Acegi提供了多種身份驗證方式(表單驗證,CAS等),但只允許一種用戶登錄,而就個人了解,有一些系統(tǒng)是需要多種用戶登錄的。比如企業(yè)的員工需要登錄并使用系統(tǒng),企業(yè)也允許客戶登錄系統(tǒng)并使用有限的功能。以下嘗試剖析Acegi的表單驗證過程,并給出一種允許多種用戶登錄的方案。本方案基本達到“能用”的目的,但不一定是最佳方案。希望這篇文章能起到拋磚引玉的作用,給各位朋友一點參考,也希望各位提出有益的建議。
Acegi的表單驗證方式簡要分析
一個使用Acegi的表單驗證的登錄頁面通常需要在表單提交時request的j_username和j_password參數(shù)賦值,即用戶名和密碼,而表單則提交到Acegi設(shè)定到驗證地址。例如:
<form method="post" id="loginForm" action="<c:url value='/j_security_check'/>" >
<input type="text" name="j_username" id="j_username" />
<input type="password" name="j_password" id="j_password" />
<input type="submit" name="login" value="Login" />
</form>
<input type="text" name="j_username" id="j_username" />
<input type="password" name="j_password" id="j_password" />
<input type="submit" name="login" value="Login" />
</form>
服務(wù)器的Servlet容器收到請求后會傳遞給Acegi的FilterToBeanProxy,這需要在web.xml中進行配置。例如:
<filter>
<filter-name>securityFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.acegisecurity.util.FilterToBeanProxy</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>targetClass</param-name>
<param-value>org.acegisecurity.util.FilterChainProxy</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>securityFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter-name>securityFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.acegisecurity.util.FilterToBeanProxy</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>targetClass</param-name>
<param-value>org.acegisecurity.util.FilterChainProxy</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>securityFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
FilterToBeanProxy基本上只起到調(diào)用轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)的作用。在它的doFilter方法中會找到類型為FilterChainProxy的bean,調(diào)用后者的doFilter方法,同時把request、response會chain參數(shù)都傳遞過去。代碼如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!initialized) {
doInit();
}
delegate.doFilter(request, response, chain);
}
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!initialized) {
doInit();
}
delegate.doFilter(request, response, chain);
}
上面的代碼中的delegate就是找到的類型FilterChainProxy的bean。FilterChainProxy的典型配置如下:
<bean id="filterChainProxy" class="org.acegisecurity.util.FilterChainProxy">
<property name="filterInvocationDefinitionSource">
<value>
CONVERT_URL_TO_LOWERCASE_BEFORE_COMPARISON
PATTERN_TYPE_APACHE_ANT
/**=httpSessionContextIntegrationFilter,authenticationProcessingFilter,
</value>
</property>
</bean>
<property name="filterInvocationDefinitionSource">
<value>
CONVERT_URL_TO_LOWERCASE_BEFORE_COMPARISON
PATTERN_TYPE_APACHE_ANT
/**=httpSessionContextIntegrationFilter,authenticationProcessingFilter,

</value>
</property>
</bean>
對于上面的配置,引用一段Acegi聯(lián)機幫助中的說明來幫助理解:
Internally Acegi Security will use a PropertyEditor to convert the string presented in the above XML fragment into a FilterInvocationDefinitionSource object. What's important to note at this stage is that a series of filters will be run - in the order specified by the declaration - and each of those filters are actually the <bean id> of another bean inside the application context.
實際上,F(xiàn)ilterChainProxy的doFilter方法會執(zhí)行如下處理:
1.讀取配置,如果配置為空,則直接調(diào)用chain.doFilter,返回
2.如果配置不為空,則根據(jù)配置找到各個bean,放入Filter數(shù)組中。如果配置中沒有配置任何bean,則直接調(diào)用chain.doFilter,返回
3.FilterChainProxy創(chuàng)建一個VirtualFilterChain對象,并將chain封裝為一個FilterInvocation對象,將它和Filter數(shù)組一起傳遞給VirtualFilterChain的構(gòu)造函數(shù)。VirtualFilterChain的構(gòu)造函數(shù)初始化了一個指針currentPosition,指向Filter數(shù)組的第一個元素additionalFilters[0]
4.FilterChainProxy調(diào)用VirtualFilterChain的doFilter方法,在該方法中將指針currentPosition前移,調(diào)用additionalFilters[0]的doFilter方法。注意這里VirtualFilterChain把自身作為參數(shù)傳遞給additionalFilters[0]的doFilter方法,這樣additionalFilters[0]的doFilter方法最后會調(diào)用VirtualFilterChain的doFilter方法,這樣控制就又回到了VirtualFilterChain!于是VirtualFilterChain又將currentPosition前移,調(diào)用additionalFilters[1]的doFilter方法......
5.當additionalFilters中所有元素的doFilter都執(zhí)行完畢,VirtualFilterChain執(zhí)行fi.getChain().doFilter,而fi.getChain()的值就是FilterChainProxy的doFilter方法中的參數(shù)chain的值。這樣我們就理解了FilterChainProxy是怎樣讓調(diào)用兜了個圈,又傳遞出去的。
重新回到FilterChainProxy的配置,看到它調(diào)用了authenticationProcessingFilter這個Filter。讓我們看看它的配置:
<bean id="authenticationProcessingFilter"
class="org.acegisecurity.ui.webapp.AuthenticationProcessingFilter">
<property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager"/>
<property name="authenticationFailureUrl" value="/login.jsp?error=true"/>
<property name="defaultTargetUrl" value="/"/>
<property name="filterProcessesUrl" value="/j_security_check"/>
<property name="rememberMeServices" ref="rememberMeServices"/>
</bean>
class="org.acegisecurity.ui.webapp.AuthenticationProcessingFilter">
<property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager"/>
<property name="authenticationFailureUrl" value="/login.jsp?error=true"/>
<property name="defaultTargetUrl" value="/"/>
<property name="filterProcessesUrl" value="/j_security_check"/>
<property name="rememberMeServices" ref="rememberMeServices"/>
</bean>
authenticationProcessingFilter的其中一個作用就是獲取客戶端提交的用戶名和密碼,將它們封裝為一個Token,傳遞給authenticationManager的authenticate方法,由后者負責(zé)驗證。
看看authenticationManager的配置:
<bean id="authenticationManager" class="org.acegisecurity.providers.ProviderManager">
<property name="providers">
<list>
<ref local="daoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="anonymousAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="rememberMeAuthenticationProvider"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<property name="providers">
<list>
<ref local="daoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="anonymousAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="rememberMeAuthenticationProvider"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
authenticationManager依次調(diào)用每個provider的authenticate方法。如果某個provider驗證成功則返回;如果所有的驗證都不成功,則拋出異常。
讓我們看看daoAuthenticationProvider的配置:
<bean id="daoAuthenticationProvider" class="org.acegisecurity.providers.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider">
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="userDao"/>
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder"/>
</bean>
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="userDao"/>
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder"/>
</bean>
daoAuthenticationProvider在authenticate方法中調(diào)用retrieveUser方法取得用戶信息,執(zhí)行基本的驗證,然后調(diào)用additionalAuthenticationChecks執(zhí)行附加的驗證(比如驗證密碼是否正確)。在retrieveUser方法中調(diào)用userDetailsService的loadUserByUsername方法取得用戶信息,而userDetailsService是一個名為userDao的bean。讓我們看看userDao的配置:
<bean id="userDao" class="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.appfuse.dao.hibernate.EmployeeDaoHibernate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
userDao實現(xiàn)了Acegi的UserDetailsService接口,該接口只有l(wèi)oadUserByUsername方法。loadUserByUsername方法根據(jù)傳入的username取得相應(yīng)的Employee對象(Employee實現(xiàn)了UserDetails接口),該對象返回給daoAuthenticationProvider,由它和authenticationManager聯(lián)合完成驗證的任務(wù)。
以上對Acegi對表單驗證過程進行了簡單對分析,限于篇幅,無法深入分析源碼。但從配置可以畫出驗證過程的對象圖如下:
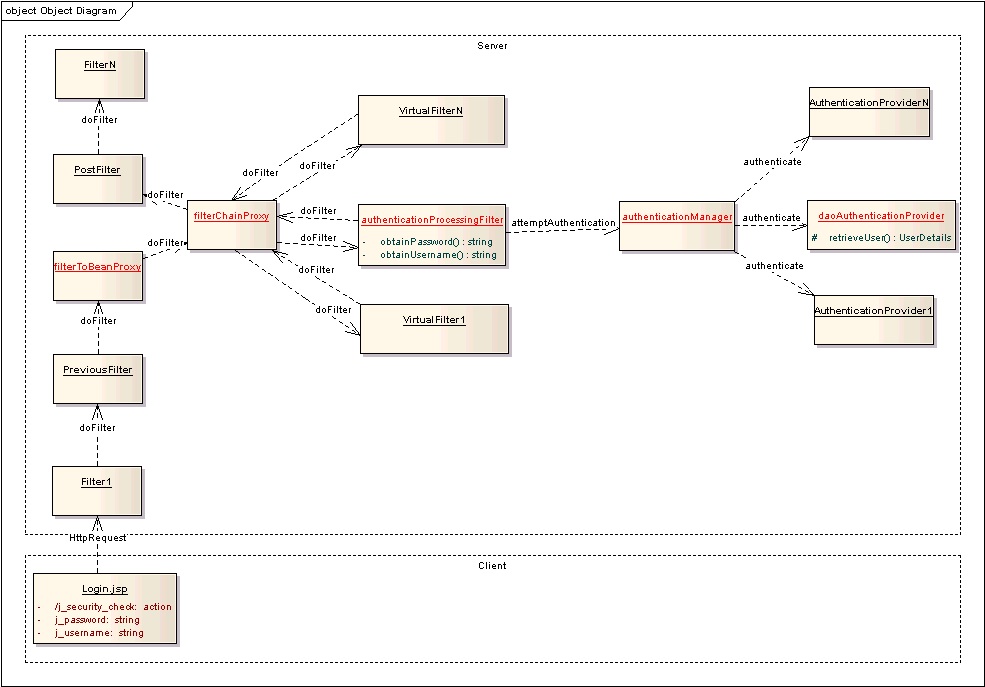
從圖中可以看出,盡管Acegi調(diào)用了多個Filter來完成驗證過程,關(guān)鍵點卻在三處:
1.在客戶端輸入身份驗證信息,包括用戶名和密碼
2.AuthenticationProcessingFilter取出用戶名和密碼,封裝為一個Token往后傳遞
3.DaoAuthenticationProvider從系統(tǒng)中找出用戶資料,并和ProviderManager一起執(zhí)行驗證
實現(xiàn)多種用戶登錄
很明顯,要讓系統(tǒng)識別不同種類的用戶,必須設(shè)立一個用戶類型標志。問題就轉(zhuǎn)化為:
1.用戶在客戶端輸入身份信息時系統(tǒng)就必須設(shè)立相應(yīng)的標志
2.該標志如何傳遞到DaoAuthenticationProvider
3.DaoAuthenticationProvider如何識別該標志,并從相應(yīng)類型的用戶中找到指定用戶
我不打算改動Acegi的源碼,只打算擴展出我需要的功能。
首先在登錄頁面中加入用戶類型標志j_userkind。在登錄頁面中加入如下代碼:
<input type="hidden" name="j_userkind" id="j_userkind" value="0">
其中0代碼員工,1代碼客戶。可以考慮在登錄頁面中增加一個選項,如果用戶要以員工身份登錄,則把j_userkind置為0;如果用戶要以客戶身份登錄,則把j_userkind置為1。也可以提供兩個登錄頁面,其中一個員工專用(j_userkind被強制置為0),另一個客戶專用(j_userkind被強制置為1)
系統(tǒng)如何根據(jù)收到的用戶類型標志去讀取指定的用戶呢?如果在代碼中寫死(比如當用戶類型標志=0時,讀取員工;當用戶類型標志=1時,讀取客戶)非常不好,還是通過配置來確定比較靈活。首先編寫UserKindComparisonAware接口:
package cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers;
public interface UserKindComparisonAware {
public void setExpectedUserKind(String expectedUserKind);
public void setCurrentUserKind(String currentUserKind);
}
public interface UserKindComparisonAware {
public void setExpectedUserKind(String expectedUserKind);
public void setCurrentUserKind(String currentUserKind);
}
該接口說明實現(xiàn)類需要實現(xiàn)兩個方法,setExpectedUserKind用于接受一個期望的用戶類型標志(通常該標志通過配置來設(shè)置),setCurrentUserKind用于接受當前登錄用戶的用戶類型標志(系統(tǒng)在運行時捕獲,并傳遞給實現(xiàn)類)
編寫MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider類:
package cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.dao;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.BadUserKindException;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.UserKindComparisonAware;
import org.acegisecurity.AuthenticationException;
import org.acegisecurity.providers.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.acegisecurity.providers.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UserDetails;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.util.LoggerUtil;
public class MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider extends DaoAuthenticationProvider implements
UserKindComparisonAware {
private String expectedUserKind;
private String currentUserKind;
public String getExpectedUserKind() {
return expectedUserKind;
}
public void setExpectedUserKind(String expectedUserKind) {
this.expectedUserKind = expectedUserKind;
}
public String getCurrentUserKind() {
return currentUserKind;
}
public void setCurrentUserKind(String currentUserKind) {
this.currentUserKind = currentUserKind;
}
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
LoggerUtil.getLogger().debug("expectedUserKind = '" + expectedUserKind + "', currentUserKind = '" + currentUserKind + "'");
if (currentUserKind.equals(expectedUserKind))
super.additionalAuthenticationChecks(userDetails, authentication);
else
throw new BadUserKindException(
"Flag UserKind does not match");
}
}
import cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.BadUserKindException;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.UserKindComparisonAware;
import org.acegisecurity.AuthenticationException;
import org.acegisecurity.providers.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.acegisecurity.providers.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UserDetails;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.util.LoggerUtil;
public class MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider extends DaoAuthenticationProvider implements
UserKindComparisonAware {
private String expectedUserKind;
private String currentUserKind;
public String getExpectedUserKind() {
return expectedUserKind;
}
public void setExpectedUserKind(String expectedUserKind) {
this.expectedUserKind = expectedUserKind;
}
public String getCurrentUserKind() {
return currentUserKind;
}
public void setCurrentUserKind(String currentUserKind) {
this.currentUserKind = currentUserKind;
}
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
LoggerUtil.getLogger().debug("expectedUserKind = '" + expectedUserKind + "', currentUserKind = '" + currentUserKind + "'");
if (currentUserKind.equals(expectedUserKind))
super.additionalAuthenticationChecks(userDetails, authentication);
else
throw new BadUserKindException(
"Flag UserKind does not match");
}
}
該類繼承自DaoAuthenticationProvider并實現(xiàn)UserKindComparisonAware接口,在additionalAuthenticationChecks方法中判斷當前登錄用戶的用戶類型標志與期望的用戶類型標志是否一致,如果一致則執(zhí)行父類的additionalAuthenticationChecks,完成驗證;否則拋出一個BadUserKindException異常,表明驗證失敗。BadUserKindException繼承自org.acegisecurity.AuthenticationException,具體的代碼略
在applicationContext.xml中刪除daoAuthenticationProvider相關(guān)的配置,增加如下配置:
<bean id="customerDaoAuthenticationProvider" class="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.dao.MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider">
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="customerDao"/>
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder"/>
<property name="expectedUserKind" value="1"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userDaoAuthenticationProvider" class="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.dao.MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider">
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="userDao"/>
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder"/>
<property name="expectedUserKind" value="0"/>
</bean>
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="customerDao"/>
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder"/>
<property name="expectedUserKind" value="1"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userDaoAuthenticationProvider" class="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.dao.MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider">
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="userDao"/>
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder"/>
<property name="expectedUserKind" value="0"/>
</bean>
可以看出customerDaoAuthenticationProvider僅用于驗證客戶(其expectedUserKind被指定為1),而userDaoAuthenticationProvider僅用于驗證員工(其expectedUserKind被指定為0)。customerDao的配置如下:
<bean id="customerDao" class="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.appfuse.dao.hibernate.CustomerDaoHibernate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
CustomerDaoHibernate的代碼如下:
package cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.appfuse.dao.hibernate;
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.model.Customer;
import org.appfuse.dao.hibernate.GenericDaoHibernate;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomerDaoHibernate extends GenericDaoHibernate<Customer, Long> implements UserDetailsService {
public CustomerDaoHibernate() {
super(Customer.class);
}
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username)
throws UsernameNotFoundException, DataAccessException {
List<Customer> users = getHibernateTemplate().find("from Customer where username=?", username);
if (users == null || users.isEmpty()) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Customer '" + username + "' not found ");
");
} else {
return (UserDetails) users.get(0);
}
}
}
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.acegisecurity.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.model.Customer;
import org.appfuse.dao.hibernate.GenericDaoHibernate;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomerDaoHibernate extends GenericDaoHibernate<Customer, Long> implements UserDetailsService {
public CustomerDaoHibernate() {
super(Customer.class);
}
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username)
throws UsernameNotFoundException, DataAccessException {
List<Customer> users = getHibernateTemplate().find("from Customer where username=?", username);
if (users == null || users.isEmpty()) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Customer '" + username + "' not found
 ");
");} else {
return (UserDetails) users.get(0);
}
}
}
可以看出CustomerDaoHibernate是取得一個Customer對象(實現(xiàn)了UserDetails接口),而不是Employee。
修改authenticationManager的配置如下:
<bean id="authenticationManager" class="org.acegisecurity.providers.ProviderManager">
<property name="providers">
<list>
<ref local="customerDaoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="userDaoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="anonymousAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="rememberMeAuthenticationProvider"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<property name="providers">
<list>
<ref local="customerDaoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="userDaoAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="anonymousAuthenticationProvider"/>
<ref local="rememberMeAuthenticationProvider"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
在哪里捕獲當前登錄用戶的用戶類型標志,并傳遞給MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider呢?我決定增加一個名為PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter的Filter,放在AuthenticationProcessingFilter之前,代碼如下:
package cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.ui.webapp;
import cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.UserKindComparisonAware;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryUtils;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
public class PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter implements Filter, ApplicationContextAware {
public static final String ACEGI_SECURITY_FORM_USERKIND = "j_userkind";
private FilterConfig filterConfig;
private boolean initialized = false;
private Map targetBeans;
private String targetClass;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public String getTargetClass() {
return targetClass;
}
public void setTargetClass(String targetClass) {
this.targetClass = targetClass;
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public void destroy() {
}
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
this.filterConfig = filterConfig;
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException,
ServletException {
if (!(request instanceof HttpServletRequest)) {
throw new ServletException("Can only process HttpServletRequest");
}
if (!initialized) {
doInit();
}
String userKind = obtainUserKind((HttpServletRequest)request);
for (Iterator it = targetBeans.values().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
UserKindComparisonAware comparison = (UserKindComparisonAware)it.next();
comparison.setCurrentUserKind(userKind);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private synchronized void doInit() throws ServletException {
if ((targetClass == null) || "".equals(targetClass)) {
throw new ServletException("targetClass must be specified");
}
Class _targetClass;
try {
_targetClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(targetClass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ServletException("Class of type " + targetClass + " not found in classloader");
}
targetBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, _targetClass, true, true);
if (targetBeans.size() == 0) {
throw new ServletException("Bean context must contain at least one bean of type " + targetClass);
}
for (Iterator it = targetBeans.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)it.next();
if (!(entry.getValue() instanceof UserKindComparisonAware)) {
throw new ServletException("Bean '" + entry.getKey() +
"' does not implement cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.UserKindComparisonAware");
}
}
// Set initialized to true at the end of the synchronized method, so
// that invocations of doFilter() before this method has completed will not
// cause NullPointerException
initialized = true;
}
protected String obtainUserKind(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(ACEGI_SECURITY_FORM_USERKIND);
}
}
import cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.UserKindComparisonAware;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryUtils;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
public class PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter implements Filter, ApplicationContextAware {
public static final String ACEGI_SECURITY_FORM_USERKIND = "j_userkind";
private FilterConfig filterConfig;
private boolean initialized = false;
private Map targetBeans;
private String targetClass;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public String getTargetClass() {
return targetClass;
}
public void setTargetClass(String targetClass) {
this.targetClass = targetClass;
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public void destroy() {
}
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
this.filterConfig = filterConfig;
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException,
ServletException {
if (!(request instanceof HttpServletRequest)) {
throw new ServletException("Can only process HttpServletRequest");
}
if (!initialized) {
doInit();
}
String userKind = obtainUserKind((HttpServletRequest)request);
for (Iterator it = targetBeans.values().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
UserKindComparisonAware comparison = (UserKindComparisonAware)it.next();
comparison.setCurrentUserKind(userKind);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private synchronized void doInit() throws ServletException {
if ((targetClass == null) || "".equals(targetClass)) {
throw new ServletException("targetClass must be specified");
}
Class _targetClass;
try {
_targetClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(targetClass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ServletException("Class of type " + targetClass + " not found in classloader");
}
targetBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, _targetClass, true, true);
if (targetBeans.size() == 0) {
throw new ServletException("Bean context must contain at least one bean of type " + targetClass);
}
for (Iterator it = targetBeans.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)it.next();
if (!(entry.getValue() instanceof UserKindComparisonAware)) {
throw new ServletException("Bean '" + entry.getKey() +
"' does not implement cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.UserKindComparisonAware");
}
}
// Set initialized to true at the end of the synchronized method, so
// that invocations of doFilter() before this method has completed will not
// cause NullPointerException
initialized = true;
}
protected String obtainUserKind(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(ACEGI_SECURITY_FORM_USERKIND);
}
}
PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter需要在初始化參數(shù)中指定targetClass,該參數(shù)的值是一個類,該類實現(xiàn)了UserKindComparisonAware接口。PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter找到容器中所有該類的實例,并把捕獲的當前登錄用戶的用戶類型標志賦值給它們。PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter的配置如下:
<bean id="preAuthenticationProcessingFilter"
class="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.ui.webapp.PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter">
<property name="targetClass"
value="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.dao.MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider"/>
</bean>
class="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.ui.webapp.PreAuthenticationProcessingFilter">
<property name="targetClass"
value="cn.net.cogent.summer.extension.acegisecurity.providers.dao.MKUDaoAuthenticationProvider"/>
</bean>
還需要把preAuthenticationProcessingFilter加入到filterChainProxy的配置中:
<bean id="filterChainProxy" class="org.acegisecurity.util.FilterChainProxy">
<property name="filterInvocationDefinitionSource">
<value>
CONVERT_URL_TO_LOWERCASE_BEFORE_COMPARISON
PATTERN_TYPE_APACHE_ANT
/**= ,preAuthenticationProcessingFilter,authenticationProcessingFilter,
,preAuthenticationProcessingFilter,authenticationProcessingFilter,
</value>
</property>
</bean>
<property name="filterInvocationDefinitionSource">
<value>
CONVERT_URL_TO_LOWERCASE_BEFORE_COMPARISON
PATTERN_TYPE_APACHE_ANT
/**=
 ,preAuthenticationProcessingFilter,authenticationProcessingFilter,
,preAuthenticationProcessingFilter,authenticationProcessingFilter,
</value>
</property>
</bean>
注意把它放在authenticationProcessingFilter的前面
至此我們初步實現(xiàn)了使用Acegi實現(xiàn)多種用戶登錄



