(fù)責(zé)監(jiān)管著 GUI 的資源并管理著和操作系統(tǒng)的通信。它不光要關(guān)注著它自己的窗口是如何顯示、移動(dòng)和重畫(huà)的,還同時(shí)要確保諸如鼠標(biāo)點(diǎn)擊、鍵盤(pán)敲擊等事件送達(dá)widgets并去處理它們。
是任何
SWT
和
JFace
應(yīng)用程序的承載著,無(wú)論你是用
SWT/JFace
開(kāi)發(fā)或是單用
SWT
開(kāi)發(fā),你必須在你的程序中包含這個(gè)類(lèi)的一個(gè)實(shí)例。
Display
類(lèi)的主要任務(wù)就是負(fù)責(zé)將你的代碼重的
SWT
和
JFace
命令翻譯成底層的命令來(lái)調(diào)取操作系統(tǒng)。
這一過(guò)程包含了兩部分:
1.Display
對(duì)象構(gòu)建一個(gè)代表著操作系統(tǒng)平臺(tái)的
OS
類(lèi)的實(shí)例;這個(gè)類(lèi)通過(guò)一系列被稱之為native methods的特殊
Java
程序提供了接觸計(jì)算機(jī)底層資源的途徑。2.
這個(gè)
Display
對(duì)象使用這些方法來(lái)直接指令操作系統(tǒng)并向應(yīng)用程序傳達(dá)用戶動(dòng)作。
if any features in your operating system aren’t incorporated into SWT, you can use the Java Native Interface to add them yourself.All it requires is a native Java method in the SWT package and a C function in the native graphics library that calls the operating system.
- Display 類(lèi)的方法
1.Display()--Allocates platform resources and creates a Display object
must be used in any SWT-based GUI.它產(chǎn)生一個(gè)Display類(lèi)的實(shí)例并將其和GUI相聯(lián)系
2.getCurrent()--Returns the user-interface thread
must be used in any SWT-based GUI.它返回一個(gè)應(yīng)用程序的主線程,用戶界面線程,通常和dispose()一起使用來(lái)結(jié)束Display的操作。
3.readAndDispatch()--Display object interprets events and passes them to receiver
enable the application to receive notifications from the operating system whenever the user takes an action associated with the GUI.
accesses the operating system’s event queue and determines whether any of the user’s actions are related to the GUI.
Using this method, the HelloSWT class knows whether the user has decided to dispose of the Shell. If so, the method returns TRUE, and the application ends. Otherwise, the Display object invokes its sleep() method, and the application continues waiting.
4.sleep()--Display object waits for events
enable the application to receive notifications from the operating system whenever the user takes an action associated with the GUI.
The Shell class accesses the operating system through the OS class to an extent, but only to keep track of opening, activating, maximizing, minimizing, and closing the main window.
The main function of the Shell class is to provide a common connection point for the containers, widgets, and events that need to be integrated into the GUI. Shell serves as the parent class to these components.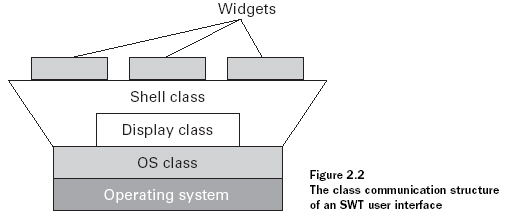
attached to the Display的shell--top-level shells
NOT directly attached to the Display instance的shell--secondary shell
在你的GUI之內(nèi),你可以設(shè)定shell或其他小部件的風(fēng)格參數(shù)值,若是多個(gè)值則可以用“|”相連.除了提到的屬性,默認(rèn)為“SHELL_TRIM”。
SHELL_TRIM--有一個(gè)標(biāo)題欄(SWT.TITLE)和用戶可以最小化SWT.MIN)、最大化(SWT.MAX)、改變尺寸(SWT.RESIZE)和關(guān)閉(SWT.CLOSE)
DIALOG_TRIM--有一個(gè)標(biāo)題欄、一個(gè)活動(dòng)區(qū)的邊界(SWT.BORDER)和被關(guān)閉的能力
你還可以確定shell的形態(tài),以限定用戶修改shell的modality,如A modal dialog box不能被移動(dòng)或是改變尺寸,只可以使用給予的按鈕關(guān)閉或是取消。
NOT?every platform can render these properties in GUI components.
| |||||||||
| 日 | 一 | 二 | 三 | 四 | 五 | 六 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 | 30 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |||
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | |||
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | |||
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 1 | 2 | |||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||
常用鏈接
留言簿(2)
隨筆分類(lèi)(23)
- Beginning JavaServer Pages

- Contributing to Eclipse

- Core JAVA 7th Edition

- Introduction to ABAP/4 Programming for SAP(1)

- SWT & JFace IN ACTION(22)

隨筆檔案(22)
文章檔案(1)
相冊(cè)
Neighbor
搜索
最新評(píng)論

- 1.?re: 4.2 Event processing in JFace
- great
- --cai niao
