Lucene源碼分析筆記之[org.apache.lucene.store](二)
IndexInput/IndexOutput類系
綜述:Lucene在存儲(chǔ)和讀取索引的時(shí)候,把文件內(nèi)容都當(dāng)作字節(jié)來(lái)對(duì)待。Int型拆分成1-5個(gè)byte分別存儲(chǔ);float則拆分成1-10個(gè)byte分別存儲(chǔ)。Char型拆分成1-3個(gè)byte來(lái)存儲(chǔ)。
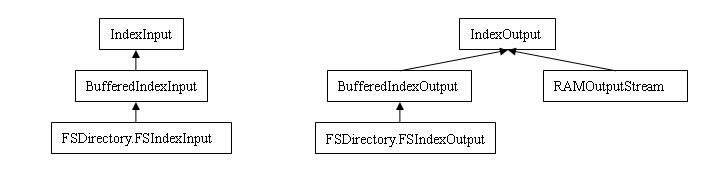
1. IndexInput/IndexOutput類系的層次圖
其中,FSDirectory.FSIndexInput和FSDirectory.FSIndexOutput是FSDirectory的內(nèi)部類(protected static)。
2.部分代碼說(shuō)明
IndexInput/IndexOutput類
在綜述里說(shuō)過(guò),Lucene把文本都以字節(jié)為單位進(jìn)行處理。下面是IndexInput/IndexOutput部分方法的代碼清單,從中我們能清楚的理解Lucene的文本處理方式。
writeInt(int)方法把int型變量處理成4個(gè)字節(jié),從高位到低位分別存儲(chǔ)。
 public void writeInt(int i) throws IOException {
public void writeInt(int i) throws IOException {2
 writeByte((byte) (i >> 24)); // 寫高8位
writeByte((byte) (i >> 24)); // 寫高8位3
 writeByte((byte) (i >> 16)); // 寫次高8位
writeByte((byte) (i >> 16)); // 寫次高8位4
 writeByte((byte) (i >> 8)); // 寫次次高8位
writeByte((byte) (i >> 8)); // 寫次次高8位5
 writeByte((byte) i); //寫低8位
writeByte((byte) i); //寫低8位6
 }
}writeVInt(int)方法把int型變量處理成1-5個(gè)字節(jié),從低位到高位分別存儲(chǔ)。值小的,占用的字節(jié)數(shù)就少;值大的,占用的字節(jié)數(shù)就多。這個(gè)就是Lucene壓縮存儲(chǔ)的基石了。
 public void writeVInt(int i) throws IOException {
public void writeVInt(int i) throws IOException {2
 while ((i & ~0x7F) != 0) { // 當(dāng)最高位不為0,執(zhí)行循環(huán)體
while ((i & ~0x7F) != 0) { // 當(dāng)最高位不為0,執(zhí)行循環(huán)體3
 writeByte((byte) ((i & 0x7f) | 0x80)); // 寫入低7位,最高位置1
writeByte((byte) ((i & 0x7f) | 0x80)); // 寫入低7位,最高位置14
 i >>>= 7; // 向右偏移7位,也就是往高位移動(dòng)7位
i >>>= 7; // 向右偏移7位,也就是往高位移動(dòng)7位5
 }
}6
 writeByte((byte) i); // 寫入數(shù)據(jù)最高位(肯定不足7位了),最高位顯然是0
writeByte((byte) i); // 寫入數(shù)據(jù)最高位(肯定不足7位了),最高位顯然是07
 }
}IndexInput中的readInt()和readVInt()用來(lái)讀取文件內(nèi)容。
readInt()在讀取時(shí),把讀取的4個(gè)字節(jié)從高位到底位依次拼接。這一點(diǎn)在下面的代碼中可以很容易看出來(lái)。
 public int readInt() throws IOException {
public int readInt() throws IOException {2
 return ((readByte() & 0xFF) << 24) | ((readByte() & 0xFF) << 16)
return ((readByte() & 0xFF) << 24) | ((readByte() & 0xFF) << 16)3
 | ((readByte() & 0xFF) << 8) | (readByte() & 0xFF);
| ((readByte() & 0xFF) << 8) | (readByte() & 0xFF);4
 }
}readVInt()稍微有點(diǎn)復(fù)雜,它的讀取順序是由低位到高位,步驟如下:
(1).讀入一個(gè)字節(jié)存入變量b
(2).b取后7位,存入變量i;若b首位是0,則返回i
(3).讀取下個(gè)字節(jié)存入b,b往左偏移7*(n-1)位后與i拼接后存入i,轉(zhuǎn)到(2)
注:
A.n為循環(huán)次數(shù)
B.其實(shí)只要理解了writeVInt(int)的寫入方式后,readVInt()就不難理解了。
下面是readVInt()的代碼清單:
 public int readVInt() throws IOException {
public int readVInt() throws IOException {2
 byte b = readByte(); // 讀取第一個(gè)字節(jié)
byte b = readByte(); // 讀取第一個(gè)字節(jié)3
 int i = b & 0x7F; // 取后7位
int i = b & 0x7F; // 取后7位4
 for (int shift = 7; (b & 0x80) != 0; shift += 7) { // 當(dāng)該字節(jié)首位不為0,執(zhí)行循環(huán)體
for (int shift = 7; (b & 0x80) != 0; shift += 7) { // 當(dāng)該字節(jié)首位不為0,執(zhí)行循環(huán)體5
 b = readByte(); // 讀取下個(gè)字節(jié)
b = readByte(); // 讀取下個(gè)字節(jié)6
 i |= (b & 0x7F) << shift; // 取該字節(jié)后7位,偏移到高位,跟原i值拼接
i |= (b & 0x7F) << shift; // 取該字節(jié)后7位,偏移到高位,跟原i值拼接7
 }
}8
 return i;
return i;9
 }
}至于writeLong(long),它在形式上把long拆成2個(gè)int來(lái)處理;writeVLong(long)/readVLong()思路(代碼)跟writeVInt(int)/readVLong()除了方法名之外,完全一樣;realLong()通過(guò)兩次readInt(),第一個(gè)值偏移32位后拼接第二個(gè)值。
writeChars(char[],int,int)用來(lái)把一個(gè)符合UTF-8編碼的字符數(shù)組寫入文件,它同樣把字符拆分成字節(jié)來(lái)對(duì)待。對(duì)每個(gè)字符,按照其有效位數(shù)n(去掉高位的0)的不同,采用有三種不同的寫入方法:
(1).0< n <=7,取后7位,首位置0寫入文件
(2).7< n <=11或者n=0,取高1-5位,首3位置110;取后6位,首2位置10;寫入文件
(3).11< n <=16,取高0-4位,首4位置1110;取中6位,首2位置10;取后6位,首2位置10;寫入文件
其代碼及注釋如下:
 public void writeChars(char[] s, int start, int length) throws IOException {
public void writeChars(char[] s, int start, int length) throws IOException {2
 // start為開始的字符在char[]中的位置,length為需要寫的字符的個(gè)數(shù)
// start為開始的字符在char[]中的位置,length為需要寫的字符的個(gè)數(shù)3
 final int end = start + length;
final int end = start + length;4
 for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { // 循環(huán)遍歷char[]中從start到end的字符
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { // 循環(huán)遍歷char[]中從start到end的字符5
 final int code = (int) s[i];
final int code = (int) s[i];6
 if (code >= 0x01 && code <= 0x7F)
if (code >= 0x01 && code <= 0x7F) 7
 // code值在0x01-0x7F,直接寫入
// code值在0x01-0x7F,直接寫入8
 // code的有效位數(shù)為1-7位
// code的有效位數(shù)為1-7位9
 writeByte((byte) code);
writeByte((byte) code);10
 else if (((code >= 0x80) && (code <= 0x7FF)) || code == 0) {
else if (((code >= 0x80) && (code <= 0x7FF)) || code == 0) {11
 // code值在0x80-0x7FF或者為0,則分兩個(gè)字節(jié)寫入
// code值在0x80-0x7FF或者為0,則分兩個(gè)字節(jié)寫入12
 // code的有效位數(shù)8-11位
// code的有效位數(shù)8-11位13
 writeByte((byte) (0xC0 | (code >> 6))); // 寫高2-5位,首3位置110
writeByte((byte) (0xC0 | (code >> 6))); // 寫高2-5位,首3位置11014
 writeByte((byte) (0x80 | (code & 0x3F))); // 寫低6位,首2位置10
writeByte((byte) (0x80 | (code & 0x3F))); // 寫低6位,首2位置1015
 } else {
} else {16
 //0x7FF之后的用3個(gè)字節(jié)寫入,code有效位數(shù)12-16位
//0x7FF之后的用3個(gè)字節(jié)寫入,code有效位數(shù)12-16位17
 writeByte((byte) (0xE0 | (code >>> 12))); // 寫高0-4位,首4位置1110
writeByte((byte) (0xE0 | (code >>> 12))); // 寫高0-4位,首4位置111018
 writeByte((byte) (0x80 | ((code >> 6) & 0x3F))); //寫此高位6位,首2位置10
writeByte((byte) (0x80 | ((code >> 6) & 0x3F))); //寫此高位6位,首2位置1019
 writeByte((byte) (0x80 | (code & 0x3F))); //寫低6位,首2位置10
writeByte((byte) (0x80 | (code & 0x3F))); //寫低6位,首2位置1020
 }
}21
 }
}22
 }
}writeChars(String, int, int)思路(代碼)跟上面是一樣的。
與writeChars(char[], int, int)對(duì)應(yīng)的readChars(char[], int, int)代碼及注釋如下:
 public void readChars(char[] buffer, int start, int length)
public void readChars(char[] buffer, int start, int length)2
 throws IOException {
throws IOException {3
 final int end = start + length;
final int end = start + length;4
 for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {5
 byte b = readByte(); // 讀取一個(gè)字節(jié)
byte b = readByte(); // 讀取一個(gè)字節(jié)6
 if ((b & 0x80) == 0) // 如果首位不為1,說(shuō)明該字節(jié)單獨(dú)為一字符
if ((b & 0x80) == 0) // 如果首位不為1,說(shuō)明該字節(jié)單獨(dú)為一字符7
 buffer[i] = (char) (b & 0x7F);
buffer[i] = (char) (b & 0x7F);8
 else if ((b & 0xE0) != 0xE0) { // 首4位不為1110
else if ((b & 0xE0) != 0xE0) { // 首4位不為11109
 buffer[i] = (char) (((b & 0x1F) << 6) | (readByte() & 0x3F));
buffer[i] = (char) (((b & 0x1F) << 6) | (readByte() & 0x3F));10
 } else {
} else {11
 buffer[i] = (char) (((b & 0x0F) << 12)
buffer[i] = (char) (((b & 0x0F) << 12)12
 | ((readByte() & 0x3F) << 6) | (readByte() & 0x3F));
| ((readByte() & 0x3F) << 6) | (readByte() & 0x3F));13
 }
}14
 }
}15
 }
} writeString(String)用來(lái)寫入字符串。它先寫入該字符串的長(zhǎng)度,然后調(diào)用writeChars(String, int, int)寫入字符串。代碼及注釋如下:
 public void writeString(String s) throws IOException {
public void writeString(String s) throws IOException {2
 int length = s.length(); // 字符串長(zhǎng)度
int length = s.length(); // 字符串長(zhǎng)度3
 writeVInt(length); // 寫入字符串長(zhǎng)度
writeVInt(length); // 寫入字符串長(zhǎng)度4
 writeChars(s, 0, length); //寫入字符串
writeChars(s, 0, length); //寫入字符串5
 }
}readString()在讀取的時(shí)候利用了IndexInput類的私有變量(private char[] chars)來(lái)緩存字符串,唯一需要注意的就是在需要時(shí),要給char擴(kuò)充容量。代碼及注釋如下:
 public String readString() throws IOException {
public String readString() throws IOException { int length = readVInt();
int length = readVInt(); if (chars == null || length > chars.length) // 需要時(shí),給chars擴(kuò)容
if (chars == null || length > chars.length) // 需要時(shí),給chars擴(kuò)容 chars = new char[length];
chars = new char[length]; readChars(chars, 0, length);
readChars(chars, 0, length); return new String(chars, 0, length);
return new String(chars, 0, length); }
}BufferedIndexInput/BufferedIndexOutput類
BufferedIndexInput/BufferedIndexOutput依然是抽象類,它們給出了部分IndexInput/IndexOutput未曾實(shí)現(xiàn)的抽象方法,如getFilePointer(),writeByte()/readByte()等等。還提供了writeBytes()/readBytes()這樣的在索引優(yōu)化合并時(shí)使用的方法。
BufferedIndexOutput中的變量說(shuō)明:
 static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 16384; // buffer的總?cè)萘?/span>
static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 16384; // buffer的總?cè)萘?/span>2

3
 private final byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; // 用于寫文件時(shí)的緩沖區(qū)
private final byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; // 用于寫文件時(shí)的緩沖區(qū)4
 private long bufferStart = 0; // position in file of buffer: buffer 在文件中的偏移量
private long bufferStart = 0; // position in file of buffer: buffer 在文件中的偏移量5
 private int bufferPosition = 0; // position in buffer : 在buffer中的偏移量
private int bufferPosition = 0; // position in buffer : 在buffer中的偏移量
writeByte(byte)為往buffer中寫入byte,代碼比較簡(jiǎn)單,如下:
 public void writeByte(byte b) throws IOException {
public void writeByte(byte b) throws IOException {2
 if (bufferPosition >= BUFFER_SIZE) // 注意buffer裝滿時(shí)需要flush()
if (bufferPosition >= BUFFER_SIZE) // 注意buffer裝滿時(shí)需要flush()3
 flush();
flush();4
 buffer[bufferPosition++] = b;
buffer[bufferPosition++] = b; 5
 }
} writeBytes(byte[], int, int)從名字就知道是存儲(chǔ)一個(gè)byte數(shù)組。代碼及注釋如下:
 public void writeBytes(byte[] b, int offset, int length) throws IOException { // 該方法在索引優(yōu)化合并時(shí)使用
public void writeBytes(byte[] b, int offset, int length) throws IOException { // 該方法在索引優(yōu)化合并時(shí)使用2
 // offset: 首個(gè)字節(jié)在b中的位置; length: 序列長(zhǎng)度(字節(jié)數(shù))
// offset: 首個(gè)字節(jié)在b中的位置; length: 序列長(zhǎng)度(字節(jié)數(shù))3
 int bytesLeft = BUFFER_SIZE - bufferPosition; // bytesLeft: buffer剩余容量
int bytesLeft = BUFFER_SIZE - bufferPosition; // bytesLeft: buffer剩余容量4
 // is there enough space in the buffer?
// is there enough space in the buffer?5
 if (bytesLeft >= length) { // 剩余容量可以放下長(zhǎng)度length的字節(jié)數(shù)
if (bytesLeft >= length) { // 剩余容量可以放下長(zhǎng)度length的字節(jié)數(shù)6
 // we add the data to the end of the buffer
// we add the data to the end of the buffer7
 System.arraycopy(b, offset, buffer, bufferPosition, length);
System.arraycopy(b, offset, buffer, bufferPosition, length);8
 bufferPosition += length;
bufferPosition += length;9
 // if the buffer is full, flush it
// if the buffer is full, flush it10
 if (BUFFER_SIZE - bufferPosition == 0)
if (BUFFER_SIZE - bufferPosition == 0)11
 flush();
flush();12
 } else { // 剩余容量放不下
} else { // 剩余容量放不下13
 // is data larger then buffer?
// is data larger then buffer?14
 if (length > BUFFER_SIZE) { // BUFFER_SIZE < length 時(shí)
if (length > BUFFER_SIZE) { // BUFFER_SIZE < length 時(shí)15
 // we flush the buffer
// we flush the buffer16
 if (bufferPosition > 0)
if (bufferPosition > 0)17
 flush();
flush();18
 // and write data at once
// and write data at once19
 flushBuffer(b, offset, length);
flushBuffer(b, offset, length);20
 bufferStart += length;
bufferStart += length;21
 } else { // bytesLeft < length < BUFFER_SIZE 時(shí),分2次寫入
} else { // bytesLeft < length < BUFFER_SIZE 時(shí),分2次寫入22
 // we fill/flush the buffer (until the input is written)
// we fill/flush the buffer (until the input is written)23
 int pos = 0; // position in the input data
int pos = 0; // position in the input data24
 int pieceLength; // 一次往buffer中寫入的字節(jié)數(shù)
int pieceLength; // 一次往buffer中寫入的字節(jié)數(shù)25
 while (pos < length) { // 我仰天狂吼:為什么?為什么要用循環(huán)?!為什么?天呀,為什么你如此偏愛它?
while (pos < length) { // 我仰天狂吼:為什么?為什么要用循環(huán)?!為什么?天呀,為什么你如此偏愛它?26
 // 剩余字節(jié)數(shù)(length - pos)小于bytesLeft,pieceLength = lenght - pos,否則,pieceLength = bytesLeft
// 剩余字節(jié)數(shù)(length - pos)小于bytesLeft,pieceLength = lenght - pos,否則,pieceLength = bytesLeft27
 pieceLength = (length - pos < bytesLeft) ? length - pos
pieceLength = (length - pos < bytesLeft) ? length - pos28
 : bytesLeft;
: bytesLeft;29
 System.arraycopy(b, pos + offset, buffer, bufferPosition, pieceLength);
System.arraycopy(b, pos + offset, buffer, bufferPosition, pieceLength);30
 pos += pieceLength;
pos += pieceLength;31
 bufferPosition += pieceLength; // 改變bufferPosiotion
bufferPosition += pieceLength; // 改變bufferPosiotion32
 // if the buffer is full, flush it
// if the buffer is full, flush it33
 bytesLeft = BUFFER_SIZE - bufferPosition; // 計(jì)算剩余容量
bytesLeft = BUFFER_SIZE - bufferPosition; // 計(jì)算剩余容量34
 if (bytesLeft == 0) { // b裝滿則flush()
if (bytesLeft == 0) { // b裝滿則flush()35
 flush();
flush();36
 bytesLeft = BUFFER_SIZE; // flush()后bytesLeft自然就要跟 BUFFER_SIZE 一樣了
bytesLeft = BUFFER_SIZE; // flush()后bytesLeft自然就要跟 BUFFER_SIZE 一樣了37
 }
}38
 }
}39
 }
}40
 }
}41
 }
} flush():把buffer中內(nèi)容寫入文件,清空buffer。代碼及注釋如下:
 public void flush() throws IOException {
public void flush() throws IOException {2
 flushBuffer(buffer, bufferPosition); // buffer中的內(nèi)容寫入文件
flushBuffer(buffer, bufferPosition); // buffer中的內(nèi)容寫入文件3
 bufferStart += bufferPosition; // 更改buffer在文件中的偏移量
bufferStart += bufferPosition; // 更改buffer在文件中的偏移量4
 bufferPosition = 0; // buffer為空,則 bufferPosition = 0
bufferPosition = 0; // buffer為空,則 bufferPosition = 05
 }
}readByte(): 從buffer中讀取一個(gè)字節(jié)。
 public byte readByte() throws IOException {
public byte readByte() throws IOException {2
 if (bufferPosition >= bufferLength) //當(dāng)前讀取位置超過(guò)buffer中內(nèi)容有效長(zhǎng)度,refill()
if (bufferPosition >= bufferLength) //當(dāng)前讀取位置超過(guò)buffer中內(nèi)容有效長(zhǎng)度,refill()3
 refill();
refill();4
 return buffer[bufferPosition++];
return buffer[bufferPosition++];5
 }
}refill():重新裝填buffer。
 private void refill() throws IOException {
private void refill() throws IOException {2
 long start = bufferStart + bufferPosition; // 計(jì)算在文件中的偏移位置
long start = bufferStart + bufferPosition; // 計(jì)算在文件中的偏移位置3
 long end = start + bufferSize; // 結(jié)束位置
long end = start + bufferSize; // 結(jié)束位置4
 if (end > length()) // don't read past EOF: 超出文件大小
if (end > length()) // don't read past EOF: 超出文件大小5
 end = length();
end = length();6
 int newLength = (int) (end - start); // 能讀取的長(zhǎng)度
int newLength = (int) (end - start); // 能讀取的長(zhǎng)度7
 if (newLength <= 0)
if (newLength <= 0)8
 throw new IOException("read past EOF");
throw new IOException("read past EOF");9

10
 if (buffer == null) { // 需要初始化buffer
if (buffer == null) { // 需要初始化buffer11
 buffer = new byte[bufferSize]; // allocate buffer lazily
buffer = new byte[bufferSize]; // allocate buffer lazily12
 seekInternal(bufferStart);
seekInternal(bufferStart);13
 }
}14
 readInternal(buffer, 0, newLength); // 這里才是真正的裝填buffer
readInternal(buffer, 0, newLength); // 這里才是真正的裝填buffer15
 bufferLength = newLength; // 設(shè)置buffer中有效字節(jié)數(shù)
bufferLength = newLength; // 設(shè)置buffer中有效字節(jié)數(shù)16
 bufferStart = start; // 設(shè)置buffer在文件中的偏移量
bufferStart = start; // 設(shè)置buffer在文件中的偏移量17
 bufferPosition = 0; // 當(dāng)前buffer中的偏移量
bufferPosition = 0; // 當(dāng)前buffer中的偏移量18
 }
}readBytes(byte[], int, int, boolean):讀取字節(jié)數(shù)組,跟writeBytes()一樣,在索引優(yōu)化合并時(shí)使用。源碼中的注釋本身已足夠清晰了,我就偷了回懶,沒(méi)寫自己的注釋,就粘過(guò)來(lái)了。
 public void readBytes(byte[] b, int offset, int len, boolean useBuffer)
public void readBytes(byte[] b, int offset, int len, boolean useBuffer)2
 throws IOException {
throws IOException {3

4
 if (len <= (bufferLength - bufferPosition)) {
if (len <= (bufferLength - bufferPosition)) {5
 // the buffer contains enough data to satisfy this request
// the buffer contains enough data to satisfy this request6
 if (len > 0) // to allow b to be null if len is 0
if (len > 0) // to allow b to be null if len is 0
7
 System.arraycopy(buffer, bufferPosition, b, offset, len);
System.arraycopy(buffer, bufferPosition, b, offset, len);8
 bufferPosition += len;
bufferPosition += len;9
 } else {
} else {10
 // the buffer does not have enough data. First serve all we've got.
// the buffer does not have enough data. First serve all we've got.11
 int available = bufferLength - bufferPosition;
int available = bufferLength - bufferPosition;12
 if (available > 0) {
if (available > 0) {13
 System.arraycopy(buffer, bufferPosition, b, offset, available);
System.arraycopy(buffer, bufferPosition, b, offset, available);14
 offset += available;
offset += available;15
 len -= available;
len -= available;16
 bufferPosition += available;
bufferPosition += available;17
 }
}18
 // and now, read the remaining 'len' bytes:
// and now, read the remaining 'len' bytes:19
 if (useBuffer && len < bufferSize) {
if (useBuffer && len < bufferSize) {20
 // If the amount left to read is small enough, and
// If the amount left to read is small enough, and21
 // we are allowed to use our buffer, do it in the usual
// we are allowed to use our buffer, do it in the usual22
 // buffered way: fill the buffer and copy from it:
// buffered way: fill the buffer and copy from it:23
 refill();
refill();24
 if (bufferLength < len) {
if (bufferLength < len) {25
 // Throw an exception when refill() could not read len
// Throw an exception when refill() could not read len26
 // bytes:
// bytes:27
 System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, b, offset, bufferLength);
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, b, offset, bufferLength);28
 throw new IOException("read past EOF");
throw new IOException("read past EOF");29
 } else {
} else {30
 System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, b, offset, len);
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, b, offset, len);31
 bufferPosition = len;
bufferPosition = len;32
 }
}33
 } else {
} else {34
 // The amount left to read is larger than the buffer
// The amount left to read is larger than the buffer35
 // or we've been asked to not use our buffer -
// or we've been asked to not use our buffer -36
 // there's no performance reason not to read it all
// there's no performance reason not to read it all37
 // at once. Note that unlike the previous code of
// at once. Note that unlike the previous code of38
 // this function, there is no need to do a seek
// this function, there is no need to do a seek39
 // here, because there's no need to reread what we
// here, because there's no need to reread what we40
 // had in the buffer.
// had in the buffer.41
 long after = bufferStart + bufferPosition + len;
long after = bufferStart + bufferPosition + len;42
 if (after > length())
if (after > length())43
 throw new IOException("read past EOF");
throw new IOException("read past EOF");44
 readInternal(b, offset, len);
readInternal(b, offset, len);45
 bufferStart = after;
bufferStart = after;46
 bufferPosition = 0;
bufferPosition = 0;47
 bufferLength = 0; // trigger refill() on read
bufferLength = 0; // trigger refill() on read48
 }
}49
 }
}50
 }
} FSIndexInput/FSIndexOutput類
FSIndexInput/FSIndexOutput繼承自BufferedIndexInput/BufferedIndexOutput,它最終補(bǔ)充實(shí)現(xiàn)了該類系所需提供服務(wù)的全部實(shí)現(xiàn)。
FSIndexOutput的flushBuffer(byte[], int, int)方法,它的功能在于真正的完成buffer到文件的數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)。
 public void flushBuffer(byte[] b, int offset, int size)
public void flushBuffer(byte[] b, int offset, int size)2
 throws IOException {
throws IOException {3
 file.write(b, offset, size); // 寫文件
file.write(b, offset, size); // 寫文件4
 }
}與flushBuffer()對(duì)應(yīng)的,readInternal(byte[], int, int)從底層真正的把數(shù)據(jù)從文件提取到buffer中。
 protected void readInternal(byte[] b, int offset, int len) // 從文件中讀取內(nèi)容到buffer
protected void readInternal(byte[] b, int offset, int len) // 從文件中讀取內(nèi)容到buffer2
 throws IOException {
throws IOException {3
 synchronized (file) { // file需要同步訪問(wèn)
synchronized (file) { // file需要同步訪問(wèn)4
 long position = getFilePointer(); // 獲取當(dāng)前文件讀取位置
long position = getFilePointer(); // 獲取當(dāng)前文件讀取位置5
 if (position != file.position) { // file定位到當(dāng)前讀取位置
if (position != file.position) { // file定位到當(dāng)前讀取位置6
 file.seek(position);
file.seek(position);7
 file.position = position;
file.position = position;8
 }
}9
 int total = 0;
int total = 0;10
 do {
do { 11
 /* 一般情況下,此循環(huán)體只會(huì)執(zhí)行一次,只有在第一次循環(huán)時(shí),file中內(nèi)容不能使b全部裝滿,
/* 一般情況下,此循環(huán)體只會(huì)執(zhí)行一次,只有在第一次循環(huán)時(shí),file中內(nèi)容不能使b全部裝滿,12
 * 這時(shí),total < len,而下次循環(huán),已讀到文件尾部,i = -1,拋出異常。
* 這時(shí),total < len,而下次循環(huán),已讀到文件尾部,i = -1,拋出異常。13
 * 也就是說(shuō),當(dāng)b不能讀滿時(shí),此方法必會(huì)拋出異常
* 也就是說(shuō),當(dāng)b不能讀滿時(shí),此方法必會(huì)拋出異常 14
 */
*/15
 int i = file.read(b, offset + total, len - total);
int i = file.read(b, offset + total, len - total);16
 if (i == -1)
if (i == -1)17
 throw new IOException("read past EOF");
throw new IOException("read past EOF");18
 file.position += i;
file.position += i;19
 total += i;
total += i;20
 } while (total < len);
} while (total < len);21
 }
}22
 }
}
RAMOutputStream類
RAMOutputStream繼承自IndexOutput,是用于處理在內(nèi)存中建索引時(shí)的寫數(shù)據(jù)類,它在實(shí)例化是需要RAMFile類型的參數(shù)。實(shí)現(xiàn)了IndexOutput的writeByte()方法,也提供了在索引間拷貝數(shù)據(jù)用的writeBytes()和writeTo()方法。
writeByte():往內(nèi)存緩沖區(qū)中寫一個(gè)字節(jié)數(shù)據(jù)。
 public void writeByte(byte b) throws IOException { // 寫單個(gè)字節(jié)到buffer,如果當(dāng)前buffer已滿,則切換到下個(gè)buffer
public void writeByte(byte b) throws IOException { // 寫單個(gè)字節(jié)到buffer,如果當(dāng)前buffer已滿,則切換到下個(gè)buffer2
 if (bufferPosition == bufferLength) {
if (bufferPosition == bufferLength) {3
 currentBufferIndex++;
currentBufferIndex++;4
 switchCurrentBuffer(); // 切換buffer
switchCurrentBuffer(); // 切換buffer5
 }
}6
 currentBuffer[bufferPosition++] = b; // 寫入 b
currentBuffer[bufferPosition++] = b; // 寫入 b7
 }
} writeBytes():索引間拷貝數(shù)據(jù)用。
 public void writeBytes(byte[] b, int offset, int len) throws IOException {
public void writeBytes(byte[] b, int offset, int len) throws IOException {2
 while (len > 0) { //
while (len > 0) { // 3
 if (bufferPosition == bufferLength) { // 如果buffer裝滿,切換下個(gè)buffer
if (bufferPosition == bufferLength) { // 如果buffer裝滿,切換下個(gè)buffer4
 currentBufferIndex++;
currentBufferIndex++;5
 switchCurrentBuffer(); // 切換buffer
switchCurrentBuffer(); // 切換buffer6
 }
}7

8
 int remainInBuffer = currentBuffer.length - bufferPosition; // buffer中剩余容量
int remainInBuffer = currentBuffer.length - bufferPosition; // buffer中剩余容量9
 int bytesToCopy = len < remainInBuffer ? len : remainInBuffer; // 實(shí)際拷貝長(zhǎng)度
int bytesToCopy = len < remainInBuffer ? len : remainInBuffer; // 實(shí)際拷貝長(zhǎng)度10
 System.arraycopy(b, offset, currentBuffer, bufferPosition,
System.arraycopy(b, offset, currentBuffer, bufferPosition,11
 bytesToCopy); // 拷貝
bytesToCopy); // 拷貝12
 offset += bytesToCopy; // 調(diào)整偏移量
offset += bytesToCopy; // 調(diào)整偏移量13
 len -= bytesToCopy; // 調(diào)整長(zhǎng)度
len -= bytesToCopy; // 調(diào)整長(zhǎng)度14
 bufferPosition += bytesToCopy; // 調(diào)整buffer中當(dāng)前位置
bufferPosition += bytesToCopy; // 調(diào)整buffer中當(dāng)前位置15
 }
}16
 }
}writeTo(IndexOutput):把數(shù)據(jù)從當(dāng)前內(nèi)存緩沖區(qū)寫到參數(shù)指定的IndexOutput中。
 public void writeTo(IndexOutput out) throws IOException { // 拷貝整個(gè)緩沖區(qū)數(shù)據(jù)到out
public void writeTo(IndexOutput out) throws IOException { // 拷貝整個(gè)緩沖區(qū)數(shù)據(jù)到out2
 flush();
flush();3
 final long end = file.length; // file總長(zhǎng)度
final long end = file.length; // file總長(zhǎng)度4
 long pos = 0; // 開始偏移位置
long pos = 0; // 開始偏移位置5
 int buffer = 0; // buffer索引
int buffer = 0; // buffer索引6
 while (pos < end) {
while (pos < end) {7
 int length = BUFFER_SIZE;
int length = BUFFER_SIZE;8
 long nextPos = pos + length;
long nextPos = pos + length;9
 if (nextPos > end) { // at the last buffer
if (nextPos > end) { // at the last buffer10
 length = (int) (end - pos);
length = (int) (end - pos);11
 }
}12
 out.writeBytes((byte[]) file.getBuffer(buffer++), length); // 拷貝數(shù)據(jù)
out.writeBytes((byte[]) file.getBuffer(buffer++), length); // 拷貝數(shù)據(jù)13
 pos = nextPos; // 更改偏移位置
pos = nextPos; // 更改偏移位置14
 }
}15
 }
}posted on 2008-11-13 21:25 Rolandz 閱讀(1615) 評(píng)論(1) 編輯 收藏