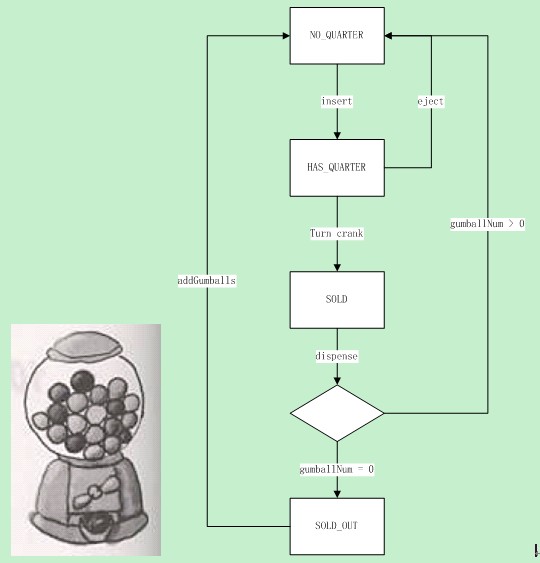
最基本的實現思路如下:用四個整型數表示四種狀態,用四個函數表達四個操作,每次進行操作的時候都要判斷一下是否處于可進行這步操作的狀態,操作完成后,需要更新狀態到下一步。
package javaapplication41;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gm = new GumballMachine();
gm.addGumballsToMachine(2);
gm.insertQuarter();
gm.turnsCrank();
System.out.println("------------------");
gm.insertQuarter();
gm.insertQuarter();
gm.turnsCrank();
gm.ejectQuarter();
gm.turnsCrank();
}
}
class GumballMachine {
final int SOLD_OUT = 0;
final int NO_QUARTER = 1;
final int HAS_QUARTER = 2;
final int SOLD = 3;
int state;
int gumballs = 0;
public GumballMachine() {
state = SOLD_OUT;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("inserting the quarter");
state = HAS_QUARTER;
}
else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter");
}
else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("ejecting the quarter....");
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't insert the quarter");
}
else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
}
public void turnsCrank() {
if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("turning on the crank");
state = SOLD;
dispense();
}
else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't insert the quarter");
}
else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
}
private void dispense() {
if (state == SOLD) {
if (gumballs == 0) {
System.out.println("out of gumballs");
state = SOLD_OUT;
}
else {
System.out.println("dispensing the gumball");
gumballs--;
System.out.println("there are " + gumballs + " gumballs in the machine.");
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
}
else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't insert the quarter");
}
else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
}
public void addGumballsToMachine(int num) {
gumballs += num;
System.out.println("adding " + num + " gumballs to the machine.");
System.out.println("there are " + gumballs + " gumballs in the machine.");
System.out.println("--------------------");
if (gumballs > 0) {
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
}
}
現在添加一個新的流程:當turns crank的時候,判斷是否為1/10概率產生的幸運兒,如果是,則彈出兩個糖果,如果不是,則仍彈出一個糖果。

實現如下:
package javaapplication41;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gm = new GumballMachine();
gm.addGumballsToMachine(2);
gm.insertQuarter();
gm.turnsCrank();
System.out.println("------------------");
gm.insertQuarter();
gm.insertQuarter();
gm.turnsCrank();
gm.ejectQuarter();
gm.turnsCrank();
}
}
class GumballMachine {
final int SOLD_OUT = 0;
final int NO_QUARTER = 1;
final int HAS_QUARTER = 2;
final int SOLD = 3;
final int SOLD_TO_WINNER = 4;
int state;
int gumballs = 0;
public GumballMachine() {
state = SOLD_OUT;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("inserting the quarter");
state = HAS_QUARTER;
}
else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter");
}
else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
else if (state == SOLD_TO_WINNER) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("ejecting the quarter....");
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't insert the quarter");
}
else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
else if (state == SOLD_TO_WINNER) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
}
public void turnsCrank() {
if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("turning on the crank");
state = SOLD;
dispense();
}
else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't insert the quarter");
}
else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
else if (state == SOLD_TO_WINNER) {
System.out.println("already has the quarter and have turn the crank");
}
}
private void dispense() {
if (state == SOLD) {
if (gumballs == 0) {
System.out.println("out of gumballs");
state = SOLD_OUT;
}
else {
System.out.println("dispensing the gumball");
gumballs--;
System.out.println("there are " + gumballs + " gumballs in the machine.");
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
}
else if (state == SOLD_TO_WINNER) {
if (gumballs == 0) {
System.out.println("out of gumballs");
state = SOLD_OUT;
}
else if (gumballs == 1) {
System.out.println("dispensing the gumball");
gumballs--;
System.out.println("there are " + gumballs + " gumballs in the machine.");
state = SOLD_OUT;
}
else if (gumballs > 1) {
System.out.println("dispensing the 2 gumballs");
gumballs -= 2;
System.out.println("there are " + gumballs + " gumballs in the machine.");
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
}
else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't insert the quarter");
}
else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("you haven't turn the crank");
}
else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("there is no gumballs in the machine");
}
}
public void addGumballsToMachine(int num) {
gumballs += num;
System.out.println("adding " + num + " gumballs to the machine.");
System.out.println("there are " + gumballs + " gumballs in the machine.");
System.out.println("--------------------");
if (gumballs > 0) {
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
}
}
可見,為了添加一個流程,我們首先需要添加一個狀態SOLD_TO_WINNER = 4,然后在每個流程里面都要判斷一下是否處于這個狀態,故而每個流程都添加了一個else if….
這樣的代碼,維護起來是可怕的,也就是說,這樣的設計思路是不易于擴展的。
看到上面的程序,讓我想到了以前寫的“郵件收發程序”,繁復的else if…判斷語句讓我修改到最后,實在連看都不想看!不過好了,現在有了state pattern,專門處理怎樣寫業務流程。
State Pattern 的前提條件是:經常發生改變的是狀態(也就是業務流程),而不是“操作”。在上面的例子中,我們把四個“操作”寫成了類,但發生變化的不是操作,而是if…else中的狀態。所以反其道而行之,我們把各個狀態寫成類(把易變化的隔離的單獨的類里面去)。如下:(未增加新狀態前)
package javaapplication42;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gm = new GumballMachine();
gm.addGumballs(2);
gm.state.insertQuarter();//并沒有指明是哪種狀態,全部都用state,這就是代理
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.ejectQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.addGumballs(1);
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
}
}
interface State { //四個狀態都繼承它,這樣我們可以“代理”,每個狀態都有如下四個操作。
public void insertQuarter();
public void ejectQuarter();
public void turnCrank();
public void dispense();
}
class GumballMachine {
State state;
State noQuarterState;
State hasQuarterState;
State soldState;
State soldOutState;
int gumballNum;//機器內糖果的數量
public GumballMachine() {
noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
soldState = new SoldState(this);
soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
this.state = soldOutState;//initialize "state",這個state將貫穿整個執行過程
gumballNum = 0;
}
public void setState(State state) {
this.state = state;
}
public void play() {
state.insertQuarter();
state.turnCrank();
state.dispense();
}
public void addGumballs(int num) {
gumballNum += num;
if (gumballNum > 0) {
this.state = noQuarterState;
}
System.out.println("the machine has "+gumballNum+" gumball(s)");
}
}
class NoQuarterState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("insert a quarter...");
gm.setState(gm.hasQuarterState);//執行完后,改變狀態
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't eject quarter, for you haven't insert yet 1");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("you can't turn crank, for you haven't insert yet 2");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("you can't dispense, for you haven't insert yet 3");
}
}
class HasQuarterState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't insert quarter, for you have insert one already");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("eject quarter...");
gm.setState(gm.noQuarterState);
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("turning the crank...");
gm.setState(gm.soldState);
gm.state.dispense();
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("when you turn the crank, the machine will dispense the gumball");
}
}
class SoldState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public SoldState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported yet.");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported yet.");
}
public void turnCrank() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported yet.");
}
public void dispense() {
gm.gumballNum--;
System.out.println("dispense one gumball...");
if (gm.gumballNum > 0) {
gm.setState(gm.noQuarterState);
}
else {
System.out.println("Machine has no gumball");
gm.setState(gm.soldOutState);
}
}
}
class SoldOutState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public SoldOutState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't insert quarter, for the machine has no gumball");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't eject quarter, for the machine has no gumball");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("you can't turn crank, for the machine has no gumball");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("you can't dispense, for the machine has no gumball");
}
}

現在,我們新增SoldToWinnerState流程(1/10的概率獲得兩個gumball):
package javaapplication42;
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gm = new GumballMachine();
gm.addGumballs(2);
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.ejectQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
gm.addGumballs(1);
gm.state.insertQuarter();
gm.state.turnCrank();
}
}
interface State {
public void insertQuarter();
public void ejectQuarter();
public void turnCrank();
public void dispense();
}
class GumballMachine {
State state;
State noQuarterState;
State hasQuarterState;
State soldState;
State soldOutState;
State soldToWinnerState;
int gumballNum;//機器內糖果的數量
public GumballMachine() {
noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
soldState = new SoldState(this);
soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
soldToWinnerState = new SoldToWinnerState(this);
this.state = soldOutState;//initialize "state",這個state將貫穿整個執行過程
gumballNum = 0;
}
public void setState(State state) {
this.state = state;
}
public void play() {
state.insertQuarter();
state.turnCrank();
state.dispense();
}
public void addGumballs(int num) {
gumballNum += num;
if (gumballNum > 0) {
this.state = noQuarterState;
}
System.out.println("the machine has " + gumballNum + " gumball(s)");
}
}
class SoldToWinnerState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public SoldToWinnerState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("you have insert one quarter already");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("you have turn crank already");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("you have turn crank already");
}
public void dispense() {
gm.gumballNum -= 2; //具體細節,比如機器里只有一個糖果,暫不考慮,不是重點
System.out.println("*************you are winner!************");
System.out.println("dispense two gumball...");
if (gm.gumballNum > 0) {
gm.setState(gm.noQuarterState);
}
else {
System.out.println("Machine has no gumball");
gm.setState(gm.soldOutState);
}
}
}
class NoQuarterState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("insert a quarter...");
gm.setState(gm.hasQuarterState);
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't eject quarter, for you haven't insert yet 1");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("you can't turn crank, for you haven't insert yet 2");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("you can't dispense, for you haven't insert yet 3");
}
}
class HasQuarterState implements State {
Random rm;
GumballMachine gm;
public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
rm = new Random();
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't insert quarter, for you have insert one already");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("eject quarter...");
gm.setState(gm.noQuarterState);
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("turning the crank...");
if (rm.nextFloat() * 10 == 9) { //產生0-9之間的隨機數
gm.setState(gm.soldToWinnerState);
}
else {
gm.setState(gm.soldState);
}
gm.state.dispense();
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("when you turn the crank, the machine will dispense the gumball");
}
}
class SoldState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public SoldState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported yet.");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported yet.");
}
public void turnCrank() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported yet.");
}
public void dispense() {
gm.gumballNum--;
System.out.println("dispense one gumball...");
if (gm.gumballNum > 0) {
gm.setState(gm.noQuarterState);
}
else {
System.out.println("Machine has no gumball");
gm.setState(gm.soldOutState);
}
}
}
class SoldOutState implements State {
GumballMachine gm;
public SoldOutState(GumballMachine gm) {
this.gm = gm;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't insert quarter, for the machine has no gumball");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("you can't eject quarter, for the machine has no gumball");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("you can't turn crank, for the machine has no gumball");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("you can't dispense, for the machine has no gumball");
}
}

可見,在state pattern中,新增一個狀態,只需要新增一個(表達這個狀態的)類,并在該狀態的“上游狀態”做少許改動即可。



