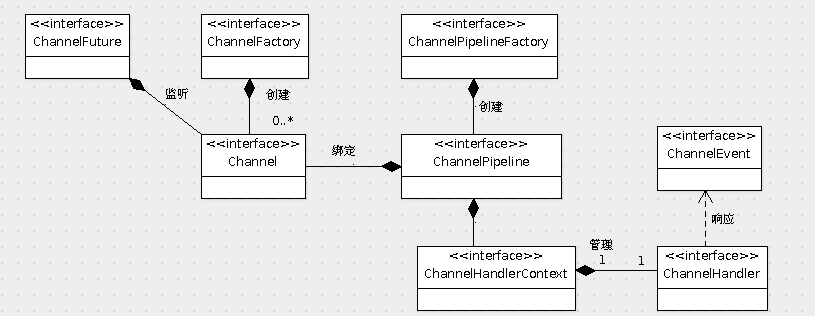
上一篇分析了serverboostrap的啟動,接下來分析netty的數據讀取。
在nioworker的,負責讀取操作是由,在該方法中,如果當前channel的(readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_READ) != 0 || readyOps == 0,且此時
ch.read(buff)<0,則判斷客戶端已經斷開連接
private boolean read(SelectionKey k) {
final SocketChannel ch = (SocketChannel) k.channel();
final NioSocketChannel channel = (NioSocketChannel) k.attachment();
final ReceiveBufferSizePredictor predictor =
channel.getConfig().getReceiveBufferSizePredictor();
//默認1024個字節空間
final int predictedRecvBufSize = predictor.nextReceiveBufferSize();
int ret = 0;
int readBytes = 0;
boolean failure = true;
//分配連續的1024個byte空間
ByteBuffer bb = recvBufferPool.acquire(predictedRecvBufSize);
try {
while ((ret = ch.read(bb)) > 0) {
readBytes += ret;
if (!bb.hasRemaining()) {
break;
}
}
failure = false;
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
// Can happen, and does not need a user attention.
} catch (Throwable t) {
fireExceptionCaught(channel, t);
}
if (readBytes > 0) {
bb.flip();
final ChannelBufferFactory bufferFactory =
channel.getConfig().getBufferFactory();
final ChannelBuffer buffer = bufferFactory.getBuffer(readBytes);
buffer.setBytes(0, bb);
buffer.writerIndex(readBytes);
recvBufferPool.release(bb);
// Update the predictor.
predictor.previousReceiveBufferSize(readBytes);
//觸發消息接收事件,根據pipeline中upstreamhandler由上到下的順序,調用messageReceived方法
fireMessageReceived(channel, buffer);
} else {
recvBufferPool.release(bb);
}
if (ret < 0 || failure) {
close(channel, succeededFuture(channel));
return false;
}
return true;
}
在pipelinefactory中的第一個upstreamhandler為DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder,繼承自FrameDecoder
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
// Create a default pipeline implementation.
ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// Add the text line codec combination first,
pipeline.addLast("framer", new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(
8192, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
// and then business logic.
pipeline.addLast("handler", new TelnetServerHandler());
return pipeline;
}
會調用FrameDecoder的messageReceived
public void messageReceived(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
Object m = e.getMessage();
if (!(m instanceof ChannelBuffer)) {
ctx.sendUpstream(e);
return;
}
ChannelBuffer input = (ChannelBuffer) m;
if (!input.readable()) {
return;
}
ChannelBuffer cumulation = cumulation(ctx);
if (cumulation.readable()) {
cumulation.discardReadBytes();
cumulation.writeBytes(input);
callDecode(ctx, e.getChannel(), cumulation, e.getRemoteAddress());
} else {
//這里調用子類的decode方法
callDecode(ctx, e.getChannel(), input, e.getRemoteAddress());
if (input.readable()) {
cumulation.writeBytes(input);
}
}
}
//在這個upstreamhandler中,會一直讀取數據,直到遇到協議約定的結束標志才將messagereceived事件傳給下一個
private void callDecode(
ChannelHandlerContext context, Channel channel,
ChannelBuffer cumulation, SocketAddress remoteAddress) throws Exception {
while (cumulation.readable()) {
int oldReaderIndex = cumulation.readerIndex();
Object frame = decode(context, channel, cumulation);
if (frame == null) {
if (oldReaderIndex == cumulation.readerIndex()) {
// Seems like more data is required.
// Let us wait for the next notification.
break;
} else {
// Previous data has been discarded.
// Probably it is reading on.
continue;
}
} else if (oldReaderIndex == cumulation.readerIndex()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"decode() method must read at least one byte " +
"if it returned a frame (caused by: " + getClass() + ")");
}
//將messagereceive事件傳給下個upstreamhandler
unfoldAndFireMessageReceived(context, remoteAddress, frame);
}
}
看子類的decode是如何判斷數據讀取完畢
protected Object decode(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws Exception {
// Try all delimiters and choose the delimiter which yields the shortest frame.
int minFrameLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
ChannelBuffer minDelim = null;
//獲取\r\n的位置
for (ChannelBuffer delim: delimiters) {
int frameLength = indexOf(buffer, delim);
if (frameLength >= 0 && frameLength < minFrameLength) {
minFrameLength = frameLength;
minDelim = delim;
}
}
//如果找到\r\n,表明客戶端數據發送完畢
if (minDelim != null) {
int minDelimLength = minDelim.capacity();
ChannelBuffer frame;
if (discardingTooLongFrame) {
// We've just finished discarding a very large frame.
// Go back to the initial state.
discardingTooLongFrame = false;
buffer.skipBytes(minFrameLength + minDelimLength);
// TODO Let user choose when the exception should be raised - early or late?
// If early, fail() should be called when discardingTooLongFrame is set to true.
int tooLongFrameLength = this.tooLongFrameLength;
this.tooLongFrameLength = 0;
fail(ctx, tooLongFrameLength);
return null;
}
if (minFrameLength > maxFrameLength) {
// Discard read frame.
buffer.skipBytes(minFrameLength + minDelimLength);
fail(ctx, minFrameLength);
return null;
}
if (stripDelimiter) {
//這里讀取全部數據
frame = buffer.readBytes(minFrameLength);
buffer.skipBytes(minDelimLength);
} else {
frame = buffer.readBytes(minFrameLength + minDelimLength);
}
return frame;
} else {
if (!discardingTooLongFrame) {
if (buffer.readableBytes() > maxFrameLength) {
// Discard the content of the buffer until a delimiter is found.
tooLongFrameLength = buffer.readableBytes();
buffer.skipBytes(buffer.readableBytes());
discardingTooLongFrame = true;
}
} else {
// Still discarding the buffer since a delimiter is not found.
tooLongFrameLength += buffer.readableBytes();
buffer.skipBytes(buffer.readableBytes());
}
return null;
}
}
因為unfold默認是false,會執行,調用下一個upstreamhandler,這里是stringdecoder,通過stringdecoder,將channelbuffer中的數據轉為string
然后再觸發下一個upstreamhandler的messagereceive,這里是TelnetServerHandler
public void messageReceived(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) {
// Cast to a String first.
// We know it is a String because we put some codec in TelnetPipelineFactory.
String request = (String) e.getMessage();
// Generate and write a response.
String response;
boolean close = false;
if (request.length() == 0) {
response = "Please type something."r"n";
} else if (request.toLowerCase().equals("bye")) {
response = "Have a good day!"r"n";
close = true;
} else {
response = "Did you say '" + request + "'?"r"n";
}
// We do not need to write a ChannelBuffer here.
// We know the encoder inserted at TelnetPipelineFactory will do the conversion.
ChannelFuture future = e.getChannel().write(response);
// Close the connection after sending 'Have a good day!'
// if the client has sent 'bye'.
if (close) {
future.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
數據讀取分析完畢,接著繼續分析服務器端數據的發送