|
The Goal
Keep walking…… |
graphic context是在GC類(lèi)中的,GC對(duì)象是附著于現(xiàn)存的Controls。
要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建一個(gè)graphically oriented的應(yīng)用程序,首先要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建graphic context,并將其與一個(gè)component相關(guān)聯(lián),這兩步都可通過(guò)GC的constructor來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)。共有2個(gè)構(gòu)造函數(shù),見(jiàn)下:
1. GC(Drawable)--Creates a GC and configures it for the Drawable object
2. GC(Drawable, int)--Creates and configures a GC and sets the text-display style,第二個(gè)參數(shù)可以是RIGHT_TO_LEFT或LEFT_TO_RIGHT(默認(rèn)值);
第一個(gè)參數(shù)需要實(shí)現(xiàn)Drawable接口的對(duì)象, 此接口包含了與graphic context.內(nèi)部相聯(lián)系的方法。SWT提供了三個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn)Drawable接口的類(lèi):Image, Device,?和 Control.

Control子類(lèi)雖然都能包含圖形,但只有一個(gè)類(lèi)是特別適合GC對(duì)象的:Canvas。它不僅提供了一個(gè)Composite的containment property,還可以用一系列的風(fēng)格來(lái)定義圖形在此區(qū)域內(nèi)如何顯示
示例:
package com.swtjface.Ch7;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
public class DrawExample
{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
Display display = new Display();
Shell shell = new Shell(display);
shell.setText("Drawing Example");
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(shell, SWT.NONE);
canvas.setSize(150, 150);
canvas.setLocation(20, 20);//在shell中創(chuàng)建canvas
shell.open ();
shell.setSize(200,220);
GC gc = new GC(canvas);//在canvas中創(chuàng)建graphic context
gc.drawRectangle(10, 10, 40, 45);
gc.drawOval(65, 10, 30, 35);
gc.drawLine(130, 10, 90, 80);
gc.drawPolygon(new int[] {20, 70, 45, 90, 70, 70});
gc.drawPolyline(new int[] {10,120,70,100,100,130,130,75});
gc.dispose();//釋放Color對(duì)象
while (!shell.isDisposed())
{
?if (!display.readAndDispatch())
?display.sleep();
?}
?display.dispose();
?}
?}
有兩點(diǎn)需要注意:1.在調(diào)用shell.open()之前構(gòu)建Canvas對(duì)象,然后在調(diào)用shell.open()之后創(chuàng)建和使用GC對(duì)象
???????????????????? 2.在使用完之后一定要立即釋放GC object
如上例所示GC提供了一系列在Drawable對(duì)象上畫(huà)圖形的方法,如下:

但是上例中有個(gè)問(wèn)題:當(dāng)shell被變灰過(guò)或者最小化過(guò)之后,圖形就會(huì)被擦去。所以我們需要解決的事,無(wú)論window怎么變化,圖形都保持可見(jiàn)。因此SWT在一個(gè)Drawable對(duì)象被刷新后讓你自行控制。這個(gè)更新的過(guò)程就被稱(chēng)為painting。
Painting and PaintEvents
當(dāng)一個(gè)GC方法在一個(gè)Drawabel對(duì)象上畫(huà)出一個(gè)圖案,它僅執(zhí)行這個(gè)painting過(guò)程一次。如果用戶(hù)改變對(duì)象尺寸或是用另一個(gè)窗口去覆蓋它,則圖形會(huì)被消除。因此,應(yīng)用程序能否在外界事件影響下維持其外觀這一點(diǎn)相當(dāng)重要。
這些外部事件被稱(chēng)為PaintEvents,接收它們的程序接口是PaintListener。一個(gè)Control在任何時(shí)候當(dāng)其外觀被應(yīng)用程序或是外界活動(dòng)改變都會(huì)觸發(fā)一個(gè)PaintEvent。這些類(lèi)對(duì)于事件和監(jiān)聽(tīng)器的使用方式都和我們?cè)诘谒恼聝?nèi)提到的類(lèi)似。由于PaintListener只有一個(gè)事件處理方法,所以不需要使用adapter類(lèi)
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(shell, SWT.NONE);
canvas.setSize(150, 150);
canvas.setLocation(20, 20);
canvas.addPaintListener(new PaintListener()
{
public void paintControl(PaintEvent pe)
{
GC gc = pe.gc;//每一個(gè)PaintEvent對(duì)象都包含有其自己的GC
gc.drawPolyline(new int[] {10,120,70,100,100,130,130,75});
}
});
shell.open();
每一個(gè)PaintEvent對(duì)象都包含有其自己的GC,主要有2個(gè)原因:1.因?yàn)檫@個(gè)GC instance是由事件產(chǎn)生的,所以PaintEvent會(huì)負(fù)責(zé)釋放他。2.應(yīng)用程序可以在shell open之前創(chuàng)建GC,這樣可以使圖形在一個(gè)獨(dú)立的類(lèi)中被創(chuàng)建。
SWT在PaintListener接口內(nèi)優(yōu)化painting過(guò)程,SWT的開(kāi)發(fā)者強(qiáng)烈建議Control的painting僅對(duì)PaintEvent作出反應(yīng)。如果一個(gè)應(yīng)用程序因?yàn)槠渌虮仨毟缕鋱D形,則他們推薦使用control的redraw()方法,這會(huì)在隊(duì)列中加入一個(gè)paint請(qǐng)求。之后,你可以調(diào)用update()方法來(lái)處理所有的綁定于該對(duì)象的paint請(qǐng)求。
需要牢記的是,雖然對(duì)于Control對(duì)象推薦在一個(gè)PaintListener內(nèi)painting,但是由于Device和Image對(duì)象并不能在該接口內(nèi)使用。如果你需要在一個(gè)image或device內(nèi)生成圖形,你必須單獨(dú)地生成一個(gè)GC對(duì)象并在使用結(jié)束后將其銷(xiāo)毀。
要客制化layout,需要繼承抽象類(lèi)Layout,需要寫(xiě)2個(gè)方法——computeSize() 和layout().
computeSize()
protected Point computeSize(Composite composite,
int wHint, int hHint,
boolean flushCache)
{
Point maxDimensions =
calculateMaxDimensions(composite.getChildren());
int stepsPerHemisphere =
stepsPerHemisphere(composite.getChildren().length);
int maxWidth = maxDimensions.x;
int maxHeight = maxDimensions.y;
int dimensionMultiplier = (stepsPerHemisphere + 1);
int controlWidth = maxWidth * dimensionMultiplier;
int controlHeight = maxHeight * dimensionMultiplier;
int diameter = Math.max(controlWidth, controlHeight);
Point preferredSize = new Point(diameter,
diameter);
... // code to handle case when our calculations
// are too large
return preferredSize;
}
參數(shù):
1.composite--The object we’re going to populate. At the time this method is called, it has children, but neither the composite nor the children have been sized or positioned on the screen.
2.wHint and hHint--layout所需的最大長(zhǎng)寬。若帶有參數(shù)SWT.DEFAULT,表示此layout可以隨意使用use whatever sizes it decides it needs.
3.flushCache--作為flag,to tell the layout whether it’s safe to use any cached values that it may be maintaining.
computeSize()的目的主要在于計(jì)算我們要layout的composite有多大
layout()
……
與之前所述的layout不同,form layout不是基于行和列的,它是基于與其他control之間的相對(duì)位置的。
FormLayout十分簡(jiǎn)單,你只要:1.設(shè)定頁(yè)邊距(高,寬)屬性。 2.設(shè)定spacing屬性,即所有control間的距離(in pixels)
同樣可以使用FormData來(lái)配置單個(gè)的control。
FormData
如果一個(gè)control沒(méi)有一個(gè)FormData實(shí)例來(lái)描述它的話,就會(huì)默認(rèn)放在composite的右上角
width和height屬性指定了control的尺寸,in pixels.
top, bottom, right, 和left屬性,每一個(gè)都有一個(gè)FormAttachment實(shí)例,這些attachments描述了control與其他control之間的關(guān)系。
FormAttachment
有2個(gè)使用途徑:
1.通過(guò)使用percentage of the parent composite.
2.通過(guò)設(shè)定一個(gè)control和另一個(gè)control之間的相對(duì)位置?
《圖》
package com.swtjface.Ch6;
import org.eclipse.swt.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.*;
public class Ch6FormLayoutComposite extends Composite {
public Ch6FormLayoutComposite(Composite parent) {
super(parent, SWT.NONE);
FormLayout layout = new FormLayout();
setLayout(layout);
Text t = new Text(this, SWT.MULTI);
FormData data = new FormData();
data.top = new FormAttachment(0, 0);
data.left = new FormAttachment(0, 0);
data.right = new FormAttachment(100);
data.bottom = new FormAttachment(75);//確定text的位置,因?yàn)樽笊辖鞘亲鴺?biāo)原點(diǎn),所以right的百分?jǐn)?shù)為100。
t.setLayoutData(data);
Button ok = new Button(this, SWT.NONE);
ok.setText("Ok");
Button cancel = new Button(this, SWT.NONE);
cancel.setText("Cancel");
data = new FormData();
data.top = new FormAttachment(t);
data.right = new FormAttachment(cancel);//ok按鈕在text下面,cancel左邊
ok.setLayoutData(data);
data = new FormData();
data.top = new FormAttachment(t);
data.right = new FormAttachment(100);//cancel按鈕在text下面,在最右邊
cancel.setLayoutData(data);
}
}
最常用的一種layout.以row layout為基礎(chǔ)。
package com.swtjface.Ch6;
import org.eclipse.swt.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.*;
public class Ch6GridLayoutComposite extends Composite {
public Ch6GridLayoutComposite(Composite parent) {
super(parent, SWT.NONE);
GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(4,false);//每一行有4個(gè)control,后一個(gè)參數(shù)是a
boolean to indicate whether the columns should take up an even amount of
space. By passing false, you tell the layout to only use the minimum amount of
space needed for each column.
setLayout(layout);
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
Button button = new Button(this, SWT.NONE);
button.setText("Cell " + i);
}
}
}
Using GridData styles
十分類(lèi)似于RowData對(duì)象。可通過(guò)其構(gòu)造函數(shù)來(lái)設(shè)定STYLE,這些STYLE可分為3類(lèi):FILL, HORIZONTAL_ALIGN, and VERTICAL_ALIGN.
1.FILL:此cell是否fill所有的availabe的空間。可用的值還包括FILL_HORIZONTAL(水平擴(kuò)張),FILL_VERTICAL(垂直擴(kuò)張),FILL_BOTH。
2.ALIGN,用來(lái)指定control在cell中的什么位置。值包括BEGINNING, END, CENTER和FILL。
具體參見(jiàn)下表
Using GridData size attributes
與RowData不同,GridData還有很多的public屬性。其中有些是布爾值類(lèi)型的,一般會(huì)根據(jù)所設(shè)置的不同styles而自動(dòng)管理,所以無(wú)需對(duì)其直接操作。還有一些是integer值,用來(lái)確定單個(gè)cells的大小。具體件下表: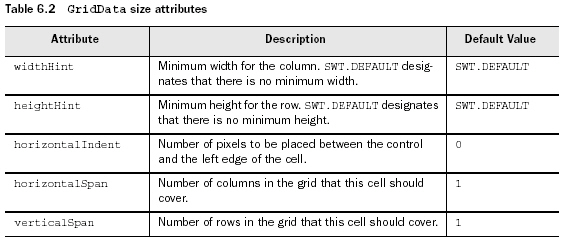
package com.swtjface.Ch6;
import org.eclipse.swt.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.*;
public class Ch6RowLayoutComposite extends Composite {
public Ch6RowLayoutComposite(Composite parent) {
super(parent, SWT.NONE);
RowLayout layout = new RowLayout(SWT.HORIZONTAL);
setLayout(layout);
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
Button button = new Button(this, SWT.NONE);
button.setText("Sample Text");
}
}
}
wrap——默認(rèn)為true,若設(shè)為false,所有的controls都在同一行。
pack——默認(rèn)為true.使所有的child controls都大小一樣。
justify——默認(rèn)為false. 若為true,每一行的control都會(huì)以間隔相同的方式排列。
RowData
可以通過(guò)setLayoutData()來(lái)設(shè)定每個(gè)control的大小,如:button.setLayoutData(new RowData(200 + 5 * i, 20 + i));
默認(rèn)為從左到右排放的,根據(jù)每個(gè)control實(shí)際所需的大小來(lái)分配空間,此composite中多于出來(lái)的空間,再平攤到每個(gè)control上。隨著composite的大小調(diào)整,control的大小也會(huì)跟著調(diào)整。
package com.swtjface.Ch6;
import org.eclipse.swt.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.*;
public class Ch6FillLayoutComposite extends Composite {
public Ch6FillLayoutComposite(Composite parent) {
super(parent, SWT.NONE);
FillLayout layout = new FillLayout( SWT.VERTICAL); //默認(rèn)是SWT.HORIZONTAL
setLayout(layout);//為此Composite設(shè)定一個(gè)layout.如果漏了此語(yǔ)句,會(huì)顯示不出child control。
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
Button button = new Button(this, SWT.NONE);
button.setText("Sample Text");
}
}
}
ProgressIndicator indicator = new ProgressIndicator(parent);
...
indicator.beginTask(10);
...
Display.getCurrent()display.asyncExec(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
//Inform the indicator that some amount of work has been done
indicator.worked(1);
}
});
正如上例所示,使用ProgressIndicator需要2步:
1.讓indicator知道總共有多少工作,通過(guò)使用beginTask().只有這個(gè)方法被調(diào)用了之后,這個(gè)control才會(huì)在屏幕上顯示。
2.每當(dāng)有一部分工作被完成了,就調(diào)用worked()。為了防止非ui的線程來(lái)update widgets,所以使用asyncExec()來(lái)解決這個(gè)問(wèn)題。
ProgressIndicator也提供animated模式,即總工作量不知道的情況。在這種模式下,the bar continually fills and empties
until done() is called. 要使用這個(gè)模式,就要用beginAnimatedTask()代替beginTask();并且不需要worked()方法了 ProgressBar,進(jìn)度條,是ProgressIndicator的簡(jiǎn)化版本。大多數(shù)情況下推薦使用ProgressIndicator。如果你決定直接使用ProgressBar,需要手動(dòng)改變此bar的外觀。如下
//Style can be SMOOTH, HORIZONTAL, or VERTICAL
ProgressBar bar = new ProgressBar(parent, SWT.SMOOTH);
bar.setBounds(10, 10, 200, 32);
bar.setMaximum(100);
...
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//Take care to only update the display from its
//own thread
Display.getCurrent().asyncExec(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
//Update how much of the bar should be filled in
bar.setSelection((int)(bar.getMaximum() * (i+1) / 10));
}
});
}
setSelection()causes the widget to be updated every time.This behavior is unlike that of ProgressIndicator or ProgressMonitorDialog,which will update the display only if it has changed by an amount that will be visible to the end user. 類(lèi)似于scrollbars。scrollbars僅限于用在可滑動(dòng)的item上,如text。
可通過(guò)setMinimum()和setMaximum()來(lái)設(shè)定它的范圍。可通過(guò)setThumb()來(lái)設(shè)定滑塊的值。在有些OS上,thumb的大小是常數(shù)。每按一下箭頭,所移動(dòng)的值稱(chēng)為increment.可通過(guò)setIncrement()來(lái)設(shè)定,按滑塊和箭頭間的空間所滑動(dòng)的值為page increment,可通過(guò)PageIncrement()來(lái)設(shè)定。以上這些數(shù)據(jù)可以通過(guò)void setValues( int selection, int minimum, int maximum, int thumb, int increment, int pageIncrement)來(lái)一次性設(shè)定,其中selection是thumb的出發(fā)點(diǎn)。
Slider有個(gè)屬性用來(lái)設(shè)定其是水平還是垂直的,默認(rèn)為水平。
package com.swtjface.Ch5;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Slider;
public class Ch5Slider extends Composite {
public Ch5Slider(Composite parent) {
super(parent, SWT.NONE);
setLayout(new FillLayout());
Slider slider = new Slider(this, SWT.HORIZONTAL);
slider.setValues(1000, 400, 1600, 200, 10, 100);
}
}
類(lèi)似于ToolBar的升級(jí)。他們的區(qū)別在于CoolBar上的item可以被重新配置,重新定大小。CoolBar的一般用途就是包含toolbars或按鈕。
String[] coolItemTypes = {"File", "Formatting", "Search"};
CoolBar coolBar = new CoolBar(parent, SWT.NONE);
for(int i = 0; i < coolItemTypes.length; i++)
{
CoolItem item = new CoolItem(coolBar, SWT.NONE);
ToolBar tb = new ToolBar(coolBar, SWT.FLAT);
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
ToolItem ti = new ToolItem(tb, SWT.NONE);
ti.setText(coolItemTypes[i] + " Item #" + j);
}
}
是JFace的類(lèi),繼承自ContributionManager,凡是繼承了IAction或IContribution接口的對(duì)象都可被加至ToolBarManager.你只要花時(shí)間為T(mén)oolBarManager添加Action,Toolbar和ToolItem實(shí)例會(huì)自動(dòng)產(chǎn)生。
你可通過(guò)調(diào)用ApplicationWindow的createToolBarManager()來(lái)為你的應(yīng)用程序添加一個(gè)toolbar。與MenuManager不同的是,createToolBarManager()需要一個(gè)style參數(shù),這個(gè)參數(shù)用來(lái)設(shè)定ToolBar所用的按鈕的風(fēng)格:flat或normal。
- ControlContribution
除了MenuManager所用的ContributionItems之外,還有一個(gè)新的ContributionItem,只能被ToolBarManager使用——ControlContribution。這個(gè)類(lèi)可將任何能被用于toolbar的Control打包進(jìn)去。
要使用ControlContribution類(lèi),必須要實(shí)現(xiàn)抽象方法createControl().
toolBarManager.add(new ControlContribution("Custom") {
protected Control createControl(Composite parent) {
SashForm sf = new SashForm(parent, SWT.NONE);
Button b1 = new Button(sf, SWT.PUSH);
b1.setText("Hello");
Button b2 = new Button(sf, SWT.PUSH);
b2.setText("World");
b2.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() {
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e) {
System.out.println("Selected:" + e);
}
});
return sf;
}
});
如果你希望有任何的事件發(fā)生,必須在你的controls上實(shí)現(xiàn)SelectionListeners
- Creating toolbars by hand
如果你不想ToolBarManager來(lái)創(chuàng)建toolbar的話,可以手動(dòng)創(chuàng)建,需要用到ToolBar和ToolItem類(lèi).
Toolbar
是一個(gè)composite control,包含多個(gè)ToolItems.Toolbar由多個(gè)小圖標(biāo)按鈕組成,一般是16-by-16bitmap圖片。每個(gè)按鈕都對(duì)應(yīng)一個(gè)ToolItem。Toolbar可以是水平的也可以是垂直的,默認(rèn)為水平
ToolItem
每一個(gè)ToolItem都有一個(gè)圖片,如果沒(méi)有,默認(rèn)為紅色方塊。When the user selects a ToolItem from the menu, it broadcasts the event to any registered SelectionListeners.Your application should register a listener with each ToolItem and use that listener to perform whatever logic corresponds to the menu item.
三種類(lèi)型的Combo control:
1.Simple:默認(rèn)類(lèi)型,一個(gè)可編輯的text field和一個(gè)供選擇的list
2.Drop-down:下拉列表,文本框可編輯
3.Read-only:文本框不可編輯的下拉列表,可用select( 0 )來(lái)將其默認(rèn)選中列表中的首項(xiàng)。
以上三種類(lèi)型可在構(gòu)造函數(shù)中通過(guò)STYLE.*來(lái)設(shè)置。
| |||||||||
| 日 | 一 | 二 | 三 | 四 | 五 | 六 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 1 | |||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |||
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | |||
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | |||
| 30 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
常用鏈接
留言簿(2)
隨筆分類(lèi)(23)
- Beginning JavaServer Pages

- Contributing to Eclipse

- Core JAVA 7th Edition

- Introduction to ABAP/4 Programming for SAP(1)

- SWT & JFace IN ACTION(22)

隨筆檔案(22)
文章檔案(1)
相冊(cè)
Neighbor
搜索
最新評(píng)論

- 1.?re: 4.2 Event processing in JFace
- great
- --cai niao
