createTree(1, orgNodeTree, sameOrgNodes, 0);@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Getter
@Setter
public class NodeTree {
private String pName;
private String name;
private int level;
private List<NodeTree> children;
}
private void createTree(int leave, int ind, Map<String, NodeTree> pIndexNodeNameMap, List<NodeVo> childNodes) {
Map<String, NodeTree> cIndexNodeNameMap = new HashMap();
//構建樹
int treeNo = pIndexNodeNameMap.size();
if (treeNo == 0) {
return;
}
int group = 0;
for (int i = ind; i < childNodes.size(); i++) {
NodeVo node = childNodes.get(i);
long index = node.getId() % treeNo;
NodeTree pNode = pIndexNodeNameMap.get(index + "");
List<NodeTree> children = pNode.getChildren();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(children)) {
children = new ArrayList();
}
if (children.size() > 2) {
leave++;
createTree(leave, i, cIndexNodeNameMap, childNodes);
break;
} else {
NodeTree child = new NodeTree();
child.setLevel(leave);
child.setPName(pNode.getName());
child.setName(node.getNodeName());
children.add(child);
pNode.setChildren(children);
cIndexNodeNameMap.put(group + "", child);
group++;
}
}
}private boolean createTree(int level, List<NodeTree> parentNodes, List<NodeVo> childNodes, int beginIndex) {
//構建樹
List<NodeTree> nextLevelNodes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = beginIndex; i < childNodes.size(); i++) {
int parentCount = 1;
for (NodeTree pNode : parentNodes) {
List<NodeTree> children = pNode.getChildren();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(children)) {
children = new ArrayList();
pNode.setChildren(children);
}
if (children.size() >= 3) {
if(parentCount >= parentNodes.size()){
return createTree(++level, nextLevelNodes, childNodes, beginIndex);
}
} else {
if (beginIndex >= childNodes.size()) {
return true;
}
NodeTree child = new NodeTree();
child.setLevel(level);
child.setPName(pNode.getName());
NodeVo node = childNodes.get(beginIndex);
child.setName(node.getNodeName());
pNode.getChildren().add(child);
nextLevelNodes.add(child);
beginIndex++;
}
parentCount++;
}
}
return true;
}
2020年9月7日 #
2018年5月20日 #
git pull github master --allow-unrelated-histories
執行結果如下:
remote: Counting objects: 3, done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 3
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done.
From https://github.com/abocode/jfaster
* branch master -> FETCH_HEAD
* [new branch] master -> github/master
Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy.
.gitattributes | 3 +++
1 file changed, 3 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 .gitattributes
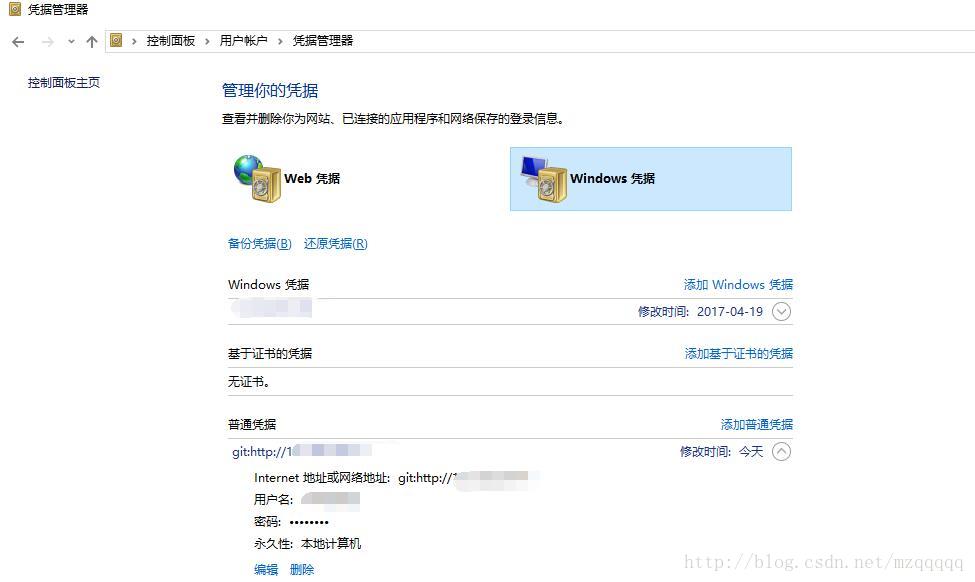
進入“控制面板”——“用戶賬戶”-憑據管理器——windows憑據
找到了git的用戶名密碼。修改正確后ok
2016年8月18日 #
元注解:
元注解的作用就是負責注解其他注解。Java5.0定義了4個標準的meta-annotation類型,它們被用來提供對其它 annotation類型作說明。Java5.0定義的元注解:
1.@Target,
2.@Retention,
3.@Documented,
4.@Inherited
以下為一個簡單場景的應用:
1.定義注解:
@Target(TYPE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Table {
/**
* (Optional) The name of the table.
* <p/>
* Defaults to the entity name.
*/
String name() default "";
}
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})2、定義實體類:
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Column {
/**
* (Optional) The name of the column. Defaults to
* the property or field name.
*/
String name() default "";
}
@Table(name = "t_s_user")
public class User {
@Column(name="name")
private String name;
@Column(name="pwd")
private String pwd;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
}
3、運行:
public static void print() {
System.out.println("table's name:" + User.class.getAnnotation(Table.class).name());
Field[] fields = User.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
Field field = fields[i];
System.out.println("field's type:" + field.getType().getName());
System.out.println("field's columnName:" + field.getAnnotation(Column.class).name());
}
}
關于注解的詳細介紹:http://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2013/04/24/3036689.html
2016年4月29日 #
2.左上角選擇添加,選擇添加java(還提供了添加maven項目),然后選擇所需要的目錄:
3.idea 會提示選擇添加什么類型的文件,我們是單純的文件,所以選擇classes
2016年1月19日 #
nginx 反向代理到 tomcat
server {
2016年1月14日 #
@SpringBootApplication2、修改pom文件:
@ComponentScan
@Import({DBConfiguration.class, ResourceConfiguration.class,AppConfiguration.class})
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
修改packaging
<packaging>war</packaging>
加入打包到tomcat的配置:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-legacy</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
3、如果不需要JMX在application.properties文件中加入配置項:
或者直接關閉:
2015年12月28日 #
Spring Data JDBC generic DAO implementation
The purpose of this project is to provide generic, lightweight and easy to use DAO implementation for relational databases based on JdbcTemplate from Spring framework, compatible with Spring Data umbrella of projects.
Design objectives
- Lightweight, fast and low-overhead. Only a handful of classes, no XML, annotations, reflection
- This is not full-blown ORM. No relationship handling, lazy loading, dirty checking, caching
- CRUD implemented in seconds
- For small applications where JPA is an overkill
- Use when simplicity is needed or when future migration e.g. to JPA is considered
- Minimalistic support for database dialect differences (e.g. transparent paging of results)
Features
Each DAO provides built-in support for:
- Mapping to/from domain objects through
RowMapperabstraction - Generated and user-defined primary keys
- Extracting generated key
- Compound (multi-column) primary keys
- Immutable domain objects
- Paging (requesting subset of results)
- Sorting over several columns (database agnostic)
- Optional support for many-to-one relationships
- Supported databases (continuously tested):
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- H2
- HSQLDB
- Derby
- MS SQL Server (2008, 2012)
- Oracle 10g / 11g (9i should work too)
- ...and most likely many others
- Easily extendable to other database dialects via
SqlGeneratorclass. - Easy retrieval of records by ID
API
Compatible with Spring Data PagingAndSortingRepository abstraction, all these methods are implemented for you:
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> {
T save(T entity);
Iterable<T> save(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
T findOne(ID id);
boolean exists(ID id);
Iterable<T> findAll();
long count();
void delete(ID id);
void delete(T entity);
void delete(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
void deleteAll();
Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort);
Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable);
Iterable<T> findAll(Iterable<ID> ids);
}
Pageable and Sort parameters are also fully supported, which means you get paging and sorting by arbitrary properties for free. For example say you have userRepository extending PagingAndSortingRepository<User, String> interface (implemented for you by the library) and you request 5th page of USERS table, 10 per page, after applying some sorting:
Page<User> page = userRepository.findAll(
new PageRequest(
5, 10,
new Sort(
new Order(DESC, "reputation"),
new Order(ASC, "user_name")
)
)
);
Spring Data JDBC repository library will translate this call into (PostgreSQL syntax):
SELECT *
FROM USERS
ORDER BY reputation DESC, user_name ASC
LIMIT 50 OFFSET 10
...or even (Derby syntax):
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT ROW_NUMBER() OVER () AS ROW_NUM, t.*
FROM (
SELECT *
FROM USERS
ORDER BY reputation DESC, user_name ASC
) AS t
) AS a
WHERE ROW_NUM BETWEEN 51 AND 60
No matter which database you use, you'll get Page<User> object in return (you still have to provide RowMapper<User> yourself to translate from ResultSet to domain object). If you don't know Spring Data project yet, Page<T> is a wonderful abstraction, not only encapsulating List<T>, but also providing metadata such as total number of records, on which page we currently are, etc.
Reasons to use
-
You consider migration to JPA or even some NoSQL database in the future.
Since your code will rely only on methods defined in
PagingAndSortingRepositoryandCrudRepositoryfrom Spring Data Commons umbrella project you are free to switch fromJdbcRepositoryimplementation (from this project) to:JpaRepository,MongoRepository,GemfireRepositoryorGraphRepository. They all implement the same common API. Of course don't expect that switching from JDBC to JPA or MongoDB will be as simple as switching imported JAR dependencies - but at least you minimize the impact by using same DAO API. -
You need a fast, simple JDBC wrapper library. JPA or even MyBatis is an overkill
-
You want to have full control over generated SQL if needed
-
You want to work with objects, but don't need lazy loading, relationship handling, multi-level caching, dirty checking... You need CRUD and not much more
-
You want to by DRY
-
You are already using Spring or maybe even
JdbcTemplate, but still feel like there is too much manual work -
You have very few database tables
Getting started
For more examples and working code don't forget to examine project tests.
Prerequisites
Maven coordinates:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.nurkiewicz.jdbcrepository</groupId>
<artifactId>jdbcrepository</artifactId>
<version>0.4</version>
</dependency>
This project is available under maven central repository.
Alternatively you can download source code as ZIP.
In order to start your project must have DataSource bean present and transaction management enabled. Here is a minimal MySQL configuration:
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Configuration
public class MinimalConfig {
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource());
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
MysqlConnectionPoolDataSource ds = new MysqlConnectionPoolDataSource();
ds.setUser("user");
ds.setPassword("secret");
ds.setDatabaseName("db_name");
return ds;
}
}
Entity with auto-generated key
Say you have a following database table with auto-generated key (MySQL syntax):
CREATE TABLE COMMENTS (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
user_name varchar(256),
contents varchar(1000),
created_time TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
First you need to create domain object User mapping to that table (just like in any other ORM):
public class Comment implements Persistable<Integer> {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String contents;
private Date createdTime;
@Override
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public boolean isNew() {
return id == null;
}
//getters/setters/constructors/...
}
Apart from standard Java boilerplate you should notice implementing Persistable<Integer> where Integer is the type of primary key. Persistable<T> is an interface coming from Spring Data project and it's the only requirement we place on your domain object.
Finally we are ready to create our CommentRepository DAO:
@Repository
public class CommentRepository extends JdbcRepository<Comment, Integer> {
public CommentRepository() {
super(ROW_MAPPER, ROW_UNMAPPER, "COMMENTS");
}
public static final RowMapper<Comment> ROW_MAPPER = //see below
private static final RowUnmapper<Comment> ROW_UNMAPPER = //see below
@Override
protected <S extends Comment> S postCreate(S entity, Number generatedId) {
entity.setId(generatedId.intValue());
return entity;
}
}
First of all we use @Repository annotation to mark DAO bean. It enables persistence exception translation. Also such annotated beans are discovered by CLASSPATH scanning.
As you can see we extend JdbcRepository<Comment, Integer> which is the central class of this library, providing implementations of all PagingAndSortingRepository methods. Its constructor has three required dependencies: RowMapper, RowUnmapper and table name. You may also provide ID column name, otherwise default "id" is used.
If you ever used JdbcTemplate from Spring, you should be familiar with RowMapper interface. We need to somehow extract columns from ResultSet into an object. After all we don't want to work with raw JDBC results. It's quite straightforward:
public static final RowMapper<Comment> ROW_MAPPER = new RowMapper<Comment>() {
@Override
public Comment mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return new Comment(
rs.getInt("id"),
rs.getString("user_name"),
rs.getString("contents"),
rs.getTimestamp("created_time")
);
}
};
RowUnmapper comes from this library and it's essentially the opposite of RowMapper: takes an object and turns it into a Map. This map is later used by the library to construct SQL CREATE/UPDATE queries:
private static final RowUnmapper<Comment> ROW_UNMAPPER = new RowUnmapper<Comment>() {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> mapColumns(Comment comment) {
Map<String, Object> mapping = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
mapping.put("id", comment.getId());
mapping.put("user_name", comment.getUserName());
mapping.put("contents", comment.getContents());
mapping.put("created_time", new java.sql.Timestamp(comment.getCreatedTime().getTime()));
return mapping;
}
};
If you never update your database table (just reading some reference data inserted elsewhere) you may skip RowUnmapper parameter or use MissingRowUnmapper.
Last piece of the puzzle is the postCreate() callback method which is called after an object was inserted. You can use it to retrieve generated primary key and update your domain object (or return new one if your domain objects are immutable). If you don't need it, just don't override postCreate().
Check out JdbcRepositoryGeneratedKeyTest for a working code based on this example.
By now you might have a feeling that, compared to JPA or Hibernate, there is quite a lot of manual work. However various JPA implementations and other ORM frameworks are notoriously known for introducing significant overhead and manifesting some learning curve. This tiny library intentionally leaves some responsibilities to the user in order to avoid complex mappings, reflection, annotations... all the implicitness that is not always desired.
This project is not intending to replace mature and stable ORM frameworks. Instead it tries to fill in a niche between raw JDBC and ORM where simplicity and low overhead are key features.
Entity with manually assigned key
In this example we'll see how entities with user-defined primary keys are handled. Let's start from database model:
CREATE TABLE USERS (
user_name varchar(255),
date_of_birth TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
enabled BIT(1) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (user_name)
);
...and User domain model:
public class User implements Persistable<String> {
private transient boolean persisted;
private String userName;
private Date dateOfBirth;
private boolean enabled;
@Override
public String getId() {
return userName;
}
@Override
public boolean isNew() {
return !persisted;
}
public void setPersisted(boolean persisted) {
this.persisted = persisted;
}
//getters/setters/constructors/...
}
Notice that special persisted transient flag was added. Contract of [CrudRepository.save()](http://static.springsource.org/spring-data/data-commons/docs/current/api/org/springframework/data/repository/CrudRepository.html#save(S)) from Spring Data project requires that an entity knows whether it was already saved or not (isNew()) method - there are no separate create() and update() methods. Implementing isNew() is simple for auto-generated keys (see Comment above) but in this case we need an extra transient field. If you hate this workaround and you only insert data and never update, you'll get away with return true all the time from isNew().
And finally our DAO, UserRepository bean:
@Repository
public class UserRepository extends JdbcRepository<User, String> {
public UserRepository() {
super(ROW_MAPPER, ROW_UNMAPPER, "USERS", "user_name");
}
public static final RowMapper<User> ROW_MAPPER = //...
public static final RowUnmapper<User> ROW_UNMAPPER = //...
@Override
protected <S extends User> S postUpdate(S entity) {
entity.setPersisted(true);
return entity;
}
@Override
protected <S extends User> S postCreate(S entity, Number generatedId) {
entity.setPersisted(true);
return entity;
}
}
"USERS" and "user_name" parameters designate table name and primary key column name. I'll leave the details of mapper and unmapper (see source code). But please notice postUpdate() and postCreate() methods. They ensure that once object was persisted, persisted flag is set so that subsequent calls to save() will update existing entity rather than trying to reinsert it.
Check out JdbcRepositoryManualKeyTest for a working code based on this example.
Compound primary key
We also support compound primary keys (primary keys consisting of several columns). Take this table as an example:
CREATE TABLE BOARDING_PASS (
flight_no VARCHAR(8) NOT NULL,
seq_no INT NOT NULL,
passenger VARCHAR(1000),
seat CHAR(3),
PRIMARY KEY (flight_no, seq_no)
);
I would like you to notice the type of primary key in Persistable<T>:
public class BoardingPass implements Persistable<Object[]> {
private transient boolean persisted;
private String flightNo;
private int seqNo;
private String passenger;
private String seat;
@Override
public Object[] getId() {
return pk(flightNo, seqNo);
}
@Override
public boolean isNew() {
return !persisted;
}
//getters/setters/constructors/...
}
Unfortunately library does not support small, immutable value classes encapsulating all ID values in one object (like JPA does with @IdClass), so you have to live with Object[] array. Defining DAO class is similar to what we've already seen:
public class BoardingPassRepository extends JdbcRepository<BoardingPass, Object[]> {
public BoardingPassRepository() {
this("BOARDING_PASS");
}
public BoardingPassRepository(String tableName) {
super(MAPPER, UNMAPPER, new TableDescription(tableName, null, "flight_no", "seq_no")
);
}
public static final RowMapper<BoardingPass> ROW_MAPPER = //...
public static final RowUnmapper<BoardingPass> UNMAPPER = //...
}
Two things to notice: we extend JdbcRepository<BoardingPass, Object[]> and we provide two ID column names just as expected: "flight_no", "seq_no". We query such DAO by providing both flight_no and seq_no (necessarily in that order) values wrapped by Object[]:
BoardingPass pass = boardingPassRepository.findOne(new Object[] {"FOO-1022", 42});
No doubts, this is cumbersome in practice, so we provide tiny helper method which you can statically import:
import static com.nurkiewicz.jdbcrepository.JdbcRepository.pk;
//...
BoardingPass foundFlight = boardingPassRepository.findOne(pk("FOO-1022", 42));
Check out JdbcRepositoryCompoundPkTest for a working code based on this example.
Transactions
This library is completely orthogonal to transaction management. Every method of each repository requires running transaction and it's up to you to set it up. Typically you would place @Transactional on service layer (calling DAO beans). I don't recommend placing @Transactional over every DAO bean.
Caching
Spring Data JDBC repository library is not providing any caching abstraction or support. However adding @Cacheable layer on top of your DAOs or services using caching abstraction in Spring is quite straightforward. See also: @Cacheable overhead in Spring.
Contributions
..are always welcome. Don't hesitate to submit bug reports and pull requests.
Testing
This library is continuously tested using Travis ( ). Test suite consists of 60+ distinct tests each run against 8 different databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, H2, HSQLDB and Derby + MS SQL Server and Oracle tests not run as part of CI.
). Test suite consists of 60+ distinct tests each run against 8 different databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, H2, HSQLDB and Derby + MS SQL Server and Oracle tests not run as part of CI.
When filling bug reports or submitting new features please try including supporting test cases. Each pull request is automatically tested on a separate branch.
Building
After forking the official repository building is as simple as running:
$ mvn install
You'll notice plenty of exceptions during JUnit test execution. This is normal. Some of the tests run against MySQL and PostgreSQL available only on Travis CI server. When these database servers are unavailable, whole test is simply skipped:
Results :
Tests run: 484, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 295
Exception stack traces come from root AbstractIntegrationTest.
Design
Library consists of only a handful of classes, highlighted in the diagram below (source):

JdbcRepository is the most important class that implements all PagingAndSortingRepository methods. Each user repository has to extend this class. Also each such repository must at least implement RowMapper and RowUnmapper (only if you want to modify table data).
SQL generation is delegated to SqlGenerator. PostgreSqlGenerator. and DerbySqlGenerator are provided for databases that don't work with standard generator.
Changelog
0.4.1
0.4
- Repackaged:
com.blogspot.nurkiewicz->com.nurkiewicz
0.3.2
- First version available in Maven central repository
- Upgraded Spring Data Commons 1.6.1 -> 1.8.0
0.3.1
- Upgraded Spring dependencies: 3.2.1 -> 3.2.4 and 1.5.0 -> 1.6.1
- Fixed #5 Allow manually injecting JdbcOperations, SqlGenerator and DataSource
0.3
- Oracle 10g / 11g support (see pull request)
- Upgrading Spring dependency to 3.2.1.RELEASE and Spring Data Commons to 1.5.0.RELEASE (see #4).
0.2
- MS SQL Server 2008/2012 support (see pull request)
0.1
- Initial revision (announcement)
License
This project is released under version 2.0 of the Apache License (same as Spring framework).
2015年9月26日 #
一、常用快捷鍵:
1.常用操作:
Ctrl+E,可以顯示最近編輯的文件列表
二、常用配置:
2015年9月22日 #
/**
2、編寫shell腳步:
#/bin/bash
3、 執行腳本:
備注:


