創(chuàng)建好ApiDemos項(xiàng)目以后,首先在模擬器上運(yùn)行該程序,可以看到主界面是一個列表。單擊列表中一個欄目后還有若干級列表,最終是一個Activity,展示了其API的一個特性。API Demos全面展示了系統(tǒng)的功能,包括界面、控件、圖像處理和媒體處理等。
 <activity android:name=".app.HelloWorld" android:label="@string/activity_hello_world">
<activity android:name=".app.HelloWorld" android:label="@string/activity_hello_world">2
 <intent-filter>
<intent-filter>3
 <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />4
 <category android:name="android.intent.category.SAMPLE_CODE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.SAMPLE_CODE" />5
 </intent-filter>
</intent-filter>6
 </activity>
</activity> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.android.apis">
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.android.apis">2


3
 </manifest>
</manifest>可以知道該類在com.example.android.apis下,同時我們可以看到很多Activity都帶有
 <intent-filter>
<intent-filter>2
 <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />3
 <category android:name="android.intent.category.SAMPLE_CODE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.SAMPLE_CODE" />4
 </intent-filter>
</intent-filter>然后我們可以找到com.example.android.apis包下的ApiDemos類,
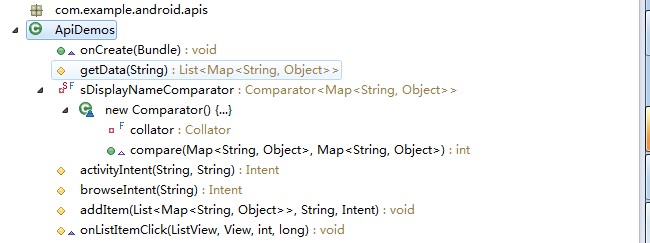
該類繼承了ListActivity,主要用來列出ApiDemos中的200多個實(shí)例,實(shí)例采取分類層次顯示。
ListActivity是一個把列表和列表內(nèi)容綁定的Activity,在用戶單擊這些列表時,響應(yīng)用戶操作。這就是說,列表只是一個框架,列表內(nèi)容是開發(fā)者指定的,列表可以和不同的數(shù)據(jù)源進(jìn)行綁定。就像這個程序的各級菜單,列表形式都一樣,只是每一級菜單的數(shù)據(jù)源不同。現(xiàn)在我們可以理解APIDemos的主要工作了:在onCreate中獲取每一級菜單的列表內(nèi)容,并和列表綁定;在onListItemClick中實(shí)現(xiàn)單擊該項(xiàng)目的響應(yīng),響應(yīng)是以Intent方法實(shí)現(xiàn)的,通過Intent來啟動另外的Activity。
在ApiDemos 的 onCreate()方法:
 @Override
@Override2
 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {3
 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);4

5
 Intent intent = getIntent();
Intent intent = getIntent();6
 String path = intent.getStringExtra("com.example.android.apis.Path");
String path = intent.getStringExtra("com.example.android.apis.Path");7

8
 if (path == null) {
if (path == null) {9
 path = "";
path = "";10
 }
}11

12
 setListAdapter(new SimpleAdapter(this, getData(path),
setListAdapter(new SimpleAdapter(this, getData(path),13
 android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, new String[] { "title" },
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, new String[] { "title" },14
 new int[] { android.R.id.text1 }));
new int[] { android.R.id.text1 }));15
 getListView().setTextFilterEnabled(true);
getListView().setTextFilterEnabled(true);16
 }
} <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>2
 <!-- Copyright (C) 2006 The Android Open Source Project
<!-- Copyright (C) 2006 The Android Open Source Project3

4
 Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");5
 you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.6
 You may obtain a copy of the License at
You may obtain a copy of the License at7

8
 http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.09

10
 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software11
 distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,12
 WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.13
 See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and14
 limitations under the License.
limitations under the License.15
 -->
-->16

17
 <TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"18
 android:id="@android:id/text1"
android:id="@android:id/text1"19
 android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"20
 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"21
 android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceListItemSmall"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceListItemSmall"22
 android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:gravity="center_vertical"23
 android:paddingLeft="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingLeft"
android:paddingLeft="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingLeft"24
 android:paddingRight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingRight"
android:paddingRight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingRight"25
 android:minHeight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeightSmall"
android:minHeight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeightSmall"26
 />
/>可以看到該布局文件僅僅顯示一個TextView,它的id為android.R.id.text11AbsListView.setTextFilterEnabled(true);
這個方法的作用是用來過濾選項(xiàng)的。例如在軟鍵盤上打出一個a,則會過濾掉除了a開頭的所有選項(xiàng)(在模擬器上可以看到效果,在真機(jī)上彈不出軟鍵盤)。
 protected List<Map<String, Object>> getData(String prefix) {
protected List<Map<String, Object>> getData(String prefix) {2
 List<Map<String, Object>> myData = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
List<Map<String, Object>> myData = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();3

4
 Intent mainIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN, null);
Intent mainIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN, null);5
 mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_SAMPLE_CODE);
mainIntent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_SAMPLE_CODE);6

7
 PackageManager pm = getPackageManager();
PackageManager pm = getPackageManager();8
 List<ResolveInfo> list = pm.queryIntentActivities(mainIntent, 0);
List<ResolveInfo> list = pm.queryIntentActivities(mainIntent, 0);9

10
 if (null == list)
if (null == list)11
 return myData;
return myData;12

13
 String[] prefixPath;
String[] prefixPath;14
 String prefixWithSlash = prefix;
String prefixWithSlash = prefix;15

16
 if (prefix.equals("")) {
if (prefix.equals("")) {17
 prefixPath = null;
prefixPath = null;18
 } else {
} else {19
 prefixPath = prefix.split("/");
prefixPath = prefix.split("/");20
 prefixWithSlash = prefix + "/";
prefixWithSlash = prefix + "/";21
 }
}22

23
 int len = list.size();
int len = list.size();24

25
 Map<String, Boolean> entries = new HashMap<String, Boolean>();
Map<String, Boolean> entries = new HashMap<String, Boolean>();26

27
 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {28
 ResolveInfo info = list.get(i);
ResolveInfo info = list.get(i);29
 CharSequence labelSeq = info.loadLabel(pm);
CharSequence labelSeq = info.loadLabel(pm);30
 String label = labelSeq != null
String label = labelSeq != null31
 ? labelSeq.toString()
? labelSeq.toString()32
 : info.activityInfo.name;
: info.activityInfo.name;33

34
 if (prefixWithSlash.length() == 0 || label.startsWith(prefixWithSlash)) {
if (prefixWithSlash.length() == 0 || label.startsWith(prefixWithSlash)) {35

36
 String[] labelPath = label.split("/");
String[] labelPath = label.split("/");37

38
 String nextLabel = prefixPath == null ? labelPath[0] : labelPath[prefixPath.length];
String nextLabel = prefixPath == null ? labelPath[0] : labelPath[prefixPath.length];39

40
 if ((prefixPath != null ? prefixPath.length : 0) == labelPath.length - 1) {
if ((prefixPath != null ? prefixPath.length : 0) == labelPath.length - 1) {41
 addItem(myData, nextLabel, activityIntent(
addItem(myData, nextLabel, activityIntent(42
 info.activityInfo.applicationInfo.packageName,
info.activityInfo.applicationInfo.packageName,43
 info.activityInfo.name));
info.activityInfo.name));44
 } else {
} else {45
 if (entries.get(nextLabel) == null) {
if (entries.get(nextLabel) == null) {46
 addItem(myData, nextLabel, browseIntent(prefix.equals("") ? nextLabel : prefix + "/" + nextLabel));
addItem(myData, nextLabel, browseIntent(prefix.equals("") ? nextLabel : prefix + "/" + nextLabel));47
 entries.put(nextLabel, true);
entries.put(nextLabel, true);48
 }
}49
 }
}50
 }
}51
 }
}52

53
 Collections.sort(myData, sDisplayNameComparator);
Collections.sort(myData, sDisplayNameComparator);54

55
 return myData;
return myData;56
 }
}知道列表的構(gòu)成和響應(yīng)后,我們接下來看看列表是如何被獲取的,獲取列表是在getData方法中,該方法獲取的數(shù)據(jù)作為SimpleAdapter的參數(shù),最終被ListActivity所使用。getData中有若干個重要的對象,如myData是我們需要獲取的菜單列表數(shù)據(jù);prefix是當(dāng)前所處的目錄,如果為空則為根目錄; prefixPath是當(dāng)前目錄的列表,列表中包含了當(dāng)前的每一級目錄的內(nèi)容;list是當(dāng)前可以被執(zhí)行的所有Activity列表。程序是怎么知道當(dāng)前有哪些可以執(zhí)行的Activity的呢?請看下面兩行代碼:
 private final static Comparator<Map<String, Object>> sDisplayNameComparator =
private final static Comparator<Map<String, Object>> sDisplayNameComparator =2
 new Comparator<Map<String, Object>>() {
new Comparator<Map<String, Object>>() {3
 private final Collator collator = Collator.getInstance();
private final Collator collator = Collator.getInstance();4

5
 public int compare(Map<String, Object> map1, Map<String, Object> map2) {
public int compare(Map<String, Object> map1, Map<String, Object> map2) {6
 return collator.compare(map1.get("title"), map2.get("title"));
return collator.compare(map1.get("title"), map2.get("title"));7
 }
}8
 };
};
loadLabel() 查找順序
1、先找activity的Lable, 如果沒有找到則下一步
2、找application的Lable, 如果沒有找到則下一步
3、找activity的name 名字一定會有的
它通過PackageManager 從 AndroidManifest.xml中讀取所以Intent-Filter含有:Intent.ACTION_MAIN和Intent.CATEGORY_SAMPLE_CODE所有Activity信息。前面說過200多個示例根據(jù)其功能分類,比如 Hello World示例它的Label為
App/Activity/Hello World,
表示它的分類為分類App下Activity子類。
getData(String prefix)根據(jù)每個Activity的Label屬性和當(dāng)前層次(prefix)來決定當(dāng)前列表中某項(xiàng)為葉子列表項(xiàng),還是分類列表項(xiàng),如果是葉子列表項(xiàng),則添加為activityIntent,當(dāng)用戶點(diǎn)擊改列表項(xiàng)時則會觸發(fā)該示例。若是分類列表項(xiàng),則添加為browseIntent,browseIntent還是觸發(fā)ApiDemos Activity,但I(xiàn)ntent帶有Extra信息,表示需要顯示改分類下的子類:
 protected Intent activityIntent(String pkg, String componentName) {
protected Intent activityIntent(String pkg, String componentName) {2

3
 Intent result = new Intent();
Intent result = new Intent();4

5
 result.setClassName(pkg, componentName);
result.setClassName(pkg, componentName);6

7
 return result;
return result;8

9
 }
}10

11

此時如果用戶點(diǎn)擊該節(jié)點(diǎn)列表項(xiàng),則會進(jìn)入該分類的下級目錄。
 @Override
@Override2
 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")3
 protected void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
protected void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {4
 Map<String, Object> map = (Map<String, Object>)l.getItemAtPosition(position);
Map<String, Object> map = (Map<String, Object>)l.getItemAtPosition(position);5

6
 Intent intent = (Intent) map.get("intent");
Intent intent = (Intent) map.get("intent");7
 startActivity(intent);
startActivity(intent);8
 }
}此外,ApiDemos還定義了ApiDemosApplication,該類繼承了Application,如果需要在多個Activity共享一些數(shù)據(jù),可以定義在Application中。
 /*
/*2
 * Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project3
 *
*4
 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");5
 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.6
 * You may obtain a copy of the License at
* You may obtain a copy of the License at7
 *
*8
 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.09
 *
*10
 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software11
 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,12
 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.13
 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and14
 * limitations under the License.
* limitations under the License.15
 */
*/16

17
 package com.example.android.apis;
package com.example.android.apis;18

19
 import android.app.Application;
import android.app.Application;20

21
 /**
/**22
 * This is an example of a {@link android.app.Application} class. This can
* This is an example of a {@link android.app.Application} class. This can23
 * be used as a central repository for per-process information about your app;
* be used as a central repository for per-process information about your app;24
 * however it is recommended to use singletons for that instead rather than merge
* however it is recommended to use singletons for that instead rather than merge25
 * all of these globals from across your application into one place here.
* all of these globals from across your application into one place here.26
 *
* 27
 * In this case, we have not defined any specific work for this Application.
* In this case, we have not defined any specific work for this Application.28
 *
* 29
 * See samples/ApiDemos/tests/src/com.example.android.apis/ApiDemosApplicationTests for an example
* See samples/ApiDemos/tests/src/com.example.android.apis/ApiDemosApplicationTests for an example30
 * of how to perform unit tests on an Application object.
* of how to perform unit tests on an Application object.31
 */
*/32
 public class ApiDemosApplication extends Application {
public class ApiDemosApplication extends Application {33
 @Override
@Override34
 public void onCreate() {
public void onCreate() {35
 }
}36
 }
}37

可以看到該類什么都干。
如果使用了自定義的Application,別忘了修改AndroidManifest.xml ,如下:
 <application android:name="ApiDemosApplication"
<application android:name="ApiDemosApplication"2
 android:label="@string/activity_sample_code"
android:label="@string/activity_sample_code"3
 android:icon="@drawable/app_sample_code"
android:icon="@drawable/app_sample_code"4
 android:hardwareAccelerated="true">
android:hardwareAccelerated="true">5



6
 </application>
</application>最后我們看下Shakespeare這個常量類,







