有關(guān)排隊系統(tǒng)的應(yīng)用是很多的,本文是針對醫(yī)院的排隊掛號流程進行的簡易設(shè)計。要設(shè)計排隊系統(tǒng),首先要分別設(shè)計出病人和專家的類,然后編寫服務(wù)器類模擬出若干等侯的病人。最后分別編寫出專家與病人的客戶端。具體步驟及代碼如下:
1.病人類。
package com.TinySK;
public class Pro {
private int proId;
private String proName;
private Patient patienter;
public Pro(Patient patienter){
this.patienter=patienter;
}
public int getProId() {
return proId;
}
public void setProId(int proId) {
this.proId = proId;
}
public String getProName() {
return proName;
}
public void setProName(String proName) {
this.proName = proName;
}
public Patient getPatienter() {
return patienter;
}
public void setPatienter(Patient patienter) {
this.patienter = patienter;
}
}
2.專家類。
package com.TinySK;
public class Pro {
private int proId;
private String proName;
private Patient patienter;
public Pro(Patient patienter){
this.patienter=patienter;
}
public int getProId() {
return proId;
}
public void setProId(int proId) {
this.proId = proId;
}
public String getProName() {
return proName;
}
public void setProName(String proName) {
this.proName = proName;
}
public Patient getPatienter() {
return patienter;
}
public void setPatienter(Patient patienter) {
this.patienter = patienter;
}
}
3.服務(wù)器端。
package com.TinySK;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
public class PatientServer {
private static int num=1;
public static int getNum() {
return num;
}
public static void setNum(int num) {
PatientServer.num = num;
}
Map<String,Queue<Patient>> per=new HashMap<String,Queue<Patient>>();
LinkedList<Patient> waiterList1 = new LinkedList<Patient>();
LinkedList<Patient> waiterList2 = new LinkedList<Patient>();
LinkedList<Patient> waiterList3 = new LinkedList<Patient>();
public Map<String,Queue<Patient>> init(){
for(int i=1;i<=30;i++,num++){
Patient w1 = new Patient();
w1.setId(num);
w1.setFormer(i-1);
waiterList1.offer(w1);
}
per.put("馮醫(yī)生",waiterList1);
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++,num++){
Patient w2 = new Patient();
w2.setId(num);
w2.setFormer(i-1);
waiterList2.offer(w2);
}
per.put("王醫(yī)生",waiterList2);
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++,num++){
Patient w3 = new Patient();
w3.setId(num);
w3.setFormer(i-1);
waiterList3.offer(w3);
}
per.put("閆醫(yī)生",waiterList3);
return per;
}
}
4.病人客戶端。
package com.TinySK;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionAdapter;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionEvent;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Font;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
public class PatientUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Display display = Display.getDefault();
final Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setMaximized(true);
shell.setText("醫(yī)院排隊客戶端");
// ------------------新插入的界面核心代碼------------------------
PatientServer ps = new PatientServer();//實例化類
final Map<String,Queue<Patient>> waiterList = ps.init();
//初始化隊列服務(wù)器
final Text txt1 = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI);
txt1.setBounds(150, 50, 200, 400);
// 事件代碼里要訪問button,所以加final
final Button button1 = new Button(shell, SWT.Activate);
button1.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() { // 加一個擇監(jiān)聽器
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e) {
Queue<Patient> patient1List=waiterList.get("馮醫(yī)生");
Patient patient1 = new Patient();
patient1.setId(patient1List.size()+1);
patient1.setFormer(patient1List.size());
patient1List.offer(patient1);
if(patient1List.size() <= 50){
txt1.setText( "您現(xiàn)在排在"+patient1.getId()+"位置上,\n您前面有"+patient1.getFormer()+"個人\n請您耐心等候吧!哈哈");
}else{
txt1.setText("您前面已經(jīng)排50個人,請考慮!\n"+"您現(xiàn)在排在"+patient1.getId()+"位置上,\n您前面有"+patient1.getFormer()+"個人\n請您耐心等候吧!哈哈");
}
}
});
button1.setBounds(200, 530, 100, 40); // 設(shè)置按鈕位置
button1.setFont(new Font(display,"宋體",12,SWT.BOLD));
button1.setText("馮醫(yī)生");// 設(shè)置按鈕上的文字
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
final Text txt2 = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI);
txt2.setBounds(550, 50, 200, 400);
// 事件代碼里要訪問button,所以加final
final Button button2 = new Button(shell, SWT.Activate);
button2.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() { // 加一個擇監(jiān)聽器
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e) {
Queue<Patient> patient2List=waiterList.get("王醫(yī)生");
Patient patient2 = new Patient();
patient2.setId(patient2List.size()+1);
patient2.setFormer(patient2List.size());
patient2List.offer(patient2);
if(patient2List.size() <= 50){
txt2.setText( "您現(xiàn)在排在"+patient2.getId()+"位置上,\n您前面有"+patient2.getFormer()+"個人\n請您耐心等候吧!哈哈");
}else{
txt2.setText("您前面已經(jīng)排50個人,請考慮!\n"+"您現(xiàn)在排在"+patient2.getId()+"位置上,\n您前面有"+patient2.getFormer()+"個人\n請您耐心等候吧!哈哈");
}
}
});
button2.setBounds(600, 530, 100, 40); // 設(shè)置按鈕位置
button2.setFont(new Font(display,"宋體",12,SWT.BOLD));
button2.setText("王醫(yī)生");// 設(shè)置按鈕上的文字
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
final Text txt3 = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI);
txt3.setBounds(950, 50, 200, 400);
// 事件代碼里要訪問button,所以加final
final Button button3 = new Button(shell, SWT.Activate);
button3.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() { // 加一個擇監(jiān)聽器
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e) {
Queue<Patient> patient3List=waiterList.get("閆醫(yī)生");
Patient patient3 = new Patient();
patient3.setId(patient3List.size()+1);
patient3.setFormer(patient3List.size());
patient3List.offer(patient3);
if(patient3List.size() <= 50){
txt3.setText( "您現(xiàn)在排在"+patient3.getId()+"位置上,\n您前面有"+patient3.getFormer()+"個人\n請您耐心等候吧!哈哈");
}else{
txt3.setText("您前面已經(jīng)排50個人,請考慮!\n"+"您現(xiàn)在排在"+patient3.getId()+"位置上,\n您前面有"+patient3.getFormer()+"個人\n請您耐心等候吧!哈哈");
}
}
});
button3.setBounds(1000, 530, 100, 40); // 設(shè)置按鈕位置
button3.setFont(new Font(display,"宋體",12,SWT.BOLD));
button3.setText("閆醫(yī)生");// 設(shè)置按鈕上的文字
shell.layout();
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
}
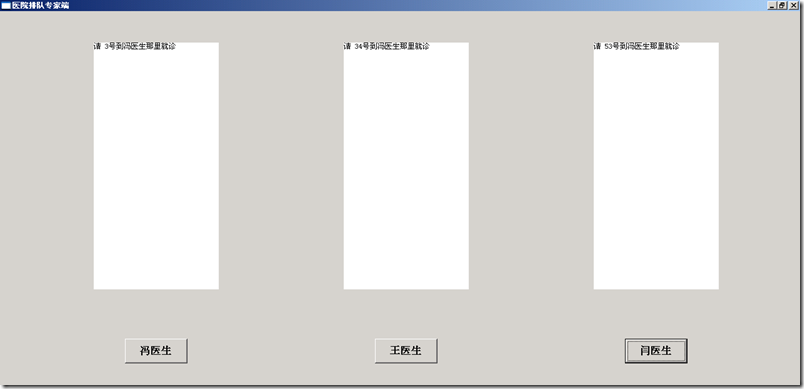
5.醫(yī)生客戶端。
package com.TinySK;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionAdapter;
import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionEvent;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Font;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;
public class ProUI {public static void main(String[] args) {
final Display display = Display.getDefault();
final Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setMaximized(true);
shell.setText("醫(yī)院排隊專家端");
// ------------------新插入的界面核心代碼------------------------
PatientServer ps = new PatientServer();//實例化類
final Map<String,Queue<Patient>> waiterList = ps.init();
//初始化隊列服務(wù)器
final Text txt1 = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI);
txt1.setBounds(150, 50, 200, 400);
// 事件代碼里要訪問button,所以加final
final Button button1 = new Button(shell, SWT.Activate);
button1.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() { // 加一個擇監(jiān)聽器
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e) {
Queue<Patient> patient1List=waiterList.get("馮醫(yī)生");
Patient patient1 = patient1List.poll();
txt1.setText("請 " + patient1.getId()+"號到馮醫(yī)生那里就診");
}
});
button1.setBounds(200, 530, 100, 40); // 設(shè)置按鈕位置
button1.setFont(new Font(display,"宋體",12,SWT.BOLD));
button1.setText("馮醫(yī)生");// 設(shè)置按鈕上的文字
// ------------------Second--------------------------------------------
final Text txt2 = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI);
txt2.setBounds(550, 50, 200, 400);
// 事件代碼里要訪問button,所以加final
final Button button2 = new Button(shell, SWT.Activate);
button2.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() { // 加一個擇監(jiān)聽器
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e) {
Queue<Patient> patient2List=waiterList.get("王醫(yī)生");
Patient patient2 = patient2List.poll();
txt2.setText("請 " + patient2.getId()+"號到馮醫(yī)生那里就診");
}
});
button2.setBounds(600, 530, 100, 40); // 設(shè)置按鈕位置
button2.setFont(new Font(display,"宋體",12,SWT.BOLD));
button2.setText("王醫(yī)生");// 設(shè)置按鈕上的文字
//---------------------Third--------------------------------------------------------
final Text txt3 = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI);
txt3.setBounds(950, 50, 200, 400);
// 事件代碼里要訪問button,所以加final
final Button button3 = new Button(shell, SWT.Activate);
button3.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() { // 加一個擇監(jiān)聽器
public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent e) {
Queue<Patient> patient3List=waiterList.get("閆醫(yī)生");
Patient patient3 = patient3List.poll();
txt3.setText("請 " + patient3.getId()+"號到馮醫(yī)生那里就診");
}
});
button3.setBounds(1000, 530, 100, 40); // 設(shè)置按鈕位置
button3.setFont(new Font(display,"宋體",12,SWT.BOLD));
button3.setText("閆醫(yī)生");// 設(shè)置按鈕上的文字
shell.layout();
shell.open();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
}
有關(guān)醫(yī)院排隊系統(tǒng)的簡易模型就此完成,對于界面的美化,不再過多介紹。還有對于服務(wù)器端的模擬不太真實,這部分在實際應(yīng)用中會很重要,而且要占一大部分內(nèi)容,本文只是簡單的模擬了一下服務(wù)器端。有關(guān)服務(wù)器端與用戶端的結(jié)合使用,將在以后分析。本文寫的不是很完善,若有問題請批評指正。