JMX分析1-MBean的實現
本文只是JDK7中JMX在本地,MBeanServer管理MBeans的默認實現的探索學習,沒有涉及JMX Remote。
JMX 使用了 Java Bean 模式來傳遞信息。一般說來,JMX 使用有名的 MBean,其內部包含了數據信息,這些信息可能是:應用程序配置信息、模塊信息、系統信息、統計信息等。另外,MBean 也可以設立可讀寫的屬性、直接操作某些函數甚至啟動 MBean 可發送的 notification 等。MBean 包括 Standard,MXBean,Dynamic,Model,Open 等幾種分類,其中最簡單是標準 MBean 和 MXBean,而我們使用得最多的也是這兩種。MXBean 主要是 java.lang.management使用較多,將在下一節中介紹。我們先了解其他一些重要的 MBean 的種類。
StandardMBean
MXBean 規定了標準 MBean 也要實現一個接口,所有向外界公開的方法都要在這個接口中聲明。否則,管理系統就不能從中獲得相應的信息。此外,該接口的名字也有一定的規范:即在標準 MBean 類名之后加上“MBean”后綴。若 MBean 的類名叫做 MBeansName 的話,對應的接口就要叫做 MBeansNameMBean。
例子:
測試 :
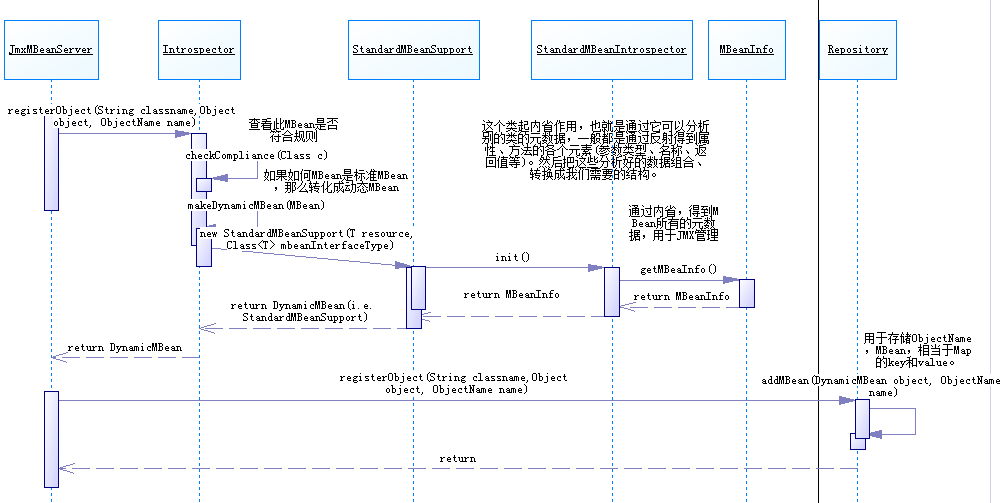
JmxMBeanServer在register一個MBean的時候,主要的步驟:
1. 查看MBean是否符合命名規則
2. 創建一個DynamicMBean,如果需要注冊的是標準MBean,那么通過內省機制,得到標準的MBean各種元數據,這些數據封裝組合到MBeanInfo中,接著創建StandardMBeanSupport(StandardMBeanSupport是DynamicMBean的子類) 。
3. JMX中按照ObjectName加上一次創建好的DynamicMBean,存入到Repository,Repository存的格式有點相當于Map的(key,value)。
其他的比如setAttribute(...),和invoke(...)方法就是把上個getAttribute(...)替換相應方法名就可以了。
參照上面流程圖和JDK中JMX的實現,可以看出JMX在內部實現中,對于標準MBean,也是轉換成DynamicMBean(StandardMBeanSupport是DynamicMBean的子類)。
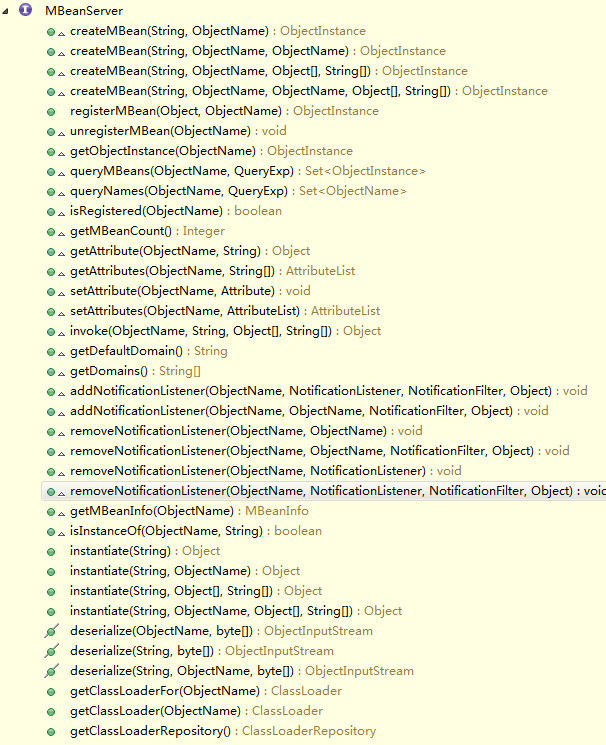
MBeanServerConnection提供一種連接到MBeanServer的途徑,可以使本地的或者遠程的。MBeanServer是作為一個本地的MBeanServerConnection,用于管理MBean的一個服務。主要提供創建、注冊、移除MBean,MBean屬性的獲得和設置,MBean的操作(invoke),消息機制的支持,MBean的查詢,MBean信息的展示。但是MBeanServer雖然目的是管理和對注冊進來的MBean進行操作,但是沒有方法是可以直接得到MBean實例的,只能通過MBeanServer對MBean進行操作。
圖:MBeanServer結構
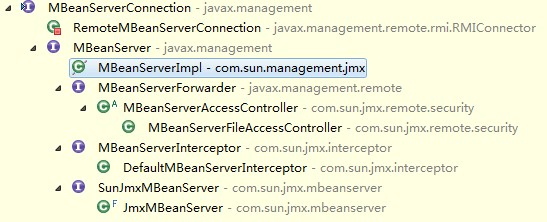
圖:MBeanServer屬性
JMX 使用了 Java Bean 模式來傳遞信息。一般說來,JMX 使用有名的 MBean,其內部包含了數據信息,這些信息可能是:應用程序配置信息、模塊信息、系統信息、統計信息等。另外,MBean 也可以設立可讀寫的屬性、直接操作某些函數甚至啟動 MBean 可發送的 notification 等。MBean 包括 Standard,MXBean,Dynamic,Model,Open 等幾種分類,其中最簡單是標準 MBean 和 MXBean,而我們使用得最多的也是這兩種。MXBean 主要是 java.lang.management使用較多,將在下一節中介紹。我們先了解其他一些重要的 MBean 的種類。
StandardMBean
MXBean 規定了標準 MBean 也要實現一個接口,所有向外界公開的方法都要在這個接口中聲明。否則,管理系統就不能從中獲得相應的信息。此外,該接口的名字也有一定的規范:即在標準 MBean 類名之后加上“MBean”后綴。若 MBean 的類名叫做 MBeansName 的話,對應的接口就要叫做 MBeansNameMBean。
例子:
1 package test.jmx;
2
3 import javax.management.Notification;
4 import javax.management.NotificationBroadcasterSupport;
5
6
7 /**
8 * 此標準MBean需實現XXXMBean這樣名稱的借口,XXX為這個類的名稱,
9 * 如果MBean需要消息事件的發送、監聽等需要實現
10 * @see javax.management.NotificationBroadcaster,
11 * 或者繼承@see javax.management.NotificationBroadcasterSupport
12
13 */
14 public class HelloWorld extends NotificationBroadcasterSupport implements HelloWorldMBean {
15 public String hello;
16
17 private long seq = 0l;
18
19 public HelloWorld() {
20 this.hello = "Hello World! I am a Standard MBean";
21 }
22
23 public HelloWorld(String hello) {
24 this.hello = hello;
25 }
26
27 public String getHello() {
28 return hello;
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public Object getInstance() {
33 return new Object();
34 }
35
36 /*
37 * 當執行message的時候,發送一個消息(事件)
38 * @see test.jmx.HelloWorldMBean#message(java.lang.String)
39 */
40 @Override
41 public String message(String ms) {
42 Notification notice = new Notification("type1",this,seq++," the message metheod is invoked,the argument ms: "+ms);
43 sendNotification(notice);
44 return " the message :
 ";
";
45 }
46
47 @Override
48 public void setHello(String hello) {
49 this.hello = hello;
50 }
51 }
52
2
3 import javax.management.Notification;
4 import javax.management.NotificationBroadcasterSupport;
5
6
7 /**
8 * 此標準MBean需實現XXXMBean這樣名稱的借口,XXX為這個類的名稱,
9 * 如果MBean需要消息事件的發送、監聽等需要實現
10 * @see javax.management.NotificationBroadcaster,
11 * 或者繼承@see javax.management.NotificationBroadcasterSupport
12
13 */
14 public class HelloWorld extends NotificationBroadcasterSupport implements HelloWorldMBean {
15 public String hello;
16
17 private long seq = 0l;
18
19 public HelloWorld() {
20 this.hello = "Hello World! I am a Standard MBean";
21 }
22
23 public HelloWorld(String hello) {
24 this.hello = hello;
25 }
26
27 public String getHello() {
28 return hello;
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public Object getInstance() {
33 return new Object();
34 }
35
36 /*
37 * 當執行message的時候,發送一個消息(事件)
38 * @see test.jmx.HelloWorldMBean#message(java.lang.String)
39 */
40 @Override
41 public String message(String ms) {
42 Notification notice = new Notification("type1",this,seq++," the message metheod is invoked,the argument ms: "+ms);
43 sendNotification(notice);
44 return " the message :

 ";
";45 }
46
47 @Override
48 public void setHello(String hello) {
49 this.hello = hello;
50 }
51 }
52
1
2 package test.jmx;
3
4 public interface HelloWorldMBean {
5 public String getHello();
6
7 public void setHello(String hello);
8
9 public Object getInstance();
10
11 public String message(String ms);
12
13 }
14
2 package test.jmx;
3
4 public interface HelloWorldMBean {
5 public String getHello();
6
7 public void setHello(String hello);
8
9 public Object getInstance();
10
11 public String message(String ms);
12
13 }
14
測試 :
1 package test.jmx;
2
3 import java.util.Set;
4
5 import javax.management.Attribute;
6 import javax.management.MBeanOperationInfo;
7 import javax.management.MBeanServer;
8 import javax.management.MBeanServerFactory;
9 import javax.management.Notification;
10 import javax.management.NotificationListener;
11 import javax.management.ObjectInstance;
12 import javax.management.ObjectName;
13 import javax.management.modelmbean.RequiredModelMBean;
14
15 import org.junit.Test;
16
17 public class JmxTest {
18
19 /**
20 * 測試標準MBean
21 * 需要被管理的方法、屬性等在接口中定義好,創建一個類,繼承此接口,然后實現時候方法,
22 * 這樣,但注冊到MBeanServer的時候,會自動管理其,接口中的各個屬性、方法。
23 * @throws Exception
24 */
25 @Test
26 public void test1StandardMBean() throws Exception{
27 // MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer("JMX2Test");
28 MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer();
29 ObjectName name = new ObjectName("Hello:type=myfirstMbean");
30
31 // ms.createMBean("HelloWorld", objectName);
32 HelloWorld hello = new HelloWorld(" yao yao , qie ke nao ");
33
34 //MBean需要實現NotificationBroadcaster接口,支持各種事件的發送和處理
35 hello.addNotificationListener(new NotificationListener() {
36 @Override
37 public void handleNotification(Notification notification, Object handback) {
38 System.out.println(" access listen : "+notification);
39 }
40 },null,null);
41
42 ms.registerMBean(hello,name );
43
44 String s1 = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "Hello");
45 System.out.println(" the init value : "+s1);
46
47 ms.setAttribute(name, new Attribute("Hello"," hi ,hi ,man "));
48 String s2 = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "Hello");
49 System.out.println(" the init value : "+s2);
50
51 ms.invoke(name, "message", new Object[]{" i as message "}, new String[]{"java.lang.String"});
52
53 ObjectName name2 = new ObjectName("*:*");
54 Set<ObjectInstance> set = ms.queryMBeans(name2, null);
55 }
56
57 /**
58 * 動態Mbean,需要實現DynamicMBean接口,并且任何需要,管理的方法、屬性,都需要在接口的方法中,
59 * 自己來實現,Mbeaninfo也需要自己設置,這樣編程的工作量大,但是有很大的可控性。
60 * @throws Exception
61 */
62 @Test
63 public void test2DynamicMBean() throws Exception{
64 HelloWorldDynamic dynamic = new HelloWorldDynamic();
65
66 MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer();
67 //創建一個ObjectName
68 ObjectName name = new ObjectName("DynamicHello:type=dinamicMbean");
69
70 //注冊動態MBean到MBeanServer服務上去
71 ms.registerMBean(dynamic, name);
72
73 //得到屬性值
74 Object o = ms.getAttribute(name, "getInstance");
75 String hello = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "gh");
76 MBeanOperationInfo operation = dynamic.getMBeanInfo().getOperations()[0];
77 System.out.println(" attribute value of getInstance:"+o+"; attribute value of gh:"+hello);
78
79 //執行一個方法(操作)
80 ms.invoke(name, operation.getName(), null, null);
81 }
82
83 @Test
84 public void test3RequiredModelMBean() throws Exception{
85 HelloWorldModelMBean hello = new HelloWorldModelMBean();
86
87 MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer();
88 RequiredModelMBean modelMbean = hello.createModelBean();
89 ObjectName name = new ObjectName("RequiredMBeanHello:type=ModelMbean");
90 //監聽屬性變化事件
91 modelMbean.addAttributeChangeNotificationListener(new NotificationListener() {
92 @Override
93 public void handleNotification(Notification notification, Object handback) {
94 System.out.println(" --Attribute已經改變-- ");
95 }
96 }, null,null);
97 ms.registerMBean(modelMbean, name);
98
99 ms.invoke(name, "setHello", new Object[]{" aaa "},new String[]{ "java.lang.String"});
100 String s = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "hello");
101 //出發Attribute改變事件
102 ms.setAttribute(name, new Attribute("hello", "bbb"));
103 String s2 = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "hello");
104 System.out.println(s);
105 System.out.println(s2);
106 }
107 }
108
2
3 import java.util.Set;
4
5 import javax.management.Attribute;
6 import javax.management.MBeanOperationInfo;
7 import javax.management.MBeanServer;
8 import javax.management.MBeanServerFactory;
9 import javax.management.Notification;
10 import javax.management.NotificationListener;
11 import javax.management.ObjectInstance;
12 import javax.management.ObjectName;
13 import javax.management.modelmbean.RequiredModelMBean;
14
15 import org.junit.Test;
16
17 public class JmxTest {
18
19 /**
20 * 測試標準MBean
21 * 需要被管理的方法、屬性等在接口中定義好,創建一個類,繼承此接口,然后實現時候方法,
22 * 這樣,但注冊到MBeanServer的時候,會自動管理其,接口中的各個屬性、方法。
23 * @throws Exception
24 */
25 @Test
26 public void test1StandardMBean() throws Exception{
27 // MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer("JMX2Test");
28 MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer();
29 ObjectName name = new ObjectName("Hello:type=myfirstMbean");
30
31 // ms.createMBean("HelloWorld", objectName);
32 HelloWorld hello = new HelloWorld(" yao yao , qie ke nao ");
33
34 //MBean需要實現NotificationBroadcaster接口,支持各種事件的發送和處理
35 hello.addNotificationListener(new NotificationListener() {
36 @Override
37 public void handleNotification(Notification notification, Object handback) {
38 System.out.println(" access listen : "+notification);
39 }
40 },null,null);
41
42 ms.registerMBean(hello,name );
43
44 String s1 = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "Hello");
45 System.out.println(" the init value : "+s1);
46
47 ms.setAttribute(name, new Attribute("Hello"," hi ,hi ,man "));
48 String s2 = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "Hello");
49 System.out.println(" the init value : "+s2);
50
51 ms.invoke(name, "message", new Object[]{" i as message "}, new String[]{"java.lang.String"});
52
53 ObjectName name2 = new ObjectName("*:*");
54 Set<ObjectInstance> set = ms.queryMBeans(name2, null);
55 }
56
57 /**
58 * 動態Mbean,需要實現DynamicMBean接口,并且任何需要,管理的方法、屬性,都需要在接口的方法中,
59 * 自己來實現,Mbeaninfo也需要自己設置,這樣編程的工作量大,但是有很大的可控性。
60 * @throws Exception
61 */
62 @Test
63 public void test2DynamicMBean() throws Exception{
64 HelloWorldDynamic dynamic = new HelloWorldDynamic();
65
66 MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer();
67 //創建一個ObjectName
68 ObjectName name = new ObjectName("DynamicHello:type=dinamicMbean");
69
70 //注冊動態MBean到MBeanServer服務上去
71 ms.registerMBean(dynamic, name);
72
73 //得到屬性值
74 Object o = ms.getAttribute(name, "getInstance");
75 String hello = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "gh");
76 MBeanOperationInfo operation = dynamic.getMBeanInfo().getOperations()[0];
77 System.out.println(" attribute value of getInstance:"+o+"; attribute value of gh:"+hello);
78
79 //執行一個方法(操作)
80 ms.invoke(name, operation.getName(), null, null);
81 }
82
83 @Test
84 public void test3RequiredModelMBean() throws Exception{
85 HelloWorldModelMBean hello = new HelloWorldModelMBean();
86
87 MBeanServer ms = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer();
88 RequiredModelMBean modelMbean = hello.createModelBean();
89 ObjectName name = new ObjectName("RequiredMBeanHello:type=ModelMbean");
90 //監聽屬性變化事件
91 modelMbean.addAttributeChangeNotificationListener(new NotificationListener() {
92 @Override
93 public void handleNotification(Notification notification, Object handback) {
94 System.out.println(" --Attribute已經改變-- ");
95 }
96 }, null,null);
97 ms.registerMBean(modelMbean, name);
98
99 ms.invoke(name, "setHello", new Object[]{" aaa "},new String[]{ "java.lang.String"});
100 String s = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "hello");
101 //出發Attribute改變事件
102 ms.setAttribute(name, new Attribute("hello", "bbb"));
103 String s2 = (String)ms.getAttribute(name, "hello");
104 System.out.println(s);
105 System.out.println(s2);
106 }
107 }
108
- MBean注冊

JmxMBeanServer在register一個MBean的時候,主要的步驟:
1. 查看MBean是否符合命名規則
2. 創建一個DynamicMBean,如果需要注冊的是標準MBean,那么通過內省機制,得到標準的MBean各種元數據,這些數據封裝組合到MBeanInfo中,接著創建StandardMBeanSupport(StandardMBeanSupport是DynamicMBean的子類) 。
3. JMX中按照ObjectName加上一次創建好的DynamicMBean,存入到Repository,Repository存的格式有點相當于Map的(key,value)。
- MBeanServer的管理MBean分析
1 JmxMBeanServer:
2 public Object getAttribute(ObjectName name, String attribute)
3 throws MBeanException, AttributeNotFoundException,
4 InstanceNotFoundException, ReflectionException {
5 //mbsInterceptor類型為DefaultMBeanServerInterceptor,也實現了MBeanServer接口,
6 //JmxMBeanServer實現的MBeanServer接口的方法,基本都是由mbs代理執行的。
7 return mbsInterceptor.getAttribute(cloneObjectName(name), attribute);
8 }
9
10 DefaultMBeanServerInterceptor:
11 public Object getAttribute(ObjectName name, String attribute)
12 throws MBeanException, AttributeNotFoundException,
13 InstanceNotFoundException, ReflectionException {
14

15 //通過ObjectName(key)從Repository中得到注冊過的MBean
16 final DynamicMBean instance = getMBean(name);
17

18 //得到Attribute的值
19 return instance.getAttribute(attribute);
20 }
21 StandardMBeanSupport:
22 public final Object gtAttribute(String attribute)
23 throws AttributeNotFoundException,
24 MBeanException,
25 ReflectionException {
26 return perInterface.getAttribute(resource, attribute, getCookie());
27 }
28 PerInterface:
29 Object getAttribute(Object resource, String attribute, Object cookie)
30 throws AttributeNotFoundException,
31 MBeanException,
32 ReflectionException {
33 //得到Attribute屬性的方法,也就是MBean接口中定義的getXXX()方法
34 final M cm = getters.get(attribute);
35 if (cm == null) {
36 final String msg;
37 if (setters.containsKey(attribute))
38 msg = "Write-only attribute: " + attribute;
39 else
40 msg = "No such attribute: " + attribute;
41 throw new AttributeNotFoundException(msg);
42 }
43 //在調用進去的話,就是通過反射調用cm方法,得到屬性的值
44 return introspector.invokeM(cm, resource, (Object[]) null, cookie);
45 }
2 public Object getAttribute(ObjectName name, String attribute)
3 throws MBeanException, AttributeNotFoundException,
4 InstanceNotFoundException, ReflectionException {
5 //mbsInterceptor類型為DefaultMBeanServerInterceptor,也實現了MBeanServer接口,
6 //JmxMBeanServer實現的MBeanServer接口的方法,基本都是由mbs代理執行的。
7 return mbsInterceptor.getAttribute(cloneObjectName(name), attribute);
8 }
9
10 DefaultMBeanServerInterceptor:
11 public Object getAttribute(ObjectName name, String attribute)
12 throws MBeanException, AttributeNotFoundException,
13 InstanceNotFoundException, ReflectionException {
14


15 //通過ObjectName(key)從Repository中得到注冊過的MBean
16 final DynamicMBean instance = getMBean(name);
17


18 //得到Attribute的值
19 return instance.getAttribute(attribute);
20 }
21 StandardMBeanSupport:
22 public final Object gtAttribute(String attribute)
23 throws AttributeNotFoundException,
24 MBeanException,
25 ReflectionException {
26 return perInterface.getAttribute(resource, attribute, getCookie());
27 }
28 PerInterface:
29 Object getAttribute(Object resource, String attribute, Object cookie)
30 throws AttributeNotFoundException,
31 MBeanException,
32 ReflectionException {
33 //得到Attribute屬性的方法,也就是MBean接口中定義的getXXX()方法
34 final M cm = getters.get(attribute);
35 if (cm == null) {
36 final String msg;
37 if (setters.containsKey(attribute))
38 msg = "Write-only attribute: " + attribute;
39 else
40 msg = "No such attribute: " + attribute;
41 throw new AttributeNotFoundException(msg);
42 }
43 //在調用進去的話,就是通過反射調用cm方法,得到屬性的值
44 return introspector.invokeM(cm, resource, (Object[]) null, cookie);
45 }
其他的比如setAttribute(...),和invoke(...)方法就是把上個getAttribute(...)替換相應方法名就可以了。
參照上面流程圖和JDK中JMX的實現,可以看出JMX在內部實現中,對于標準MBean,也是轉換成DynamicMBean(StandardMBeanSupport是DynamicMBean的子類)。
- 相關的類說明
MBeanServerConnection提供一種連接到MBeanServer的途徑,可以使本地的或者遠程的。MBeanServer是作為一個本地的MBeanServerConnection,用于管理MBean的一個服務。主要提供創建、注冊、移除MBean,MBean屬性的獲得和設置,MBean的操作(invoke),消息機制的支持,MBean的查詢,MBean信息的展示。但是MBeanServer雖然目的是管理和對注冊進來的MBean進行操作,但是沒有方法是可以直接得到MBean實例的,只能通過MBeanServer對MBean進行操作。
圖:MBeanServer結構

圖:MBeanServer屬性

PerInterface:
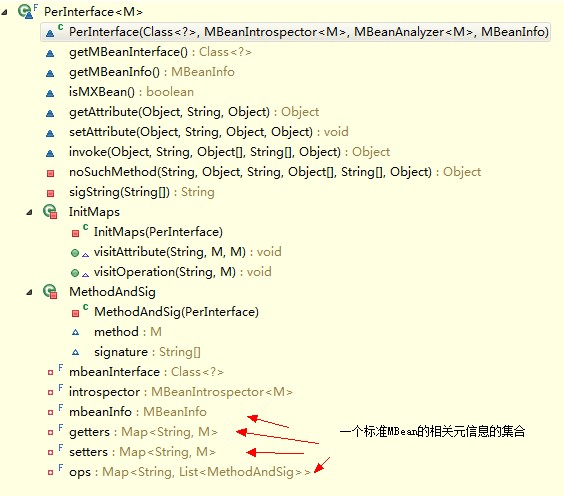
在JMX內省一個MBean的時候,代表了MBean實現的MBean接口的行為。其中的屬性getters代表了MBean接口的getXXX方法,setters代表了MBean接口的setXXX方法,ops代表了MBean的其他方法。MBean接口中的getXXX()和setXXX()方法,在標準MBean中代表了一個屬性的讀和寫,而其他的方法名,則代表著一個操作。MBeanServer調用的方式是不一樣的,前者調用getAttbute(...)和setAttbute(...),而后者是調用invoke(...);
圖:PerInterface結構在JMX內省一個MBean的時候,代表了MBean實現的MBean接口的行為。其中的屬性getters代表了MBean接口的getXXX方法,setters代表了MBean接口的setXXX方法,ops代表了MBean的其他方法。MBean接口中的getXXX()和setXXX()方法,在標準MBean中代表了一個屬性的讀和寫,而其他的方法名,則代表著一個操作。MBeanServer調用的方式是不一樣的,前者調用getAttbute(...)和setAttbute(...),而后者是調用invoke(...);

MBeanInfo、MBeanAttributeInfo、MBeanConstructorInfo、MBeanNotificationInfo、MBeanOperationInfo:
這些類構成了MBean的所有信息。JMX利用Introspection機制分析MBean的數據,得到此MBean的元數據(i.e. 描述一個方法、屬性的名稱、類型、返回值等)。
MBeanAttributeInfo用于存放屬性相關的元數據,MBeanConstructorInfo用于存放跟構造器相關的元數據,MBeanOperationInfo用于存放操作相關的元數據,MBeanNotificationInfo用于存放JMX消息(事件)相關的元數據。MBeanInfo就是存放所有的這些元數新,JMX管理系統如果想知道一個MBean能管理的屬性或者能進行什么用的操作,那么都可以從MBeanInfo中獲得信息。
圖:MBeanInfo構成
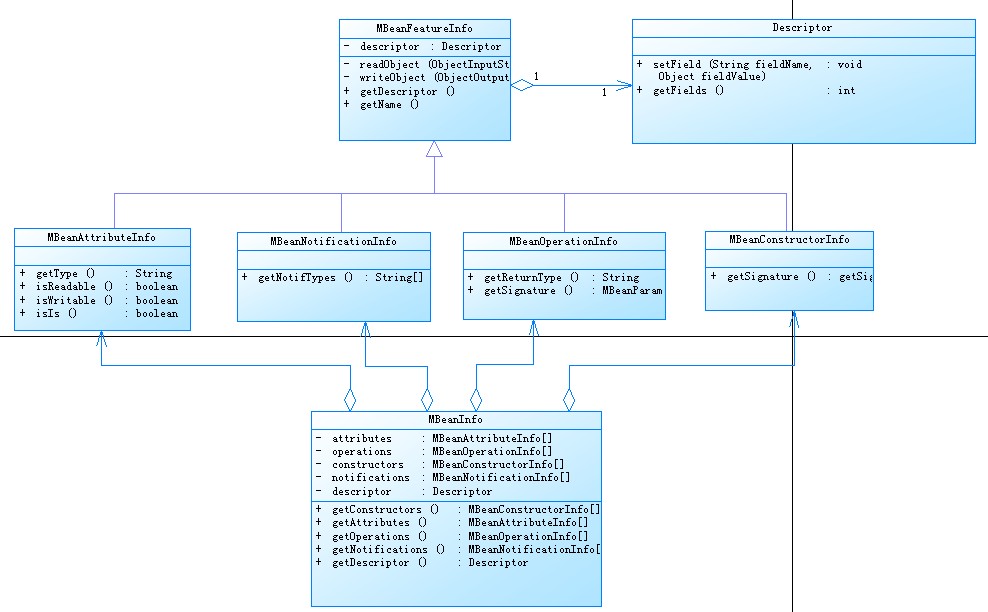
圖:消息機制的結構
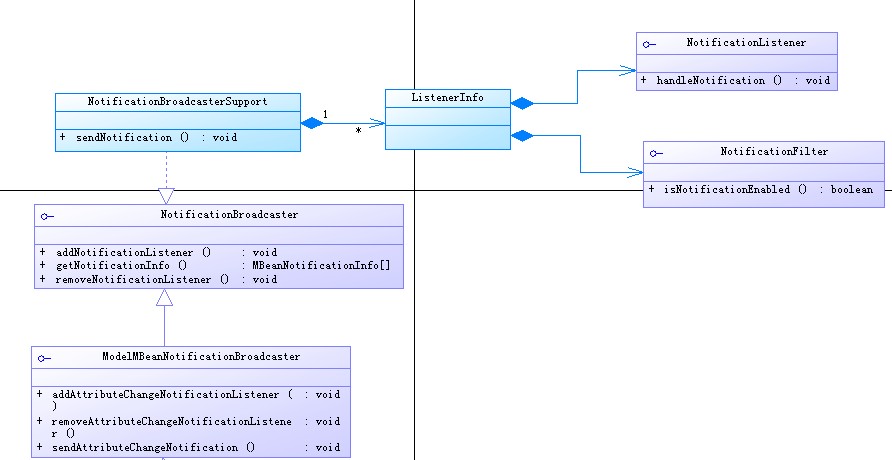
圖:Dynamic、MBeanSupport、StandardMBeanSupport、MXBeanSupport關系圖(列出部分屬性、接口)
總結:標準MBean按照一定編程規則(i.e. getXXX(),setXXX()),把需要管理的標準MBean的屬性和操作,加入到接口的方法中,然后標準MBean實現這個接口,這樣當標準MBean注冊到MBeanServer中后,MBeanServer就可以管理此MBean了。標準MBean在于想要新增一個管理的屬性或操作,都要先在接口中先新增一個方法,然后實現。
DynamicMBean
JMX管理的MBean除了標準MBean外,還可以是DynamicMBean。只要我們實現此接口,就可以被JMX Server管理。
例子:
測試此MBean請看JmxTest類中的test2DynamicMBean()。
當實現一個DynamicMBean,我們需要寫的代碼量是非常多的,MBeanInfo的信息,需要自己編碼,而且對于MBeanServer操作MBean的方法,也得自己重載實現。在動態MBean中,MBeanInfo里面的信息,主要用來展示的,具體的對DynamicMBean的操作是自己實現的。DynamicMBean的優點是對于邏輯控制是可以很靈活的。而不像標準MBean一樣,所有的操作或屬性需要在MBean接口中定義。在jdk中JMX實現DynamicMBean的流程是非常簡單的,Jmx server對于DynamicMBean的操作也是非常簡單的,相對于標準MBean,注冊的時候少了內省的步驟;其他的操作跟標準MBean一樣,只是對于getAttribute(...),setAttribute(...),invoke(...)等一些的操作都是需要自己來實現的。
ModelMBean
然而,普通的動態 Bean通常缺乏一些管理系統所需要的支持:比如持久化MBean的狀態、日志記錄、緩存等等。如果讓用戶去一一實現這些功能確實是件枯燥無聊的工作。為了減輕用戶的負擔,JMX提供商都會提供不同的 ModelBean實現。其中有一個接口是 Java 規范中規定所有廠商必須實現的:
這里,我們以 RequiredModelBean 為例討論 ModelBean。
例子:
使用ModelMBean中,有兩步很重要,第一步設置動態MBean元數據:setModelMBeanInfo(...),MBeanServer會利用這些元數據管理MBean。第二步設置ModelMBean需要管理的對象:setManagerdResourece(...),第一步的元數據其實也就是被管理對象的元數據。這二步都是可以在運行時候動態的配置的,對于ModelMBeanInfo和Resource等相關信息可以在xml文件中進行配置。所以對于ModelMBean的實現,可以很好的利用xml等工具。
測試此MBean請看JmxTest類中的test3RequiredModelMBean()方法。
代碼:RequiredModelMBean.setAttribute(...)的執行分析
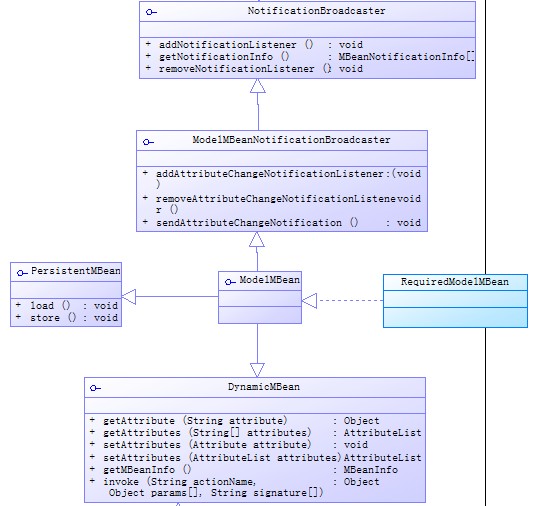
在ModelMBean中一些重要的類:
圖:ModelMBean的結構圖
ModelMBeanInfo、ModelMBeanAttributeInfo、ModelMBeanConstructorInfo、ModelMBeanNotificationInfo、ModelMBeanOperationInfo:
這些類跟DynamicMBean里面介紹的類很相似,這里的ModelXXX都是XXX的子類。而且構成也跟他們的父類是一樣的,子類只是擴展了一些信息。
RequiredModelMBean:
RequiredModelMBean實現了ModelMBean其實實現了DynamicMBean,其實它也是一個動態的MBean,規范中說明對于使用ModelMBean,第三方供應商都必須實現RequiredMoelMBean。
MBeanAttributeInfo用于存放屬性相關的元數據,MBeanConstructorInfo用于存放跟構造器相關的元數據,MBeanOperationInfo用于存放操作相關的元數據,MBeanNotificationInfo用于存放JMX消息(事件)相關的元數據。MBeanInfo就是存放所有的這些元數新,JMX管理系統如果想知道一個MBean能管理的屬性或者能進行什么用的操作,那么都可以從MBeanInfo中獲得信息。
圖:MBeanInfo構成

NotificationBroadcasterSupport、NotificationListener、NotificationFilter、NotificationBroadcaster:
這些類就是提供MBean的消息機制。給予一個MBean發送消息,過濾消息、監聽消息,執行消息等。一個MBean需要消息功能的話,就需要實現以后這些類。圖:消息機制的結構

Introspector、MBeanIntrospector:
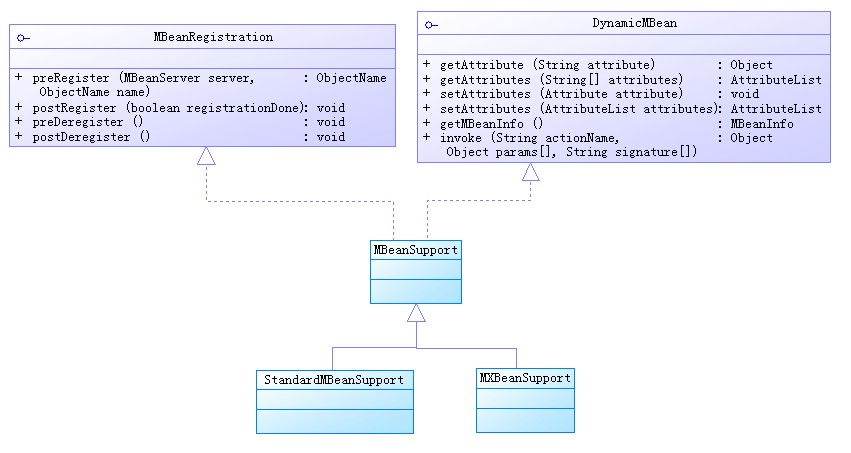
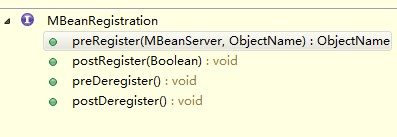
JMX用這兩個類進行內省,即通過他們能分析MBean的所有屬性、方法,然后進行封裝、轉化、存儲等,轉化成我們需要的數據結構MBeanRegistration :
用于一個MBean在注冊前后,或者注銷前后,做一些邏輯操作
圖:MBeanRegistration結構圖
Dynamic、MBeanSupport、StandardMBeanSupport、MXBeanSupport:
即使MBean是標準形式的,但是JMX實現中,還是會生成一個動態的MBean,即StandardMBeanSupport,來封裝標準MBean。用于一個MBean在注冊前后,或者注銷前后,做一些邏輯操作
圖:MBeanRegistration結構圖

Dynamic、MBeanSupport、StandardMBeanSupport、MXBeanSupport:
圖:Dynamic、MBeanSupport、StandardMBeanSupport、MXBeanSupport關系圖(列出部分屬性、接口)

總結:標準MBean按照一定編程規則(i.e. getXXX(),setXXX()),把需要管理的標準MBean的屬性和操作,加入到接口的方法中,然后標準MBean實現這個接口,這樣當標準MBean注冊到MBeanServer中后,MBeanServer就可以管理此MBean了。標準MBean在于想要新增一個管理的屬性或操作,都要先在接口中先新增一個方法,然后實現。
DynamicMBean
JMX管理的MBean除了標準MBean外,還可以是DynamicMBean。只要我們實現此接口,就可以被JMX Server管理。
例子:
1 package test.jmx;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
4
5 import javax.management.Attribute;
6 import javax.management.AttributeList;
7 import javax.management.AttributeNotFoundException;
8 import javax.management.DynamicMBean;
9 import javax.management.InvalidAttributeValueException;
10 import javax.management.MBeanAttributeInfo;
11 import javax.management.MBeanException;
12 import javax.management.MBeanInfo;
13 import javax.management.MBeanOperationInfo;
14 import javax.management.ReflectionException;
15
16 public class HelloWorldDynamic implements DynamicMBean {
17 public String hello;
18
19
20 public HelloWorldDynamic() {
21 this.hello = "Hello World! I am a Dynamic MBean";
22 }
23
24 public HelloWorldDynamic(String hello) {
25 this.hello = hello;
26 }
27
28 public String getHello() {
29 return hello;
30 }
31
32 public Object getInstance() {
33 return new Object();
34 }
35
36 public void setHello(String hello) {
37 this.hello = hello;
38 }
39
40 @Override
41 public Object getAttribute(String attribute)
42 throws AttributeNotFoundException, MBeanException,
43 ReflectionException {
44 //設置getAttribute的執行邏輯
45 if("getInstance".equals(attribute)){
46 return getInstance();
47 }
48
49 return null;
50 }
51
52 @Override
53 public AttributeList getAttributes(String[] attributes) {
54 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
55 return null;
56 }
57
58 MBeanInfo info = null;
59 @Override
60 public MBeanInfo getMBeanInfo() {
61 try {
62 Class cls = this.getClass();
63 // 用反射獲得 "getHello" 屬性的讀方法
64 //DynamicMBean中,
65 Method readMethod = cls.getMethod("getHello", new Class[0]);
66 MBeanAttributeInfo attribute = new MBeanAttributeInfo("gh",
67 " the first attribute ", readMethod, null);
68 //執行java類的method需要的一些元數據,由MBeanOperationInfo提供
69 MBeanOperationInfo operation = new MBeanOperationInfo(
70 " the first operation ", cls.getMethod("getInstance", null));
71 info = new MBeanInfo(cls.getName(), " this is a dynamic MBean ",
72 new MBeanAttributeInfo[] { attribute }, null,
73 new MBeanOperationInfo[] { operation }, null);
74 } catch (Exception e) {
75 System.out.println(e);
76 }
77 return info;
78 }
79
80 @Override
81 public Object invoke(String actionName, Object[] params, String[] signature)
82 throws MBeanException, ReflectionException {
83 System.out.println(" the HelloWorldDynamic's method invoke ");
84 return null;
85 }
86
87 @Override
88 public void setAttribute(Attribute attribute)
89 throws AttributeNotFoundException, InvalidAttributeValueException,
90 MBeanException, ReflectionException {
91
92 }
93
94 @Override
95 public AttributeList setAttributes(AttributeList attributes) {
96 return null;
97 }
98 }
99
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
4
5 import javax.management.Attribute;
6 import javax.management.AttributeList;
7 import javax.management.AttributeNotFoundException;
8 import javax.management.DynamicMBean;
9 import javax.management.InvalidAttributeValueException;
10 import javax.management.MBeanAttributeInfo;
11 import javax.management.MBeanException;
12 import javax.management.MBeanInfo;
13 import javax.management.MBeanOperationInfo;
14 import javax.management.ReflectionException;
15
16 public class HelloWorldDynamic implements DynamicMBean {
17 public String hello;
18
19
20 public HelloWorldDynamic() {
21 this.hello = "Hello World! I am a Dynamic MBean";
22 }
23
24 public HelloWorldDynamic(String hello) {
25 this.hello = hello;
26 }
27
28 public String getHello() {
29 return hello;
30 }
31
32 public Object getInstance() {
33 return new Object();
34 }
35
36 public void setHello(String hello) {
37 this.hello = hello;
38 }
39
40 @Override
41 public Object getAttribute(String attribute)
42 throws AttributeNotFoundException, MBeanException,
43 ReflectionException {
44 //設置getAttribute的執行邏輯
45 if("getInstance".equals(attribute)){
46 return getInstance();
47 }
48
49 return null;
50 }
51
52 @Override
53 public AttributeList getAttributes(String[] attributes) {
54 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
55 return null;
56 }
57
58 MBeanInfo info = null;
59 @Override
60 public MBeanInfo getMBeanInfo() {
61 try {
62 Class cls = this.getClass();
63 // 用反射獲得 "getHello" 屬性的讀方法
64 //DynamicMBean中,
65 Method readMethod = cls.getMethod("getHello", new Class[0]);
66 MBeanAttributeInfo attribute = new MBeanAttributeInfo("gh",
67 " the first attribute ", readMethod, null);
68 //執行java類的method需要的一些元數據,由MBeanOperationInfo提供
69 MBeanOperationInfo operation = new MBeanOperationInfo(
70 " the first operation ", cls.getMethod("getInstance", null));
71 info = new MBeanInfo(cls.getName(), " this is a dynamic MBean ",
72 new MBeanAttributeInfo[] { attribute }, null,
73 new MBeanOperationInfo[] { operation }, null);
74 } catch (Exception e) {
75 System.out.println(e);
76 }
77 return info;
78 }
79
80 @Override
81 public Object invoke(String actionName, Object[] params, String[] signature)
82 throws MBeanException, ReflectionException {
83 System.out.println(" the HelloWorldDynamic's method invoke ");
84 return null;
85 }
86
87 @Override
88 public void setAttribute(Attribute attribute)
89 throws AttributeNotFoundException, InvalidAttributeValueException,
90 MBeanException, ReflectionException {
91
92 }
93
94 @Override
95 public AttributeList setAttributes(AttributeList attributes) {
96 return null;
97 }
98 }
99
測試此MBean請看JmxTest類中的test2DynamicMBean()。
當實現一個DynamicMBean,我們需要寫的代碼量是非常多的,MBeanInfo的信息,需要自己編碼,而且對于MBeanServer操作MBean的方法,也得自己重載實現。在動態MBean中,MBeanInfo里面的信息,主要用來展示的,具體的對DynamicMBean的操作是自己實現的。DynamicMBean的優點是對于邏輯控制是可以很靈活的。而不像標準MBean一樣,所有的操作或屬性需要在MBean接口中定義。在jdk中JMX實現DynamicMBean的流程是非常簡單的,Jmx server對于DynamicMBean的操作也是非常簡單的,相對于標準MBean,注冊的時候少了內省的步驟;其他的操作跟標準MBean一樣,只是對于getAttribute(...),setAttribute(...),invoke(...)等一些的操作都是需要自己來實現的。
ModelMBean
然而,普通的動態 Bean通常缺乏一些管理系統所需要的支持:比如持久化MBean的狀態、日志記錄、緩存等等。如果讓用戶去一一實現這些功能確實是件枯燥無聊的工作。為了減輕用戶的負擔,JMX提供商都會提供不同的 ModelBean實現。其中有一個接口是 Java 規范中規定所有廠商必須實現的:
javax.management.modelmbean.RequiredModelBean。通過配置Descriptor信息,我們可以定制這個ModelBean,指定哪些 MBean狀態需要記入日志、如何記錄以及是否緩存某些屬性、緩存多久等等。對于Descriptor,在MBean中相當于附帶的一些信息,這些信息在MBean實現中可以作為一種策略,以此增強MBean的功能。動態MBean以及標準MBean的MBeanInfo都已經包括了Descriptor,但是在邏輯實現中沒用到此對象。在ModelMBean中,Descriptor作用非常大,持久化、日志、緩存等的策略等相關信息都是在Descriptor中定義的。開發人員可以增加相關屬性到Descriptor中,來對應用功能進行擴展 這里,我們以 RequiredModelBean 為例討論 ModelBean。
例子:
1 package test.jmx;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
4
5 import javax.management.Descriptor;
6 import javax.management.InstanceNotFoundException;
7 import javax.management.MBeanException;
8 import javax.management.MBeanOperationInfo;
9 import javax.management.MBeanParameterInfo;
10 import javax.management.RuntimeOperationsException;
11 import javax.management.modelmbean.DescriptorSupport;
12 import javax.management.modelmbean.InvalidTargetObjectTypeException;
13 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanAttributeInfo;
14 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanConstructorInfo;
15 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanInfo;
16 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanInfoSupport;
17 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanOperationInfo;
18 import javax.management.modelmbean.RequiredModelMBean;
19
20 public class HelloWorldModelMBean extends RequiredModelMBean {
21
22 public HelloWorldModelMBean() throws Exception{}
23
24 public static RequiredModelMBean createModelBean()
25 throws RuntimeOperationsException, MBeanException,
26 InstanceNotFoundException, InvalidTargetObjectTypeException {
27 // 模型MBean信息
28 ModelMBeanInfo info = buildModelMBeanInfo();
29 // 模型MBean
30 RequiredModelMBean modelMBean = new RequiredModelMBean(info);
31 //目前只支持ObjectReference,將來可能會支持ObjectReference", "Handle", "IOR", "EJBHandle",
32 // or "RMIReference,
33 //RMIReference從名字上可以看出,如果支持的話,那么以后就可以支持遠程MBean引用
34 modelMBean.setManagedResource(new HelloWorld(), "ObjectReference");
35 return modelMBean;
36 }
37
38 protected static ModelMBeanInfo buildModelMBeanInfo() throws RuntimeOperationsException, MBeanException {
39 // --
40 // attributes
41 // ------------------------------------------------------------------
42 ModelMBeanAttributeInfo[] attributes = new ModelMBeanAttributeInfo[1];
43
44 // 設置屬性
45 Descriptor nameDesc = new DescriptorSupport();
46 nameDesc.setField("name", "hello");
47 nameDesc.setField("value", "----dfdf---");
48 nameDesc.setField("displayName", "myname");
49 nameDesc.setField("setMethod", "setHello");
50 nameDesc.setField("getMethod", "getHello");
51 nameDesc.setField("descriptorType", "attribute");
52 attributes[0] = new ModelMBeanAttributeInfo("hello", "java.lang.String",
53 "name say hello to", true, true, false, nameDesc);
54
55 // --
56 // operations
57 // -------------------------------------------------------------------
58 ModelMBeanOperationInfo[] operations = new ModelMBeanOperationInfo[2];
59 String className = HelloWorld.class.getName();
60
61 // getName method
62 Descriptor getDesc = new DescriptorSupport(new String[] {
63 "name=getHello", "descriptorType=operation",
64 "class=" + className, "role=operation" });
65 operations[0] = new ModelMBeanOperationInfo("getHello", "get hello ",
",
66 null, null, MBeanOperationInfo.ACTION, getDesc);
67
68 Descriptor setDesc = new DescriptorSupport(new String[] {
69 "name=setHello", "descriptorType=operation",
70 "class=" + className, "role=operation" });
71 operations[1] = new ModelMBeanOperationInfo("setHello", "set hello ",
",
72 new MBeanParameterInfo[]{new MBeanParameterInfo("a","java.lang.String"," a method's arg ")},
73 null, MBeanOperationInfo.ACTION, setDesc);
74
75 // constructors
76 ModelMBeanConstructorInfo[] constructors = new ModelMBeanConstructorInfo[1];
77 Constructor<?>[] ctors = HelloWorld.class.getConstructors();
78
79
80 constructors[0] = new ModelMBeanConstructorInfo("default constructor",
81 ctors[0], null);
82
83 // ModelMBeanInfo
84 ModelMBeanInfo mmbeanInfo = new ModelMBeanInfoSupport(className,
85 "Simple implementation of model bean.", attributes, null,
86 operations/*null*/, null, null);
87
88 //設置一個Descriptor策略,這樣RequiredModelMBean改變 Attribute值得時候會記錄日志
89 //當然RequiredModelMBean還需要addAttributeChangeNotificationListener,注冊一個監聽器
90 Descriptor globalDescriptor = new DescriptorSupport(new String[]{
91 "name=HelloWorldModelMBean","displayName=globaldescriptor",
92 "descriptorType=mbean","log=T","logfile=hello.log"
93 });
94 mmbeanInfo.setMBeanDescriptor(globalDescriptor);
95
96 return mmbeanInfo;
97 }
98
99 }
100
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
4
5 import javax.management.Descriptor;
6 import javax.management.InstanceNotFoundException;
7 import javax.management.MBeanException;
8 import javax.management.MBeanOperationInfo;
9 import javax.management.MBeanParameterInfo;
10 import javax.management.RuntimeOperationsException;
11 import javax.management.modelmbean.DescriptorSupport;
12 import javax.management.modelmbean.InvalidTargetObjectTypeException;
13 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanAttributeInfo;
14 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanConstructorInfo;
15 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanInfo;
16 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanInfoSupport;
17 import javax.management.modelmbean.ModelMBeanOperationInfo;
18 import javax.management.modelmbean.RequiredModelMBean;
19
20 public class HelloWorldModelMBean extends RequiredModelMBean {
21
22 public HelloWorldModelMBean() throws Exception{}
23
24 public static RequiredModelMBean createModelBean()
25 throws RuntimeOperationsException, MBeanException,
26 InstanceNotFoundException, InvalidTargetObjectTypeException {
27 // 模型MBean信息
28 ModelMBeanInfo info = buildModelMBeanInfo();
29 // 模型MBean
30 RequiredModelMBean modelMBean = new RequiredModelMBean(info);
31 //目前只支持ObjectReference,將來可能會支持ObjectReference", "Handle", "IOR", "EJBHandle",
32 // or "RMIReference,
33 //RMIReference從名字上可以看出,如果支持的話,那么以后就可以支持遠程MBean引用
34 modelMBean.setManagedResource(new HelloWorld(), "ObjectReference");
35 return modelMBean;
36 }
37
38 protected static ModelMBeanInfo buildModelMBeanInfo() throws RuntimeOperationsException, MBeanException {
39 // --
40 // attributes
41 // ------------------------------------------------------------------
42 ModelMBeanAttributeInfo[] attributes = new ModelMBeanAttributeInfo[1];
43
44 // 設置屬性
45 Descriptor nameDesc = new DescriptorSupport();
46 nameDesc.setField("name", "hello");
47 nameDesc.setField("value", "----dfdf---");
48 nameDesc.setField("displayName", "myname");
49 nameDesc.setField("setMethod", "setHello");
50 nameDesc.setField("getMethod", "getHello");
51 nameDesc.setField("descriptorType", "attribute");
52 attributes[0] = new ModelMBeanAttributeInfo("hello", "java.lang.String",
53 "name say hello to", true, true, false, nameDesc);
54
55 // --
56 // operations
57 // -------------------------------------------------------------------
58 ModelMBeanOperationInfo[] operations = new ModelMBeanOperationInfo[2];
59 String className = HelloWorld.class.getName();
60
61 // getName method
62 Descriptor getDesc = new DescriptorSupport(new String[] {
63 "name=getHello", "descriptorType=operation",
64 "class=" + className, "role=operation" });
65 operations[0] = new ModelMBeanOperationInfo("getHello", "get hello
 ",
", 66 null, null, MBeanOperationInfo.ACTION, getDesc);
67
68 Descriptor setDesc = new DescriptorSupport(new String[] {
69 "name=setHello", "descriptorType=operation",
70 "class=" + className, "role=operation" });
71 operations[1] = new ModelMBeanOperationInfo("setHello", "set hello
 ",
", 72 new MBeanParameterInfo[]{new MBeanParameterInfo("a","java.lang.String"," a method's arg ")},
73 null, MBeanOperationInfo.ACTION, setDesc);
74
75 // constructors
76 ModelMBeanConstructorInfo[] constructors = new ModelMBeanConstructorInfo[1];
77 Constructor<?>[] ctors = HelloWorld.class.getConstructors();
78
79
80 constructors[0] = new ModelMBeanConstructorInfo("default constructor",
81 ctors[0], null);
82
83 // ModelMBeanInfo
84 ModelMBeanInfo mmbeanInfo = new ModelMBeanInfoSupport(className,
85 "Simple implementation of model bean.", attributes, null,
86 operations/*null*/, null, null);
87
88 //設置一個Descriptor策略,這樣RequiredModelMBean改變 Attribute值得時候會記錄日志
89 //當然RequiredModelMBean還需要addAttributeChangeNotificationListener,注冊一個監聽器
90 Descriptor globalDescriptor = new DescriptorSupport(new String[]{
91 "name=HelloWorldModelMBean","displayName=globaldescriptor",
92 "descriptorType=mbean","log=T","logfile=hello.log"
93 });
94 mmbeanInfo.setMBeanDescriptor(globalDescriptor);
95
96 return mmbeanInfo;
97 }
98
99 }
100
使用ModelMBean中,有兩步很重要,第一步設置動態MBean元數據:setModelMBeanInfo(...),MBeanServer會利用這些元數據管理MBean。第二步設置ModelMBean需要管理的對象:setManagerdResourece(...),第一步的元數據其實也就是被管理對象的元數據。這二步都是可以在運行時候動態的配置的,對于ModelMBeanInfo和Resource等相關信息可以在xml文件中進行配置。所以對于ModelMBean的實現,可以很好的利用xml等工具。
測試此MBean請看JmxTest類中的test3RequiredModelMBean()方法。
代碼:RequiredModelMBean.setAttribute(...)的執行分析
1 JmxMBeanServer:
2 public void setAttribute(ObjectName name, Attribute attribute)
3 throws InstanceNotFoundException, AttributeNotFoundException,
4 InvalidAttributeValueException, MBeanException,
5 ReflectionException {
6
7 mbsInterceptor.setAttribute(cloneObjectName(name),
8 cloneAttribute(attribute));
9 }
10
11 DefaultMBeanServerInterceptor:
12 public void setAttribute(ObjectName name, Attribute attribute)
13 throws InstanceNotFoundException, AttributeNotFoundException,
14 InvalidAttributeValueException, MBeanException,
15 ReflectionException {
16 .
.
17 //得到動態MBean
18 DynamicMBean instance = getMBean(name);
19 instance.setAttribute(attribute);
20 .
.
21 }
22
23 RequiredModelMBean:
24 public void setAttribute(Attribute attribute)
25 throws AttributeNotFoundException, InvalidAttributeValueException,
26 MBeanException, ReflectionException
27 .
.
28 //modelMBeanInfo就是最開始創建的信息,得到一個AttributeInfo
29 ModelMBeanAttributeInfo attrInfo =
30 modelMBeanInfo.getAttribute(attrName);
31 .
.
32 Descriptor mmbDesc = modelMBeanInfo.getMBeanDescriptor();
33 Descriptor attrDescr = attrInfo.getDescriptor();
34 .
.
35 //得到set方法名
36 String attrSetMethod = (String)
37 (attrDescr.getFieldValue("setMethod"));
38 //得到get方法名
39 String attrGetMethod = (String)
40 (attrDescr.getFieldValue("getMethod"));
41 .
.
42 //更具必要參數,執行set方法。改變被管理資源的值
43 invoke(attrSetMethod,
44 (new Object[] {attrValue}),
45 (new String[] {attrType}) );
46 .
.
47 //發出Attribute改變的事件
48 sendAttributeChangeNotification(oldAttr,attribute);
49 .
.
50 }
51 public void sendAttributeChangeNotification(AttributeChangeNotification
52 ntfyObj)
53 throws MBeanException, RuntimeOperationsException {
54 .
.
55 // log notification if specified in descriptor
56 Descriptor ntfyDesc =
57 modelMBeanInfo.getDescriptor(ntfyObj.getType(),"notification");
58 //這個就是在例子中設置的globalDescriptor
59 Descriptor mmbDesc = modelMBeanInfo.getMBeanDescriptor();
60 .
.
61 if (mmbDesc != null) {
62 //這些值都是我們設置在globalDescriptor的策略,也就是具體 //需要JMX的實現這需要各自實現的策略
63 logging = (String) mmbDesc.getFieldValue("log");
64 if ((logging != null) &&
65 ( logging.equalsIgnoreCase("t") ||
66 logging.equalsIgnoreCase("true") )) {
67 logfile = (String) mmbDesc.getFieldValue("logfile");
68
69 if (logfile != null) {
70 try {
71 //把相關信息寫入日志
72 writeToLog(logfile,"LogMsg: " +
73 ((new Date(ntfyObj.getTimeStamp())).toString())+
74 " " + ntfyObj.getType() + " " +
75 ntfyObj.getMessage() +
76 " Name = " + ntfyObj.getAttributeName() +
77 " Old value = " + oldv +
78 " New value = " + newv);
79 }
80

81 }
82
2 public void setAttribute(ObjectName name, Attribute attribute)
3 throws InstanceNotFoundException, AttributeNotFoundException,
4 InvalidAttributeValueException, MBeanException,
5 ReflectionException {
6
7 mbsInterceptor.setAttribute(cloneObjectName(name),
8 cloneAttribute(attribute));
9 }
10
11 DefaultMBeanServerInterceptor:
12 public void setAttribute(ObjectName name, Attribute attribute)
13 throws InstanceNotFoundException, AttributeNotFoundException,
14 InvalidAttributeValueException, MBeanException,
15 ReflectionException {
16
 .
.17 //得到動態MBean
18 DynamicMBean instance = getMBean(name);
19 instance.setAttribute(attribute);
20
 .
.21 }
22
23 RequiredModelMBean:
24 public void setAttribute(Attribute attribute)
25 throws AttributeNotFoundException, InvalidAttributeValueException,
26 MBeanException, ReflectionException
27
 .
.28 //modelMBeanInfo就是最開始創建的信息,得到一個AttributeInfo
29 ModelMBeanAttributeInfo attrInfo =
30 modelMBeanInfo.getAttribute(attrName);
31
 .
.32 Descriptor mmbDesc = modelMBeanInfo.getMBeanDescriptor();
33 Descriptor attrDescr = attrInfo.getDescriptor();
34
 .
.35 //得到set方法名
36 String attrSetMethod = (String)
37 (attrDescr.getFieldValue("setMethod"));
38 //得到get方法名
39 String attrGetMethod = (String)
40 (attrDescr.getFieldValue("getMethod"));
41
 .
.42 //更具必要參數,執行set方法。改變被管理資源的值
43 invoke(attrSetMethod,
44 (new Object[] {attrValue}),
45 (new String[] {attrType}) );
46
 .
.47 //發出Attribute改變的事件
48 sendAttributeChangeNotification(oldAttr,attribute);
49
 .
. 50 }
51 public void sendAttributeChangeNotification(AttributeChangeNotification
52 ntfyObj)
53 throws MBeanException, RuntimeOperationsException {
54
 .
.55 // log notification if specified in descriptor
56 Descriptor ntfyDesc =
57 modelMBeanInfo.getDescriptor(ntfyObj.getType(),"notification");
58 //這個就是在例子中設置的globalDescriptor
59 Descriptor mmbDesc = modelMBeanInfo.getMBeanDescriptor();
60
 .
.61 if (mmbDesc != null) {
62 //這些值都是我們設置在globalDescriptor的策略,也就是具體 //需要JMX的實現這需要各自實現的策略
63 logging = (String) mmbDesc.getFieldValue("log");
64 if ((logging != null) &&
65 ( logging.equalsIgnoreCase("t") ||
66 logging.equalsIgnoreCase("true") )) {
67 logfile = (String) mmbDesc.getFieldValue("logfile");
68
69 if (logfile != null) {
70 try {
71 //把相關信息寫入日志
72 writeToLog(logfile,"LogMsg: " +
73 ((new Date(ntfyObj.getTimeStamp())).toString())+
74 " " + ntfyObj.getType() + " " +
75 ntfyObj.getMessage() +
76 " Name = " + ntfyObj.getAttributeName() +
77 " Old value = " + oldv +
78 " New value = " + newv);
79 }
80


81 }
82
在ModelMBean中一些重要的類:
ModelMBean:
實現了DynamicMBean,說明了ModelMBean也是動態MBean的一類,PersistentMBean持久化功能接口,還實現了消息機制。圖:ModelMBean的結構圖

ModelMBeanInfo、ModelMBeanAttributeInfo、ModelMBeanConstructorInfo、ModelMBeanNotificationInfo、ModelMBeanOperationInfo:
這些類跟DynamicMBean里面介紹的類很相似,這里的ModelXXX都是XXX的子類。而且構成也跟他們的父類是一樣的,子類只是擴展了一些信息。
RequiredModelMBean:
RequiredModelMBean實現了ModelMBean其實實現了DynamicMBean,其實它也是一個動態的MBean,規范中說明對于使用ModelMBean,第三方供應商都必須實現RequiredMoelMBean。
參考:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-jse63/index.html(Java SE 6 新特性: JMX 與系統管理)posted on 2012-09-24 08:33 heavensay 閱讀(7007) 評論(0) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類: JMX


