¾U¢é¢œçŸ¥å·±ž®±æ˜¯ä¸€¿U点拨,ç‚ÒŽ‹¨ä½ 心ä¸çš„˜qähÓ|ã€?nbsp; 阅读全文
那星星点点的光亮
æ˜ è¡¬é£Žé›¨å¥ç¡•è½È›ˆçš„舞æ?br /> ˜q½é€è‡ªç”±åŞ骸的放浪
而å˜qœä¹¡æ‘沉寂在自然ä¸?br /> åªæœ‰ä¸€æ¯å¾®å¼Þq¯å½±åœ¨æ¸…风ä¸æ‘‡æ™?br /> ½{‰å¾…希冀的å†ç”?br /> 渴望冒出拔地楼房
伤é€éš˜q›æ¢¦çš„土å£?br />
Tomcat5.0.28 + JDK1.5 + xfire1.2.6
™å¹ç›®ä»ŽTomcat6.0™å¹ç›®æ‹¯‚´å›žæ¥åQŒtomcat6.0˜qè¡Œæ£å¸¸ã€?br /> 问题出在Tomcatçš?br /> \common\endorsed\ä¸?br /> åˆ é™¤æˆ–apache¾|‘站下è²æ›´æ–°˜q™ä¸¤ä¸ªjarå›_¯ã€?br />
- JPOX uses this PersistenceCapable interface, and adds it using bytecode enhancement techniques so that you never need to actually change your classes. This means that you get transparent persistence, and your classes always remain your classes. ORM tools that use a mix of reflection and/or proxies are not totally transparent.
- JPOX' use of PersistenceCapable provides transparent change tracking. When any change is made to an object the change creates a notification to JPOX allowing it to be optimally persisted. ORM tools that dont have access to such change tracking have to use reflection to detect changes. The performance of this process will break down as soon as you read a large number of objects, but modify just a handful, with these tools having to compare all object states for modification at transaction commit time.
In a JDO-enabled application there are 3 categories of classes. These are PersistenceCapable, PersistenceAware and normal classes. The Meta-Data defines which classes fit into these categories. To give an example for JDO, we have 3 classes. The class A is to be persisted in the datastore. The class B directly updates the fields of class A but doesn't need persisting. The class C is not involved in the persistence process. We would define JDO MetaData for these classes like this
2 <field name="myField">
3

4 </field>
5

6 </class>
7 <class name="B" persistence-modifier="persistence-aware">
8 </class>
So our MetaData is mainly for those classes that are PersistenceCapable and are to be persisted to the datastore (we don't really need the persistence-modifier for thse classes since this is the default). For PersistenceAware classes we simply notate that the class knows about persistence. We don't define MetaData for any class that has no knowledge of persistence.
JDO requires that all classes to be persisted must implement the PersistenceCapable interface . Users could manually do this themselves but this would impose work on them. JDO permits the use of a byte-code enhancer that converts the users normal classes to implement this interface. JPOX provides its own byte-code enhancer (this can be found in the jpox-enhancer.jar). This section describes how to use this enhancer with JPOX. The JPOX enhancer fully implements JDO2 and so is the recommended choice when persisting using the JDO2 API. The enhancement process adds the necessary methods to the users class in order to implement PersistenceCapable.
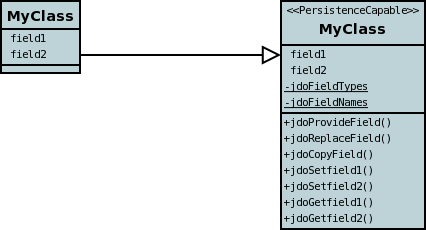
The example above doesn't show all PersistenceCapable methods, but demonstrates that all added methods and fields are prefixed with "jdo" to distinguish them from the users own methods and fields. Also each persistent field of the class will be given a jdoGetXXX, jdoSetXXX method so that accesses of these fields are intercepted so that JDO can manage their "dirty" state.
The MetaData defines which classes are required to be persisted, and also defines which aspects of persistence each class requires. For example if a class has the detachable attribute set to true, then that class will be enhanced to also implement Detachable

Again, the example above doesn't show all methods added for the Detachable interface but the main thing to know is that the detached state (object id of the datastore object, the version of the datastore object when it was detached, and which fields were detached is stored in "jdoDetachedState"). Please see the JDO spec for more details.
If the MetaData is changed in any way during development, the classes should always be recompiled and re-enhanced afterwards.
| Byte-Code Enhancement Myths |
Some groups (e.g Hibernate) perpetuated arguments against "byte-code enhancement" saying that it was somehow 'evil'. The most common were :-
- Slows down the code-test cycle. This is erroneous since you only need to enhance just before test and the provided plugins for Ant, Eclipse and Maven all do the enhancement job automatically and rapidly.
- Is less "lazy" than the proxy approach since you have to load the object as soon as you get a pointer to it. In a 1-1 relation you have to load the object then since you would cause issues with null pointers otherwise. With 1-N relations you load the elements of the collection/map only when you access them and not the collection/map. Hardly an issue then is it!
- Fail to detect changes to public fields unless you enhance your client code. Firstly very few people will be writing code with public fields since it is bad practice in an OO design, and secondly, this is why we have "PersistenceAware" classes.
So as you can see, there are no valid reasons against byte-code enhancement, and the pluses are that runtime detection of dirty events on objects is much quicker, hence your persistence layer operates faster without any need for iterative reflection-based checks. The fact is that Hibernate itself also now has a mode whereby you can do bytecode enhancement although not the default mode of Hibernate. So maybe it wasn't so evil after all ?
Actioné…ç½®
attribute="testMappingForm"
input="/jsp"
name="testMappingForm"
path="/testMapping"
scope="request"
type="com.modo.struts.action.TestMappingAction" />
ActionFormé…ç½®
<form-property name="fnames" type="java.util.HashMap"></form-property>
</form-bean>
è¯äh³¨æ„name属性,˜q™ä¸ªå±žæ€§åŽé¢è¦ç”¨åˆ°ã€?br />
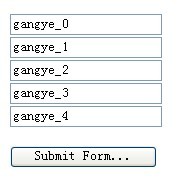
然åŽæ˜¯é¡µé¢index.jsp,˜q™é‡Œåªæ¨¡æ‹ŸåŠ¨æ€?/p>
<%
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
%>
<html:text property="<%="fnames(name_"+i+")"%>" value="<%="gangye_"+i%>"></html:text><br>
<%}%>
<br>
<html:submit value="Submit Form
 " />
" /></html:form>
è¯äh³¨æ„html:textçš„propertyæ ‡ç¾ã€?br />
index.jsp效果如下
åŽå°Action
HttpServletResponse response) {
HashMap hm=(HashMap)((DynaActionForm)form).get("fnames");
Iterator it = hm.entrySet().iterator();
Map.Entry entry = null;
while(it.hasNext()){
entry = (Map.Entry)it.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " = " + entry.getValue());
}
return null;
}
输出表啙å?/p>
 name_4 = gangye_4
name_4 = gangye_4 name_0 = gangye_0
name_0 = gangye_0 name_2 = gangye_2
name_2 = gangye_2 name_1 = gangye_1
name_1 = gangye_1 name_3 = gangye_3
name_3 = gangye_3